Intro
Treat chemical burns on skin with effective remedies. Learn about causes, symptoms, and treatments, including first aid, wound care, and scar prevention for acid, alkaline, and toxic burns.
Chemical burns on the skin can be extremely painful and potentially disfiguring, making it essential to understand the proper treatment and care for such injuries. Chemical burns occur when the skin comes into contact with a corrosive substance, such as acid or alkali, causing damage to the skin and underlying tissues. The severity of the burn can vary depending on the type of chemical, the duration of exposure, and the concentration of the substance.
The importance of prompt and proper treatment for chemical burns cannot be overstated. If left untreated or improperly treated, chemical burns can lead to serious complications, including infection, scarring, and even permanent damage to the skin and underlying tissues. Furthermore, chemical burns can also have psychological and emotional effects on the individual, making it crucial to provide compassionate and comprehensive care.
Chemical burns can occur in various settings, including workplaces, homes, and laboratories, making it essential for individuals to be aware of the potential risks and take necessary precautions to prevent such incidents. However, despite the best efforts to prevent chemical burns, accidents can still happen, and it is crucial to know how to respond and treat such injuries effectively.
Understanding Chemical Burns
Chemical burns are classified into different types based on the severity of the injury. First-degree chemical burns affect only the outer layer of the skin, causing redness, swelling, and pain. Second-degree chemical burns extend to the deeper layers of the skin, causing blisters, burns, and potential scarring. Third-degree chemical burns are the most severe, extending through all layers of the skin and potentially damaging underlying tissues, such as muscles, tendons, and bones.
Causes of Chemical Burns
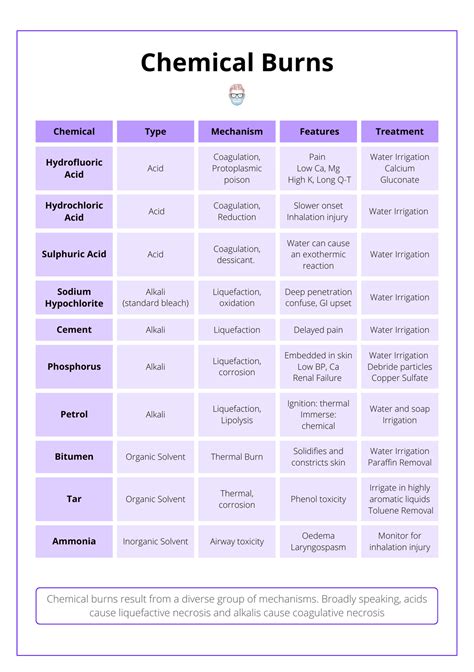
Chemical burns can be caused by a wide range of substances, including acids, alkalis, and other corrosive materials. Some common causes of chemical burns include: * Acidic substances, such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid * Alkaline substances, such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and calcium hydroxide * Other corrosive materials, such as bleach, ammonia, and drain cleanersTreatment for Chemical Burns

The treatment for chemical burns depends on the severity of the injury and the type of substance that caused the burn. For minor chemical burns, treatment may involve:
- Flushing the affected area with cool water to remove any remaining chemical substance
- Applying a topical antibiotic ointment to prevent infection
- Covering the affected area with a non-stick dressing to protect the wound
- Taking pain medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to manage pain and discomfort
For more severe chemical burns, treatment may involve:
- Immediate medical attention to assess the severity of the injury and provide prompt treatment
- Decontamination of the affected area to remove any remaining chemical substance
- Administration of pain medication and other medications to manage symptoms and prevent complications
- Surgical intervention to repair damaged tissues and promote healing
Steps for Treating Chemical Burns
Here are some steps to follow when treating chemical burns: 1. **Remove contaminated clothing**: Remove any clothing or jewelry that may have come into contact with the chemical substance to prevent further exposure. 2. **Flush the affected area**: Flush the affected area with cool water to remove any remaining chemical substance. 3. **Neutralize the chemical**: If the chemical burn is caused by an acid, apply a weak base, such as baking soda, to neutralize the acid. If the chemical burn is caused by an alkali, apply a weak acid, such as vinegar, to neutralize the alkali. 4. **Apply a topical antibiotic ointment**: Apply a topical antibiotic ointment to prevent infection and promote healing. 5. **Cover the affected area**: Cover the affected area with a non-stick dressing to protect the wound and promote healing.Prevention of Chemical Burns

Prevention is key when it comes to chemical burns. Here are some tips to prevent chemical burns:
- Wear protective gear: Wear protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and masks, when handling chemical substances.
- Read labels carefully: Read labels carefully to understand the potential risks and hazards associated with a particular chemical substance.
- Follow instructions: Follow instructions carefully when handling chemical substances to minimize the risk of exposure.
- Keep chemicals out of reach: Keep chemicals out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental exposure.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when treating chemical burns: * **Not seeking medical attention**: Failing to seek medical attention promptly can lead to serious complications and long-term damage. * **Not flushing the affected area**: Not flushing the affected area with cool water can cause the chemical substance to continue damaging the skin and underlying tissues. * **Not applying a topical antibiotic ointment**: Not applying a topical antibiotic ointment can increase the risk of infection and delay healing. * **Not covering the affected area**: Not covering the affected area with a non-stick dressing can expose the wound to further irritation and infection.Complications of Chemical Burns
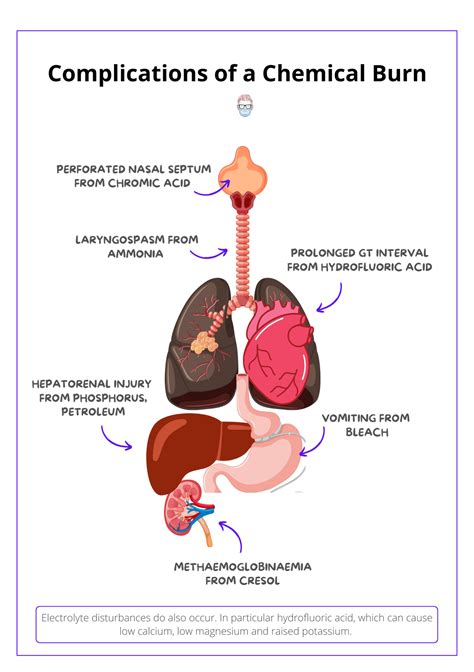
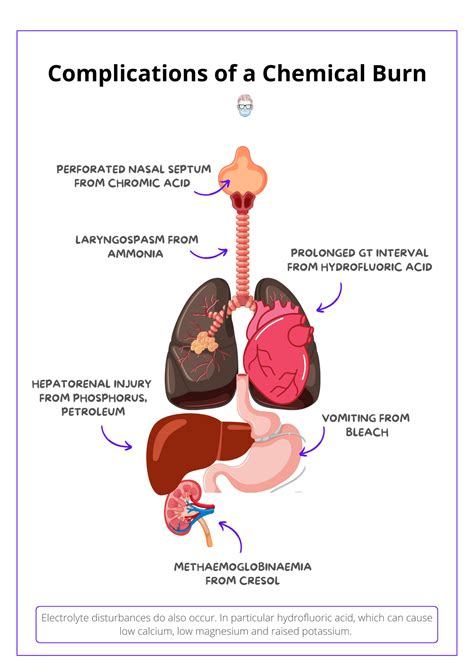
Chemical burns can lead to serious complications, including:
- Infection: Chemical burns can increase the risk of infection, particularly if the wound is not properly cleaned and dressed.
- Scarring: Chemical burns can cause scarring, particularly if the burn is deep or large.
- Permanent damage: Chemical burns can cause permanent damage to the skin and underlying tissues, particularly if the burn is severe or if treatment is delayed.
- Psychological trauma: Chemical burns can cause psychological trauma, particularly if the burn is severe or if the individual experiences pain, discomfort, or disfigurement.
Long-term Effects of Chemical Burns
The long-term effects of chemical burns can be significant, including: * **Disfigurement**: Chemical burns can cause disfigurement, particularly if the burn is severe or if scarring occurs. * **Chronic pain**: Chemical burns can cause chronic pain, particularly if the burn is severe or if nerve damage occurs. * **Emotional trauma**: Chemical burns can cause emotional trauma, particularly if the individual experiences anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). * **Physical disability**: Chemical burns can cause physical disability, particularly if the burn is severe or if the individual experiences limited mobility or function.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, chemical burns on the skin can be extremely painful and potentially disfiguring, making it essential to understand the proper treatment and care for such injuries. By following the steps outlined in this article, individuals can minimize the risk of complications and promote healing. It is also essential to take preventive measures to avoid chemical burns, such as wearing protective gear, reading labels carefully, and following instructions.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with chemical burns in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. Additionally, if you know someone who has experienced a chemical burn, please share this article with them to help promote awareness and education.
What are the common causes of chemical burns?
+Chemical burns can be caused by a wide range of substances, including acids, alkalis, and other corrosive materials. Some common causes of chemical burns include acidic substances, such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid, as well as alkaline substances, such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and calcium hydroxide.
How can I prevent chemical burns?
+Prevention is key when it comes to chemical burns. To prevent chemical burns, wear protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and masks, when handling chemical substances. Read labels carefully to understand the potential risks and hazards associated with a particular chemical substance. Follow instructions carefully when handling chemical substances to minimize the risk of exposure. Keep chemicals out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental exposure.
What are the complications of chemical burns?
+Chemical burns can lead to serious complications, including infection, scarring, permanent damage, and psychological trauma. Infection can occur if the wound is not properly cleaned and dressed. Scarring can occur, particularly if the burn is deep or large. Permanent damage can occur, particularly if the burn is severe or if treatment is delayed. Psychological trauma can occur, particularly if the individual experiences pain, discomfort, or disfigurement.
