Intro
Discover the 5 ways chloride test kits ensure water quality, preventing corrosion and damage, with accurate chloride ion measurement, water treatment, and pool maintenance insights.
The importance of water quality cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts both human health and the environment. One crucial aspect of water quality is the concentration of chloride ions, which can have significant effects on aquatic life and infrastructure. Chloride testing is a vital tool for assessing water quality, and there are various methods to determine chloride levels in water. In this article, we will delve into the world of chloride testing, exploring its significance, different testing methods, and the implications of chloride presence in water.
Water is essential for human survival, and its quality is directly linked to our well-being. Chloride ions are naturally present in water, but high concentrations can be harmful to both humans and the environment. For instance, excessive chloride levels can damage crops, corrode infrastructure, and even affect human health. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor chloride levels in water to prevent these adverse effects. Chloride testing is a straightforward process that can be performed using various methods, each with its advantages and limitations.
The presence of chloride ions in water can have far-reaching consequences, making it essential to understand the different testing methods available. Chloride testing can be performed in laboratories, on-site, or even using portable testing kits. The choice of testing method depends on the desired level of accuracy, the availability of resources, and the specific requirements of the testing scenario. In the following sections, we will explore the different methods of chloride testing, their applications, and the significance of chloride levels in water.
Introduction to Chloride Testing

Importance of Chloride Testing
Chloride testing is essential for various industries, including water treatment, agriculture, and construction. In water treatment, chloride testing helps determine the effectiveness of treatment processes and ensures that the water is safe for human consumption. In agriculture, chloride testing is crucial for assessing soil health and preventing damage to crops. In construction, chloride testing is used to evaluate the durability of infrastructure and prevent corrosion. The presence of chloride ions can have significant effects on the environment, human health, and the economy, making chloride testing a vital tool for maintaining water quality.Methods of Chloride Testing

Titrative Method
The titrative method is a widely used technique for chloride testing, which involves reacting the water sample with a known amount of silver nitrate solution. The reaction precipitates out the chloride ions, and the amount of silver nitrate required to react with all the chloride ions is directly proportional to the chloride concentration. This method is relatively simple and inexpensive but may not be as accurate as other methods.Applications of Chloride Testing

Chloride Testing in Water Treatment
Chloride testing is an essential component of water treatment, as it helps determine the effectiveness of treatment processes and ensures that the water is safe for human consumption. Chloride ions can be removed from water using various treatment methods, including reverse osmosis, distillation, and ion exchange. Chloride testing is used to monitor the chloride concentration in the treated water and adjust the treatment process as needed.Interpreting Chloride Test Results
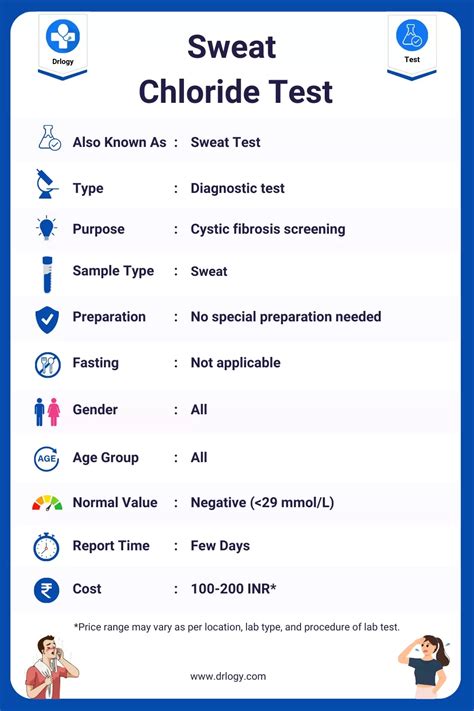
Chloride Test Result Interpretation
Chloride test result interpretation requires careful consideration of the testing method used, the potential sources of error, and the established standards and guidelines. The test results should be evaluated in the context of the specific application and the potential risks associated with chloride presence in water. It is essential to consult with a qualified professional or expert in the field to ensure accurate interpretation of the test results and to develop effective strategies for managing chloride-related issues.Chloride Testing Equipment and Supplies

Chloride Testing Kits
Chloride testing kits are widely available and offer a convenient and cost-effective way to perform chloride testing. These kits typically include all the necessary equipment and supplies, including a testing method, a calibration standard, and a data acquisition system. Chloride testing kits are available for various testing methods, including titration, colorimetry, and ion chromatography.Best Practices for Chloride Testing

Chloride Testing Protocols
Chloride testing protocols are essential for ensuring accurate and reliable test results. These protocols typically include detailed instructions for sample collection, testing, and data interpretation. Chloride testing protocols may vary depending on the specific testing method, the desired level of accuracy, and the availability of resources. It is essential to follow established protocols and guidelines to ensure accurate and reliable test results.What is chloride testing?
+Chloride testing is a process used to determine the concentration of chloride ions in water.
Why is chloride testing important?
+Chloride testing is important because high levels of chloride ions can have significant effects on the environment, human health, and the economy.
What are the different methods of chloride testing?
+The different methods of chloride testing include titration, colorimetry, and ion chromatography.
How do I interpret chloride test results?
+Interpreting chloride test results requires a good understanding of the testing method used and the potential sources of error. The test results should be compared to established standards and guidelines to determine the acceptability of the water quality.
What are the best practices for chloride testing?
+Best practices for chloride testing include following established testing protocols and guidelines, using calibrated and maintained equipment, ensuring proper sample collection and handling, minimizing potential sources of error, and interpreting test results in the context of the specific application and established standards and guidelines.
In
