Intro
Learn cat bite treatment and prevention with our guide, covering wound care, infection symptoms, and antibiotic uses to minimize cat bite complications and promote healing.
Cat bites can be a serious matter, as they can lead to infections and other complications if not treated properly. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, cat bites account for approximately 10% of all animal bites treated in emergency departments. The importance of seeking medical attention immediately after a cat bite cannot be overstated, as prompt treatment can significantly reduce the risk of infection and promote healing. In this article, we will delve into the world of cat bite treatment, exploring the benefits, working mechanisms, and steps involved in ensuring a swift and effective recovery.
The consequences of neglecting cat bite treatment can be severe, ranging from localized infections to life-threatening conditions such as sepsis. The bacteria present in a cat's mouth, including Pasteurella multocida, can cause infections that spread quickly if left untreated. Furthermore, cat bites can also lead to tetanus, rabies, and other diseases, making it essential to take proactive measures to prevent such complications. By understanding the risks associated with cat bites and taking prompt action, individuals can minimize the likelihood of developing infections and ensure a smooth recovery.
Cat bites can occur in various contexts, from playful interactions with pets to unexpected encounters with feral animals. Regardless of the circumstances, it is crucial to prioritize treatment and seek medical attention if necessary. The treatment process typically involves a combination of wound cleaning, antibiotic administration, and monitoring for signs of infection. In some cases, additional measures such as tetanus shots or rabies prophylaxis may be necessary. By familiarizing themselves with the treatment options and taking a proactive approach, individuals can reduce the risks associated with cat bites and promote a swift recovery.
Cat Bite Treatment Overview

Benefits of Prompt Treatment
The benefits of prompt treatment for cat bites cannot be overstated. By seeking medical attention immediately after a cat bite, individuals can reduce the risk of infection, promote healing, and minimize the likelihood of complications. Prompt treatment can also help prevent the spread of diseases such as rabies and tetanus, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. Furthermore, prompt treatment can reduce the risk of long-term damage, such as scarring, nerve damage, or tendon damage. By prioritizing treatment and seeking medical attention promptly, individuals can ensure a swift and effective recovery.Cat Bite Infection Symptoms
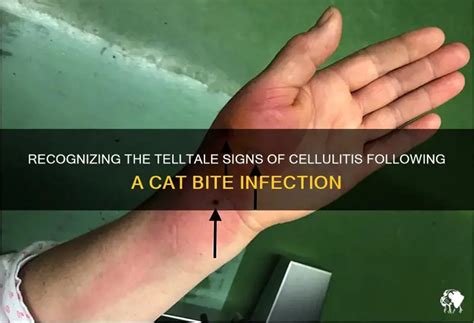
Risk Factors for Infection
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing infections after a cat bite. These include people with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, cancer, or HIV/AIDS. Additionally, individuals with a history of liver or kidney disease, as well as those taking immunosuppressive medications, may be at increased risk. Furthermore, cat bites to the hands, feet, or face may be more prone to infection due to the higher concentration of bacteria in these areas. By understanding the risk factors for infection and taking proactive measures, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing complications.Cat Bite Treatment Steps

Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotic treatment is often necessary to prevent infection and promote healing. The type and duration of antibiotic treatment will depend on the severity of the bite, the location of the wound, and the individual's overall health. In general, antibiotics such as amoxicillin-clavulanate or doxycycline may be prescribed to treat cat bite infections. By taking antibiotics as directed and completing the full course of treatment, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and promote a swift recovery.Preventing Cat Bites
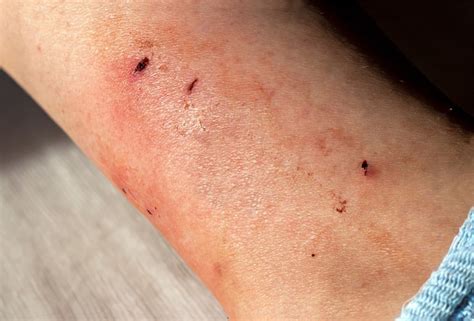
Cat Behavior and Body Language
Understanding cat behavior and body language is essential to preventing cat bites. Cats may exhibit certain behaviors or body language cues when they feel threatened or scared, such as hissing, growling, or flattening their ears. By recognizing these cues and giving cats space, individuals can reduce the likelihood of biting. Additionally, understanding cat behavior and body language can help individuals develop a stronger bond with their pets and promote a safe and healthy environment.Cat Bite Complications

Long-Term Effects of Cat Bites
The long-term effects of cat bites can be significant, ranging from scarring and nerve damage to tendon damage and chronic pain. In some cases, cat bites can lead to psychological trauma, such as anxiety or fear of cats. By seeking medical attention promptly and following treatment guidelines, individuals can reduce the risk of long-term effects and promote a swift recovery.What are the most common symptoms of a cat bite infection?
+The most common symptoms of a cat bite infection include redness, swelling, warmth, and pain around the wound. In some cases, individuals may experience fever, chills, or swollen lymph nodes.
How can I prevent cat bites?
+To prevent cat bites, avoid interacting with stray or feral cats, keep pets up-to-date on vaccinations and preventatives, supervise interactions between children and cats, and avoid teasing or provoking cats.
What are the risks of not seeking medical attention after a cat bite?
+The risks of not seeking medical attention after a cat bite include infection, abscesses, tetanus, and other serious complications. By seeking medical attention promptly, individuals can reduce the risk of these complications and promote a swift recovery.
In
