Intro
Discover Cephalexin uses and benefits, a broad-spectrum antibiotic treating bacterial infections, skin infections, and respiratory issues, with advantages including effectiveness and affordability, and related terms like antibiotic resistance and infection treatment.
The world of antibiotics is vast and complex, with various medications designed to combat different types of bacterial infections. Among these, Cephalexin stands out as a widely used and effective antibiotic. It belongs to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics, which work by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. Understanding the uses and benefits of Cephalexin is crucial for both medical professionals and patients, as it can significantly impact the treatment and management of bacterial infections.
Cephalexin is prescribed for a range of bacterial infections, including those affecting the skin, bone, and respiratory tract. Its broad-spectrum activity makes it a valuable option for treating infections caused by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The medication is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and oral suspensions, making it accessible to patients of different ages and needs. The flexibility in dosage forms, along with its effectiveness, has contributed to the popularity of Cephalexin among healthcare providers.
The importance of Cephalexin lies in its ability to provide relief from the symptoms of bacterial infections, thereby improving the quality of life for those affected. By targeting and eliminating the bacteria causing the infection, Cephalexin helps in reducing the severity of symptoms such as pain, fever, and swelling. Moreover, its use can prevent the spread of infection to other parts of the body, reducing the risk of complications. This is particularly significant in the case of infections that, if left untreated, could lead to serious health issues.
Cephalexin Mechanism of Action

Cephalexin works by interfering with the bacterial cell wall formation. It binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, resulting in the weakening of the cell wall. This weakening leads to the death of the bacterial cell due to osmotic pressure. The mechanism of action of Cephalexin is similar to that of other beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillins and cephalosporins. Understanding this mechanism is essential for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about the use of Cephalexin in treating bacterial infections.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of Cephalexin involves its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. It is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with peak serum concentrations achieved within one hour of administration. Cephalexin is distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in most body tissues and fluids. The medication is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine, with a half-life that allows for twice or four times daily dosing regimens.Cephalexin Uses
Cephalexin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Some of the most common uses include:
- Skin and soft tissue infections: Cephalexin is effective against infections such as impetigo, folliculitis, and cellulitis.
- Respiratory tract infections: It is used to treat infections like pneumonia, bronchitis, and pharyngitis.
- Bone infections: Cephalexin can be prescribed for osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone.
- Genitourinary tract infections: It is effective against infections of the urinary tract, including cystitis and pyelonephritis.
Benefits of Cephalexin
The benefits of Cephalexin are numerous, making it a preferred choice for treating bacterial infections. Some of the key benefits include: - Broad-spectrum activity: Cephalexin is effective against a wide range of bacteria, making it useful for treating various types of infections. - Oral administration: The availability of Cephalexin in oral forms makes it convenient for patients, especially when compared to intravenous antibiotics. - Good tolerability: Cephalexin is generally well-tolerated, with mild side effects that are temporary and resolve on their own. - Cost-effectiveness: Compared to some other antibiotics, Cephalexin can be more cost-effective, which is an important consideration for both patients and healthcare systems.Cephalexin Side Effects and Precautions

Like all medications, Cephalexin can cause side effects, although not everyone who takes the medication will experience them. Common side effects include:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Allergic reactions: Rash, itching, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
- Central nervous system effects: Headache, dizziness, and fatigue.
It is essential to take Cephalexin as directed by a healthcare provider to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure the effectiveness of the treatment. Patients should also be aware of potential drug interactions, especially with other antibiotics, and inform their healthcare provider about any other medications they are taking.
Special Considerations
Cephalexin is generally safe for most patients, but there are special considerations for certain groups. For example: - Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Cephalexin is classified as a category B drug, meaning it is safe to use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but only under the guidance of a healthcare provider. - Renal impairment: Patients with kidney problems may require dose adjustments to prevent accumulation of the drug. - Allergic reactions: Patients with a history of allergic reactions to penicillins or other cephalosporins should use Cephalexin with caution.Cephalexin Dosage and Administration
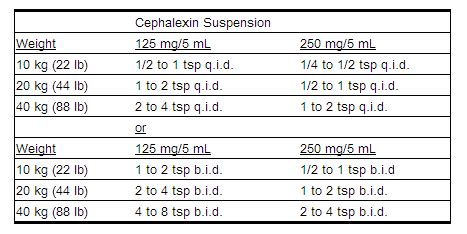
The dosage of Cephalexin varies depending on the type of infection being treated, the patient's age, weight, and renal function. The typical adult dose ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg, taken every 6 to 12 hours. For children, the dose is adjusted based on their weight. It is crucial to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure the infection is fully cleared and reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Resistance and Misuse
The misuse and overuse of antibiotics, including Cephalexin, have contributed to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. This occurs when bacteria develop mechanisms to evade the effects of the antibiotic, making the medication less effective. To combat this issue, it is essential to use Cephalexin and other antibiotics judiciously, following guidelines and prescriptions carefully, and avoiding their use for viral infections, which do not respond to antibiotic treatment.Cephalexin Interactions

Cephalexin can interact with other medications, affecting its efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Some notable interactions include:
- Metformin: Cephalexin can increase the levels of metformin, a drug used to treat diabetes, potentially leading to lactic acidosis.
- Probenecid: This medication can decrease the renal excretion of Cephalexin, leading to higher drug concentrations.
- Warfarin: Cephalexin may enhance the anticoagulant effect of warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and vitamins they are taking to minimize potential interactions.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
During treatment with Cephalexin, patients should be monitored for signs of improvement or adverse effects. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider can help in adjusting the treatment plan as necessary and ensuring the infection is fully cleared. Additionally, monitoring for signs of antibiotic resistance, such as a lack of response to treatment, is crucial for guiding further management.Cephalexin and Pregnancy

The use of Cephalexin during pregnancy is a topic of interest for many expectant mothers. As mentioned, Cephalexin is classified as a category B drug, indicating that it is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy. However, the decision to use Cephalexin should be made under the guidance of a healthcare provider, who can weigh the benefits against potential risks and monitor the pregnancy closely.
Pediatric Use
Cephalexin is also used in pediatric patients for the treatment of bacterial infections. The dosage is adjusted based on the child's weight, and the medication is available in forms that are easy for children to take, such as oral suspensions. Parents or guardians should ensure that children complete the full course of treatment as prescribed and monitor them for any signs of side effects.Cephalexin Alternatives

For patients who are allergic to Cephalexin or in whom the medication is not effective, there are several alternative antibiotics that can be considered. These include other cephalosporins, such as cefaclor or cefuroxime, as well as non-cephalosporin antibiotics like amoxicillin or azithromycin. The choice of alternative antibiotic depends on the type of infection, the causative bacteria, and the patient's medical history.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, Cephalexin is a valuable antibiotic in the treatment of various bacterial infections. Its effectiveness, combined with its broad-spectrum activity and relatively good tolerability, makes it a preferred choice for many healthcare providers. However, the growing concern of antibiotic resistance underscores the need for responsible use of Cephalexin and other antibiotics. Future directions in the management of bacterial infections may include the development of new antibiotics, improved diagnostic tools for identifying bacterial resistance, and enhanced public health initiatives to promote the judicious use of antibiotics.As we look to the future, it is essential to continue researching and developing new strategies for combating bacterial infections, including the use of Cephalexin and other antibiotics. By doing so, we can ensure that these life-saving medications remain effective for generations to come.
What is Cephalexin used for?
+Cephalexin is used to treat bacterial infections, including those of the skin, respiratory tract, bone, and genitourinary tract.
How does Cephalexin work?
+Cephalexin works by interfering with the formation of the bacterial cell wall, leading to the death of the bacterial cell.
Can I take Cephalexin during pregnancy?
+Cephalexin is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but its use should be guided by a healthcare provider to weigh the benefits against potential risks.
What are the common side effects of Cephalexin?
+Common side effects of Cephalexin include gastrointestinal disturbances, allergic reactions, and central nervous system effects.
How long does it take for Cephalexin to start working?
+Cephalexin starts working within a few hours of administration, but it may take several days to notice significant improvement in symptoms.
We hope this comprehensive overview of Cephalexin has provided you with valuable insights into its uses, benefits, and considerations for use. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with Cephalexin, please do not hesitate to comment below. Your input can help others make informed decisions about their health. Additionally, if you found this article informative, consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this knowledge. Together, we can promote responsible antibiotic use and contribute to the fight against antibiotic resistance.
