Intro
Learn about Gallbladder Surgery, also known as Cholecystectomy, a procedure to remove the gallbladder, relieving symptoms of gallstones, inflammation, and infection, with minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques for a faster recovery.
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under the liver, responsible for storing bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. While it plays a crucial role in the digestive process, the gallbladder can sometimes become diseased or inflamed, leading to severe abdominal pain, nausea, and other complications. In such cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy, may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and prevent further health issues. With advancements in medical technology, gallbladder surgery has become a relatively common and safe procedure, offering relief to thousands of patients worldwide.
Gallbladder disease is a common condition that affects millions of people, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. The most common reason for gallbladder surgery is the presence of gallstones, which are small, hard deposits that can block the flow of bile and cause inflammation. Other conditions, such as gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis) or gallbladder cancer, may also require surgical intervention. As the gallbladder is not essential for human survival, its removal can provide significant relief from symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
The decision to undergo gallbladder surgery is typically made after a thorough medical evaluation, including diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI. These tests help doctors determine the presence and severity of gallbladder disease, as well as rule out other potential causes of symptoms. In some cases, medication or other non-surgical treatments may be recommended to manage symptoms, but for many patients, surgery remains the most effective and long-term solution. With the rise of minimally invasive surgical techniques, patients can now undergo gallbladder surgery with reduced recovery time, less scarring, and minimal complications.
Gallbladder Surgery Overview
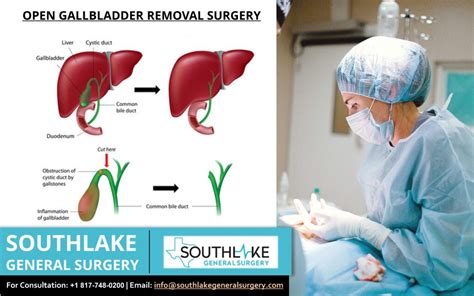
Types of Gallbladder Surgery
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the most common type of gallbladder surgery, accounting for over 90% of all procedures. This minimally invasive technique offers several benefits, including reduced recovery time, less scarring, and minimal complications. Open cholecystectomy, while less common, may be recommended for patients with severe gallbladder disease, inflammation, or other complications that require a more traditional surgical approach. In some cases, a combination of both techniques may be used, where the surgeon starts with a laparoscopic approach and then switches to an open approach if necessary.Gallbladder Surgery Procedure
Preparation and Recovery
Preparation for gallbladder surgery typically involves a series of tests and evaluations to ensure the patient is healthy enough for the procedure. Patients may be required to fast for several hours before surgery, and any medications that may interfere with the procedure may need to be adjusted or discontinued. After surgery, patients can expect to spend several hours in the recovery room, where they will be monitored for any complications or adverse reactions to the anesthesia. Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and individual factors, but most patients can return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks.Risks and Complications

Benefits and Results
The benefits of gallbladder surgery are numerous, with most patients experiencing significant relief from symptoms and improved quality of life. The procedure can help alleviate abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, and can also reduce the risk of further complications, such as gallbladder rupture or cancer. While some patients may experience temporary side effects, such as diarrhea or bloating, these typically resolve on their own within a few weeks.Life After Gallbladder Surgery
Dietary Changes
After gallbladder surgery, patients may need to make certain dietary changes to manage bile production and prevent diarrhea. These may include avoiding fatty or greasy foods, increasing fiber intake, and staying hydrated. In some cases, patients may need to take bile salts or other supplements to support digestion and prevent nutrient deficiencies.Gallbladder Surgery Cost

Insurance Coverage
Gallbladder surgery is typically covered by most insurance plans, including Medicare and Medicaid. However, coverage and out-of-pocket costs may vary depending on the individual's insurance plan and provider. Patients should review their insurance policy and discuss the costs and coverage with their surgeon and insurance provider to ensure they understand their financial responsibilities.What are the symptoms of gallbladder disease?
+Common symptoms of gallbladder disease include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. In some cases, patients may experience more severe symptoms, such as jaundice or pancreatitis.
What are the risks of gallbladder surgery?
+The risks of gallbladder surgery include bleeding, infection, bile leakage, and injury to surrounding organs. In rare cases, patients may experience more severe complications, such as respiratory or cardiac problems.
How long does it take to recover from gallbladder surgery?
+Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and individual factors, but most patients can return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks. Patients should follow the surgeon's instructions and attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to ensure a smooth and successful recovery.
In conclusion, gallbladder surgery is a safe and effective procedure for treating gallbladder disease and alleviating symptoms. While it carries certain risks and complications, the benefits of the procedure far outweigh the risks for most patients. By understanding the procedure, risks, and benefits, patients can make informed decisions about their care and take the first step towards a healthier, happier life. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with gallbladder surgery in the comments below, and to share this article with anyone who may be considering the procedure.
