Intro
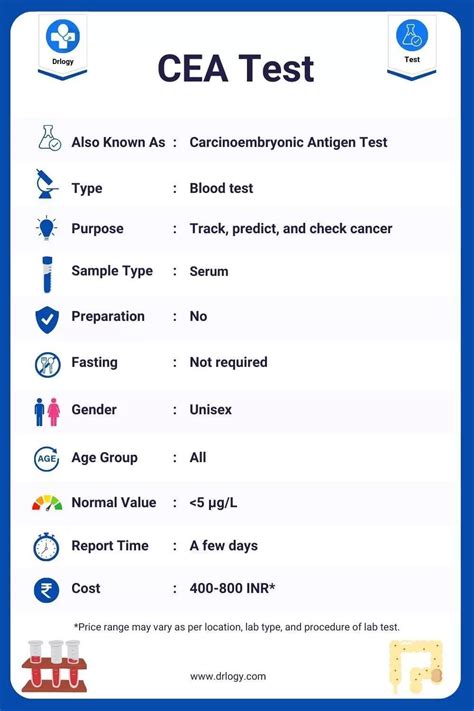
Learn about CEA blood count, a cancer screening test measuring Carcinoembryonic Antigen levels, helping diagnose and monitor colorectal, lung, and breast cancers, with results indicating tumor markers and overall health.
The CEA blood count, also known as the carcinoembryonic antigen test, is a vital diagnostic tool used to monitor and manage various types of cancer. CEA is a protein that is normally produced during fetal development, but its production typically stops before birth. However, in some cases, this protein can be found in the blood of adults, often indicating the presence of cancer. The CEA blood count measures the level of this protein in the blood, providing valuable information for healthcare providers to diagnose, treat, and monitor cancer.
The importance of the CEA blood count lies in its ability to detect and monitor certain types of cancer, such as colorectal, lung, breast, and pancreatic cancer. Elevated CEA levels can indicate the presence of cancer, while decreasing levels can suggest that treatment is effective. However, it is essential to note that CEA is not specific to cancer and can be elevated in other conditions, such as inflammation, infection, or smoking. Therefore, the CEA blood count is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to confirm a cancer diagnosis.
The CEA blood count is a relatively simple and non-invasive test that can be performed in a healthcare provider's office or laboratory. A blood sample is drawn from a vein in the arm, and the sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the test are typically available within a few days, and the healthcare provider will interpret the results to determine the next course of action. In some cases, the CEA blood count may be used to monitor cancer treatment, as changes in CEA levels can indicate the effectiveness of therapy.
Understanding CEA Blood Count Results
The results of the CEA blood count are typically reported in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). A normal CEA level is usually less than 5 ng/mL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's overall health. Elevated CEA levels can indicate the presence of cancer, but the level of elevation can also provide valuable information. For example, a mildly elevated CEA level may indicate a small tumor or early-stage cancer, while a significantly elevated level may suggest a larger tumor or more advanced disease.
Interpreting CEA Blood Count Results
To interpret CEA blood count results, healthcare providers consider several factors, including the individual's medical history, symptoms, and other diagnostic test results. The following are some general guidelines for interpreting CEA blood count results: * Normal: Less than 5 ng/mL * Mildly elevated: 5-10 ng/mL * Moderately elevated: 10-20 ng/mL * Significantly elevated: Greater than 20 ng/mLIt is essential to note that CEA blood count results should be interpreted in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and medical information. A single elevated CEA level does not necessarily indicate cancer, and further testing is often necessary to confirm a diagnosis.
CEA Blood Count in Cancer Diagnosis

The CEA blood count is commonly used to diagnose and monitor various types of cancer, including:
- Colorectal cancer: CEA is often elevated in colorectal cancer, particularly in advanced stages.
- Lung cancer: CEA can be elevated in lung cancer, especially in non-small cell lung cancer.
- Breast cancer: CEA may be elevated in breast cancer, particularly in metastatic disease.
- Pancreatic cancer: CEA can be elevated in pancreatic cancer, especially in advanced stages.
The CEA blood count is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies (e.g., CT scans, MRI scans) and biopsies, to confirm a cancer diagnosis. In some cases, the CEA blood count may be used to monitor cancer treatment, as changes in CEA levels can indicate the effectiveness of therapy.
CEA Blood Count in Cancer Monitoring
The CEA blood count can be used to monitor cancer treatment and detect cancer recurrence. The following are some ways the CEA blood count is used in cancer monitoring: * Monitoring treatment response: Changes in CEA levels can indicate the effectiveness of cancer treatment. * Detecting cancer recurrence: Elevated CEA levels can indicate cancer recurrence, even before symptoms appear. * Guiding further testing: Abnormal CEA levels may prompt further diagnostic testing, such as imaging studies or biopsies.Limitations of CEA Blood Count

While the CEA blood count is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations. The following are some of the limitations of the CEA blood count:
- Non-specificity: CEA can be elevated in non-cancerous conditions, such as inflammation or infection.
- False negatives: Some individuals with cancer may have normal CEA levels, particularly in early-stage disease.
- False positives: Elevated CEA levels can be caused by non-cancerous conditions, such as smoking or liver disease.
To overcome these limitations, the CEA blood count is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and medical information. Healthcare providers consider the individual's medical history, symptoms, and other test results when interpreting CEA blood count results.
Alternatives to CEA Blood Count
In some cases, alternative diagnostic tests may be used instead of or in addition to the CEA blood count. The following are some alternative diagnostic tests: * CA 19-9: This test measures the level of a protein called CA 19-9, which is often elevated in pancreatic cancer. * CA 125: This test measures the level of a protein called CA 125, which is often elevated in ovarian cancer. * Imaging studies: CT scans, MRI scans, and other imaging studies can be used to visualize tumors and detect cancer.These alternative diagnostic tests can provide valuable information for healthcare providers to diagnose and monitor cancer.
CEA Blood Count and Treatment
The CEA blood count can be used to monitor cancer treatment and adjust therapy as needed. The following are some ways the CEA blood count is used in cancer treatment:
- Monitoring treatment response: Changes in CEA levels can indicate the effectiveness of cancer treatment.
- Adjusting therapy: Abnormal CEA levels may prompt changes in treatment, such as switching to a different medication or adding radiation therapy.
- Detecting cancer recurrence: Elevated CEA levels can indicate cancer recurrence, even before symptoms appear.
The CEA blood count is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and medical information to guide cancer treatment.
CEA Blood Count and Prognosis
The CEA blood count can provide valuable information about prognosis, particularly in individuals with colorectal cancer. The following are some ways the CEA blood count is used to determine prognosis: * Predicting treatment response: Changes in CEA levels can indicate the likelihood of treatment response. * Estimating survival: Elevated CEA levels can indicate a poorer prognosis, particularly in advanced stages of cancer. * Guiding further testing: Abnormal CEA levels may prompt further diagnostic testing, such as imaging studies or biopsies.The CEA blood count is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and medical information to determine prognosis.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the CEA blood count is a valuable diagnostic tool used to monitor and manage various types of cancer. While it has several limitations, the CEA blood count can provide valuable information for healthcare providers to diagnose, treat, and monitor cancer. If you have questions or concerns about the CEA blood count or cancer diagnosis, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance and support to help you navigate the diagnostic and treatment process.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the CEA blood count in the comments below. Your feedback can help others better understand the importance of this diagnostic tool and its role in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
What is the normal range for CEA blood count?
+A normal CEA level is usually less than 5 ng/mL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's overall health.
Can the CEA blood count be used to diagnose cancer?
+The CEA blood count can be used to monitor and manage cancer, but it is not specific to cancer and can be elevated in other conditions. Therefore, it is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to confirm a cancer diagnosis.
How often should the CEA blood count be performed?
+The frequency of CEA blood count testing depends on the individual's medical history, symptoms, and treatment plan. Healthcare providers will determine the best testing schedule based on these factors.
