Intro
Discover key 5 CBC test facts, including complete blood count results, to understand blood cell analysis, hematocrit, and hemoglobin levels, for informed health decisions.
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in the medical field to assess various components of the blood, providing valuable insights into a person's overall health. This test is widely utilized due to its ability to detect a range of conditions, from anemia and infection to leukemia and other blood disorders. Understanding the CBC test and its implications can empower individuals to take a more proactive role in their health care.
The significance of the CBC test lies in its comprehensive nature, analyzing different blood components such as red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. Each of these components offers unique information about the body's condition. For instance, RBCs are crucial for carrying oxygen throughout the body, WBCs play a key role in the immune system, and platelets are vital for blood clotting. Abnormalities in any of these cell types can indicate specific health issues, making the CBC a versatile diagnostic tool.
The process of undergoing a CBC test is straightforward and relatively quick, involving a simple blood draw. The blood sample is then analyzed in a laboratory, where various parameters are measured and compared against normal ranges. This comparison helps healthcare providers identify any deviations that might suggest an underlying health issue. Given its non-invasive nature and the wealth of information it provides, the CBC test is a common initial step in medical evaluations, allowing for early detection and treatment of various conditions.
Introduction to CBC Test Components

The CBC test examines several key components of the blood, each providing distinct insights into health and potential disease. Red blood cells (RBCs), for example, are essential for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs. White blood cells (WBCs) are a critical part of the immune system, helping to fight infections. Platelets are small blood cells that play a crucial part in blood clotting, stopping or preventing bleeding.
Understanding Red Blood Cell Parameters
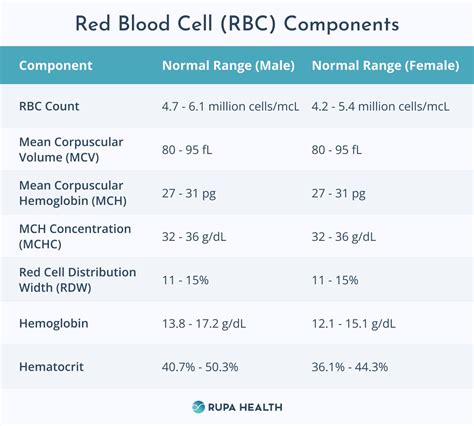
Red blood cell parameters measured in a CBC include the RBC count, hemoglobin (Hb), hematocrit (Hct), and mean corpuscular volume (MCV). The RBC count indicates the number of red blood cells in the blood, while hemoglobin measures the amount of the protein in these cells that carries oxygen. Hematocrit measures the proportion of blood volume made up by red blood cells. The mean corpuscular volume (MCV) is the average size of red blood cells, which can help in diagnosing types of anemia.CBC Test Procedure and Preparation
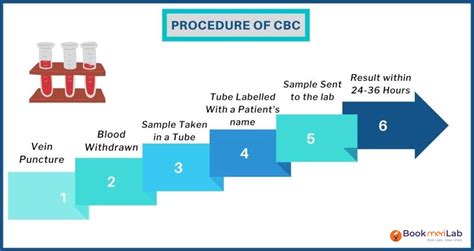
The procedure for a CBC test is straightforward and does not require extensive preparation. Typically, a healthcare provider will instruct the patient to fast for a certain period before the test, although this is not always necessary. The actual test involves a venipuncture, where a healthcare professional draws blood from a vein, usually in the arm, using a sterile needle and syringe. The blood is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually available within a day or two, depending on the laboratory's workload and the urgency of the test.
Interpreting CBC Test Results
Interpreting the results of a CBC test requires understanding the normal ranges for each parameter and how deviations from these ranges might indicate specific health issues. For example, a low RBC count or low hemoglobin level can indicate anemia, while an elevated WBC count can suggest infection or inflammation. Abnormal platelet counts can indicate bleeding or clotting disorders. Healthcare providers consider the patient's symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic tests when interpreting CBC results to make an accurate diagnosis.CBC Test Applications in Medical Diagnosis

The CBC test has a wide range of applications in medical diagnosis, making it a crucial tool in both preventive care and the management of chronic conditions. It is commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as anemia, infections, and blood clotting disorders. The test can also help in assessing the body's response to treatments, such as chemotherapy, which can affect blood cell production.
CBC in Disease Monitoring and Management
For patients with chronic conditions like leukemia or lymphoma, regular CBC tests are essential for monitoring the disease's progression and the effectiveness of treatment. Similarly, for individuals undergoing chemotherapy, CBC tests help in assessing the impact of treatment on blood cell counts, allowing for adjustments to be made to minimize side effects.Limitations and Considerations of the CBC Test
While the CBC test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has limitations and considerations. A single abnormal result does not necessarily confirm a diagnosis, as many factors can influence CBC parameters, including dehydration, stress, and certain medications. Additionally, some conditions may not be detected by a CBC alone, requiring further diagnostic testing for accurate diagnosis.
Combining CBC with Other Diagnostic Tests
In many cases, a CBC test is used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to provide a comprehensive view of a patient's health. For example, in cases of suspected infection, a CBC might be combined with blood cultures to identify the causative organism. For patients with symptoms of anemia, additional tests like iron levels or vitamin B12 levels might be ordered to determine the underlying cause.Future Directions in CBC Testing Technology

Advancements in technology are continually improving the efficiency, accuracy, and scope of CBC tests. Automated analyzers can now quickly process blood samples, providing rapid results and reducing the likelihood of human error. Furthermore, emerging technologies like point-of-care testing devices are making it possible to perform CBC tests in clinical settings, reducing the need for laboratory facilities and enabling quicker decision-making.
Point-of-Care CBC Testing
Point-of-care CBC testing refers to the use of portable, compact devices that can analyze blood samples at or near the site of patient care. These devices are particularly useful in emergency situations or in remote areas where access to laboratory facilities is limited. They offer the potential for rapid diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve patient outcomes.CBC Test and Patient Education

Educating patients about the CBC test, its purposes, and its implications can empower them to take a more active role in their healthcare. Understanding what the test entails, how it is performed, and what the results mean can alleviate anxiety and foster a more informed dialogue between patients and healthcare providers.
Patient Involvement in CBC Test Interpretation
While the interpretation of CBC test results is complex and requires professional expertise, patients can benefit from a basic understanding of their results. Healthcare providers can facilitate this by explaining the results in a clear, understandable manner, highlighting any abnormalities and discussing the necessary next steps. This approach not only enhances patient understanding but also encourages adherence to treatment plans and follow-up appointments.CBC Test in Preventive Care
The CBC test plays a significant role in preventive care, allowing for the early detection of potential health issues before symptoms become apparent. Regular health check-ups that include CBC tests can help identify risk factors for diseases, enabling individuals to make lifestyle changes or undergo preventive treatments to reduce these risks.
Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups are crucial for maintaining good health, and the CBC test is an integral part of these check-ups. By monitoring changes in blood cell counts over time, healthcare providers can identify trends that may indicate the onset of a condition, allowing for early intervention.CBC Test and Lifestyle Modifications

Lifestyle modifications can significantly impact CBC test results, reflecting changes in overall health. For example, adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to improved blood cell counts and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Nutritional Impact on CBC Results
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining healthy blood cell production. Deficiencies in essential nutrients like iron, vitamin B12, and folate can lead to anemia, which is often detected through CBC tests. A balanced diet that includes foods rich in these nutrients can help prevent anemia and ensure healthy blood cell counts.What is the purpose of a CBC test?
+A CBC test is used to evaluate the overall health and detect a range of disorders, including anemia, infection, and blood clotting disorders, by analyzing different components of the blood.
How is a CBC test performed?
+A CBC test involves a simple blood draw from a vein, typically in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What does a CBC test measure?
+A CBC test measures various parameters of the blood, including red blood cell count, white blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count, providing a comprehensive view of the blood's cellular components.
In conclusion, the CBC test is a powerful diagnostic tool that offers insights into the body's overall health, enabling the detection of various conditions at an early stage. By understanding the components of the CBC test, its applications, and its limitations, individuals can better appreciate the importance of this test in preventive care and disease management. As medical technology continues to evolve, the role of the CBC test in healthcare will likely expand, providing even more detailed information to guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes. We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about the CBC test, contributing to a broader discussion on the significance of this diagnostic tool in modern healthcare.
