Intro
Discover 7 Ceftriaxone side effects, including antibiotic resistance, allergic reactions, and gastrointestinal issues, to ensure safe usage of this cephalosporin antibiotic, minimizing risks and maximizing benefits.
The importance of understanding the potential side effects of medications cannot be overstated, particularly when it comes to antibiotics like ceftriaxone. As a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, ceftriaxone is widely used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including those affecting the skin, respiratory tract, and urinary tract. Despite its effectiveness, ceftriaxone, like all medications, can cause side effects in some individuals. Being aware of these potential side effects is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment and for healthcare providers to monitor and manage any adverse reactions that may occur.
Ceftriaxone is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, but it can cause a range of side effects, from mild and temporary to severe and potentially life-threatening. Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, as well as allergic reactions, which can manifest as rash, itching, or difficulty breathing. In rare cases, ceftriaxone can cause more serious side effects, including anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction, and Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea, a condition that can lead to severe diarrhea and colitis.
Understanding the potential side effects of ceftriaxone is essential for ensuring safe and effective treatment. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of adverse reactions, patients and healthcare providers can take prompt action to mitigate any negative effects and adjust treatment plans as needed. Moreover, being informed about the potential risks and benefits of ceftriaxone can empower patients to take a more active role in their care, asking questions and seeking guidance from their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about their treatment.
Ceftriaxone Overview

Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Ceftriaxone has a long half-life, which allows for once-daily dosing in many cases. It is widely distributed throughout the body, achieving high concentrations in tissues and fluids, including cerebrospinal fluid, making it effective for treating central nervous system infections. The pharmacodynamics of ceftriaxone involve inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, which is essential for bacterial growth and replication. This mechanism of action is similar to other beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillins, but ceftriaxone has a broader spectrum of activity due to its resistance to beta-lactamase enzymes produced by many bacteria.Ceftriaxone Side Effects

Managing Side Effects
Managing the side effects of ceftriaxone involves a combination of preventive measures, monitoring, and treatment of any adverse reactions that may occur. Patients should be advised to report any signs of allergic reactions, gastrointestinal symptoms, or other side effects to their healthcare provider promptly. In some cases, side effects can be managed with supportive care, such as anti-diarrheal medications for diarrhea or antihistamines for allergic reactions. However, in cases of severe side effects, discontinuation of ceftriaxone and initiation of alternative treatments may be necessary.Ceftriaxone Interactions
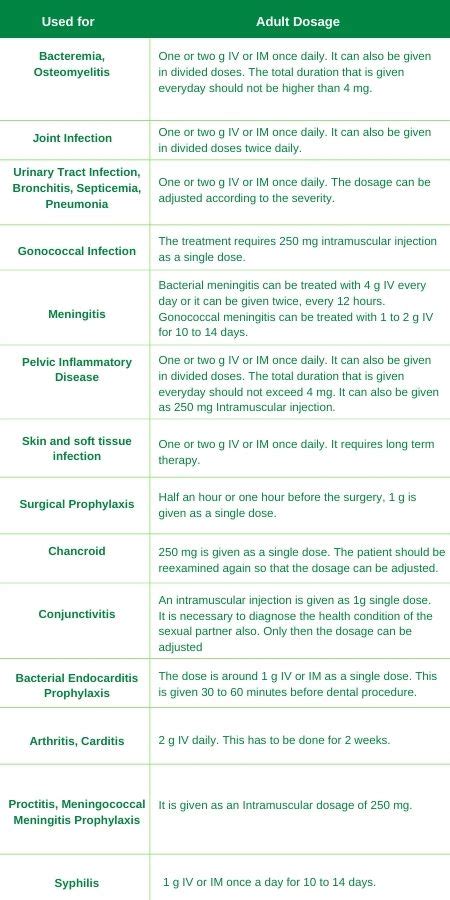
Patient Education
Educating patients about the potential side effects of ceftriaxone and the importance of adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen is crucial. Patients should be instructed to: - Complete the full course of treatment as directed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. - Monitor for signs of allergic reactions and report them immediately. - Maintain good hydration to help prevent kidney damage. - Inform their healthcare provider about any other medications they are taking.Ceftriaxone in Special Populations

Dosage Adjustments
Dosage adjustments are necessary in patients with renal impairment to prevent accumulation of the drug and potential toxicity. The dose of ceftriaxone should be reduced in patients with creatinine clearance of less than 50 mL/min. In patients with hepatic impairment, ceftriaxone is generally well-tolerated, but monitoring of liver function tests is recommended.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
As we move forward in the era of increasing antibiotic resistance, it is more important than ever to use antibiotics like ceftriaxone judiciously and with a thorough understanding of their potential benefits and risks. By doing so, we can ensure that these valuable medications remain effective for generations to come.What is ceftriaxone used for?
+Ceftriaxone is used to treat various bacterial infections, including those affecting the skin, respiratory tract, and urinary tract.
What are the common side effects of ceftriaxone?
+Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea and nausea, as well as allergic reactions such as rash and itching.
Can ceftriaxone be used in pregnant women?
+Ceftriaxone is classified as a category B drug in pregnancy, meaning it should be used only if clearly needed, as there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with ceftriaxone in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable to us, and we look forward to continuing the conversation on the safe and effective use of antibiotics like ceftriaxone.
