Intro
Discover normal CBC test values, including WBC, RBC, and platelet counts, to understand complete blood count results and diagnose health issues like anemia, infection, or blood disorders with related LSI keywords like hematology and blood work.
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is a comprehensive blood test that measures various components of the blood, providing valuable information about a person's overall health. The test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood disorders. Understanding the normal values of a CBC test is essential for interpreting the results and making informed decisions about one's health.
The importance of CBC tests cannot be overstated, as they provide a snapshot of the body's blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Abnormal results can indicate a range of health issues, from mild to severe, and prompt further testing or treatment. In this article, we will delve into the normal values of a CBC test, exploring what each component measures and what the results mean.
A CBC test typically includes several components, each measuring a different aspect of the blood. These components include hemoglobin, hematocrit, red blood cell count, white blood cell count, platelet count, and mean corpuscular volume (MCV). Each of these components has a normal range, and understanding these ranges is crucial for interpreting the results of a CBC test.
Components of a CBC Test

The components of a CBC test are measured in different units, including grams per deciliter (g/dL), liters (L), and cells per microliter (μL). The normal ranges for each component vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. However, the following are the general normal ranges for each component:
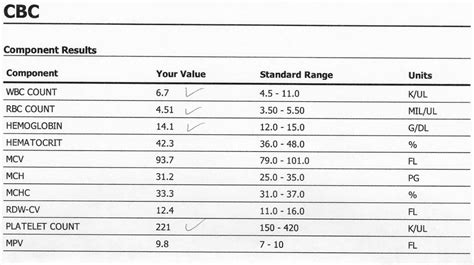
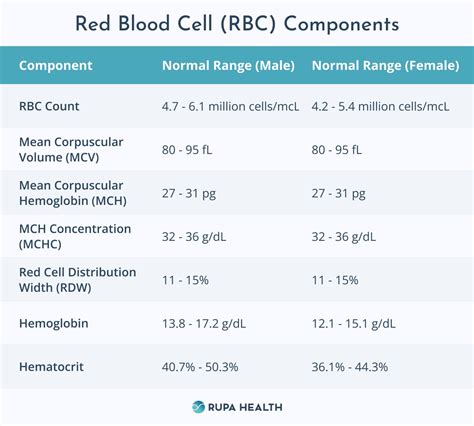
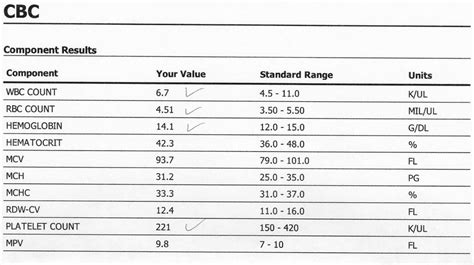
- Hemoglobin: 13.5-17.5 g/dL for men and 12-16 g/dL for women
- Hematocrit: 40-54% for men and 37-48% for women
- Red blood cell count: 4.32-5.72 million cells/μL for men and 3.90-5.03 million cells/μL for women
- White blood cell count: 3,500-10,500 cells/μL
- Platelet count: 150,000-450,000 cells/μL
- Mean corpuscular volume (MCV): 80-100 fL
Interpreting CBC Test Results
Interpreting the results of a CBC test requires a thorough understanding of the normal ranges and the potential causes of abnormal results. For example, a low hemoglobin level may indicate anemia, while a high white blood cell count may indicate infection or inflammation. The following are some common causes of abnormal CBC test results:
- Low hemoglobin: anemia, blood loss, or iron deficiency
- High hemoglobin: dehydration, polycythemia vera, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Low hematocrit: anemia, blood loss, or iron deficiency
- High hematocrit: dehydration, polycythemia vera, or COPD
- Low red blood cell count: anemia, blood loss, or bone marrow failure
- High red blood cell count: polycythemia vera, dehydration, or COPD
- Low white blood cell count: immune system disorders, bone marrow failure, or certain medications
- High white blood cell count: infection, inflammation, or immune system disorders
- Low platelet count: thrombocytopenia, bone marrow failure, or certain medications
- High platelet count: thrombocytosis, iron deficiency, or chronic inflammation
Benefits of CBC Tests

CBC tests offer several benefits, including:
- Early detection of health issues: CBC tests can detect health issues, such as anemia or infection, in their early stages, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of complications.
- Monitoring of chronic conditions: CBC tests can be used to monitor chronic conditions, such as anemia or blood disorders, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Diagnosis of blood disorders: CBC tests can help diagnose blood disorders, such as leukemia or lymphoma, and guide treatment decisions.
- Evaluation of overall health: CBC tests can provide a general overview of a person's overall health, including their risk of developing certain health conditions.
Common Applications of CBC Tests
CBC tests have several common applications, including:- Routine health check-ups: CBC tests are often included in routine health check-ups to monitor overall health and detect potential health issues.
- Pre-surgical testing: CBC tests are often used to evaluate a person's overall health before surgery and to identify potential risks.
- Monitoring of chronic conditions: CBC tests are used to monitor chronic conditions, such as anemia or blood disorders, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Diagnosis of blood disorders: CBC tests are used to diagnose blood disorders, such as leukemia or lymphoma, and guide treatment decisions.
Limitations of CBC Tests
While CBC tests are valuable diagnostic tools, they have several limitations, including:
- Limited sensitivity: CBC tests may not detect certain health issues, such as early stages of anemia or blood disorders.
- Limited specificity: CBC tests may not provide a definitive diagnosis, and further testing may be needed to confirm a diagnosis.
- Variability: CBC test results can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors.
Factors That Affect CBC Test Results
Several factors can affect CBC test results, including:- Age: CBC test results can vary depending on age, with older adults tend to have lower hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
- Sex: CBC test results can vary depending on sex, with women tend to have lower hemoglobin and hematocrit levels than men.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can affect CBC test results.
- Diet: A diet low in iron or other essential nutrients can affect CBC test results.
- Lifestyle: A sedentary lifestyle or smoking can affect CBC test results.
Preparing for a CBC Test

Preparing for a CBC test is relatively straightforward, and the following steps can help ensure accurate results:
- Fasting: Fasting for 8-12 hours before the test can help ensure accurate results.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water before the test can help ensure accurate results.
- Medications: Informing the healthcare provider about any medications or supplements being taken can help ensure accurate results.
- Lifestyle: Avoiding strenuous exercise or smoking before the test can help ensure accurate results.
What to Expect During a CBC Test
During a CBC test, a healthcare provider will typically:- Take a blood sample: A blood sample will be taken from a vein in the arm or hand.
- Label the sample: The blood sample will be labeled with the individual's name and other identifying information.
- Send the sample to a laboratory: The blood sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Understanding CBC Test Results
Understanding CBC test results requires a thorough understanding of the normal ranges and the potential causes of abnormal results. The following are some common questions and answers about CBC test results:
What is a normal hemoglobin level?
+A normal hemoglobin level is between 13.5-17.5 g/dL for men and 12-16 g/dL for women.
What is a normal white blood cell count?
+A normal white blood cell count is between 3,500-10,500 cells/μL.
What is a normal platelet count?
+A normal platelet count is between 150,000-450,000 cells/μL.
In conclusion, CBC tests are valuable diagnostic tools that provide a snapshot of the body's blood cells. Understanding the normal values of a CBC test is essential for interpreting the results and making informed decisions about one's health. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, individuals can better understand their CBC test results and take steps to maintain optimal health. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about CBC tests in the comments below, and we look forward to continuing the conversation.
