Intro
Discover causes and symptoms of low carbon dioxide in blood, also known as respiratory alkalosis, and learn about CO2 levels, blood gas tests, and hyperventilation treatments to manage this condition effectively.
The importance of maintaining proper levels of carbon dioxide in the blood cannot be overstated. Carbon dioxide, or CO2, is a vital component of the blood's gas exchange system, playing a critical role in regulating pH levels, blood pressure, and overall respiratory function. When CO2 levels in the blood are too low, it can lead to a range of symptoms and health issues, from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of carbon dioxide in the blood, exploring the causes, effects, and treatment options for low CO2 levels.
Low carbon dioxide levels in the blood, also known as hypocapnia or hypocarbia, can be caused by a variety of factors, including respiratory issues, anxiety disorders, and certain medical conditions. When we breathe, our lungs take in oxygen and expel CO2, a natural byproduct of cellular metabolism. However, when we hyperventilate or experience rapid breathing, we exhale more CO2 than usual, leading to a decrease in blood CO2 levels. This can cause a range of symptoms, including dizziness, lightheadedness, and tingling sensations in the hands and feet.
The human body is incredibly sensitive to changes in CO2 levels, and even slight deviations can have significant effects on overall health. For example, when CO2 levels drop, the blood vessels constrict, reducing blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. This can lead to decreased cognitive function, memory problems, and even seizures in severe cases. Furthermore, low CO2 levels can also disrupt the body's natural acid-base balance, leading to a condition known as respiratory alkalosis. This can cause a range of symptoms, including muscle cramps, fatigue, and heart palpitations.
Causes of Low Carbon Dioxide Levels in Blood
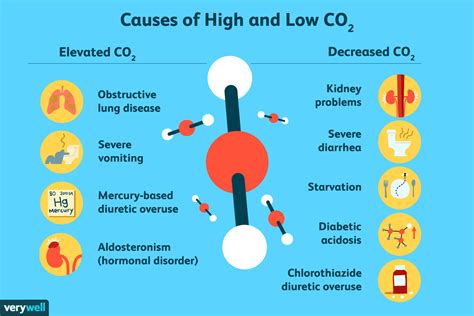
Respiratory Issues
Respiratory issues, such as asthma and COPD, can cause low CO2 levels in the blood due to impaired lung function. When the lungs are unable to properly exchange oxygen and CO2, it can lead to a buildup of CO2 in the blood, causing respiratory acidosis. However, in some cases, respiratory issues can also cause hypocapnia, particularly if the individual is experiencing rapid breathing or hyperventilation.Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder and generalized anxiety disorder, can also contribute to low CO2 levels in the blood. When we experience anxiety, our body's "fight or flight" response is triggered, causing rapid breathing and increased heart rate. This can lead to hyperventilation, which can cause a significant drop in CO2 levels.Effects of Low Carbon Dioxide Levels in Blood

Respiratory Alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition characterized by an increase in blood pH levels, caused by a decrease in CO2 levels. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including muscle cramps, fatigue, and heart palpitations. In severe cases, respiratory alkalosis can also cause seizures, coma, and even death.Cognitive Impairment
Low CO2 levels can also cause cognitive impairment, including decreased concentration, memory problems, and decreased cognitive function. This is because the brain is highly sensitive to changes in CO2 levels, and even slight deviations can have significant effects on cognitive function.Treatment Options for Low Carbon Dioxide Levels in Blood
Breathing Exercises
Breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can help increase CO2 levels in the blood. This involves slow, deep breathing, which can help slow down the heart rate and increase oxygenation of the blood.Medications
Medications, such as bronchodilators and steroids, may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of low CO2 levels. These medications can help improve lung function, reduce inflammation, and increase oxygenation of the blood.Prevention of Low Carbon Dioxide Levels in Blood

Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can contribute to low CO2 levels. These techniques can help slow down the heart rate, increase oxygenation of the blood, and reduce symptoms of hypocapnia.Avoiding Triggers
Avoiding triggers that can cause hyperventilation, such as stress and anxiety, can also help prevent low CO2 levels. This may involve avoiding certain situations or environments that can trigger anxiety, as well as practicing relaxation techniques to manage stress.What are the symptoms of low carbon dioxide levels in the blood?
+The symptoms of low carbon dioxide levels in the blood include dizziness, lightheadedness, tingling sensations in the hands and feet, muscle cramps, fatigue, and heart palpitations.
What are the causes of low carbon dioxide levels in the blood?
+The causes of low carbon dioxide levels in the blood include respiratory issues, anxiety disorders, and certain medical conditions, such as asthma, COPD, and pneumonia.
How can I prevent low carbon dioxide levels in the blood?
+Preventing low carbon dioxide levels in the blood involves maintaining proper respiratory function, managing anxiety disorders, and avoiding certain medications. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, and avoiding triggers that can cause hyperventilation can also help prevent hypocapnia.
In summary, low carbon dioxide levels in the blood can have significant effects on overall health, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. Understanding the causes, effects, and treatment options for hypocapnia is essential for maintaining proper respiratory function and preventing related health issues. By practicing relaxation techniques, avoiding triggers that can cause hyperventilation, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can help prevent low CO2 levels and maintain optimal health. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with low carbon dioxide levels in the blood, and to take action by prioritizing your respiratory health and seeking medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of hypocapnia.
