Intro
Explore 7 cellulitis leg pictures, symptoms, and treatments. Identify signs of cellulitis infection, including redness, swelling, and skin dimpling, and learn about antibiotic therapies and prevention methods for this common bacterial skin condition.
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that can affect anyone, regardless of their age or health status. It occurs when bacteria, typically Streptococcus or Staphylococcus, enter the skin through a crack or break, causing redness, swelling, and pain. Cellulitis can appear on any part of the body, but it most commonly affects the legs. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for cellulitis is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
Cellulitis can be acute or chronic, with the acute form being the most common. It typically starts as a small, red, and painful area on the skin, which can spread rapidly if left untreated. The affected area may feel warm to the touch, and the person may experience fever, chills, and fatigue. In severe cases, cellulitis can lead to more serious complications, such as abscesses, blood infections, and tissue damage.
The importance of recognizing and treating cellulitis early cannot be overstated. Delayed treatment can lead to prolonged recovery times, increased risk of complications, and higher healthcare costs. Furthermore, cellulitis can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, causing pain, discomfort, and emotional distress. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for cellulitis, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent future occurrences.
Causes and Risk Factors of Cellulitis

Types of Bacteria that Cause Cellulitis
There are several types of bacteria that can cause cellulitis, including: * Streptococcus: This bacterium is responsible for the majority of cellulitis cases. It can enter the skin through cracks, cuts, and other openings. * Staphylococcus: This bacterium is commonly found on the skin and can cause cellulitis if it enters the skin through a break or crack. * Haemophilus influenzae: This bacterium is typically found in the respiratory tract but can cause cellulitis in rare cases. * Escherichia coli: This bacterium is commonly found in the intestines but can cause cellulitis if it enters the skin through a break or crack.Symptoms of Cellulitis
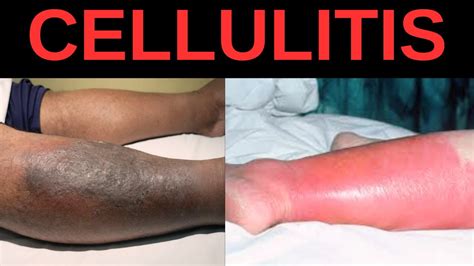
Stages of Cellulitis
Cellulitis can progress through several stages, including: 1. Mild: The affected area is red, swollen, and painful, but the symptoms are relatively mild. 2. Moderate: The symptoms worsen, and the affected area becomes more swollen and painful. 3. Severe: The symptoms are severe, and the affected area may become blistered or ulcerated.Treatment Options for Cellulitis

Preventing Cellulitis
Preventing cellulitis involves taking steps to reduce the risk of bacterial infections, such as: * Practicing good hygiene and keeping the skin clean and dry * Avoiding tight clothing that can irritate the skin * Wearing protective gear when engaging in activities that may cause skin irritation * Managing chronic conditions like diabetes and eczemaComplications of Cellulitis
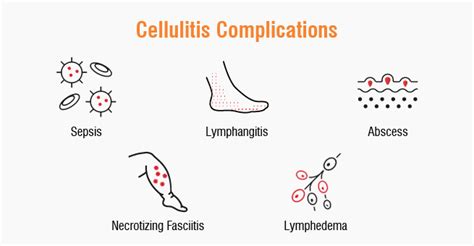
Managing Complications
Managing complications of cellulitis involves seeking prompt medical attention and following a treatment plan. Individuals can also take steps to reduce their risk of complications, such as: * Practicing good wound care and keeping the affected area clean and dry * Taking antibiotics as directed * Elevating the affected area to reduce swelling * Monitoring for signs of complications, such as increased pain, redness, or swellingCellulitis Leg Pictures
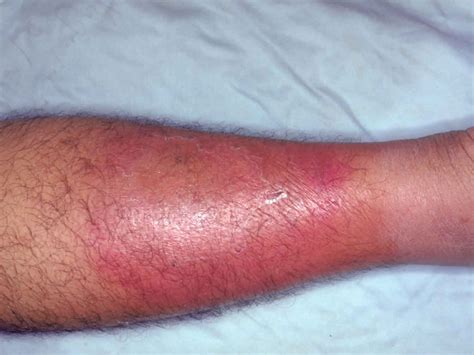
Diagnosing Cellulitis
Diagnosing cellulitis involves a physical examination and medical history. A healthcare professional may also perform tests, such as: * Blood tests to check for signs of infection * Imaging tests, such as X-rays or ultrasound, to rule out other conditions * Wound cultures to identify the type of bacteria causing the infectionWhat are the symptoms of cellulitis?
+The symptoms of cellulitis include redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area, as well as fever, chills, and fatigue.
How is cellulitis treated?
+Cellulitis is typically treated with antibiotics, which can be administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection.
Can cellulitis be prevented?
+Yes, cellulitis can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, avoiding tight clothing, and managing chronic conditions like diabetes and eczema.
What are the complications of cellulitis?
+The complications of cellulitis include abscesses, blood infections, tissue damage, and lymphedema.
How can I manage my symptoms and promote healing?
+You can manage your symptoms and promote healing by resting and elevating the affected area, applying warm compresses, taking over-the-counter pain medications, and keeping the affected area clean and dry.
In conclusion, cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for cellulitis, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent future occurrences. If you suspect you have cellulitis, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and promote healing. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be affected by cellulitis and to comment below with any questions or concerns.
