Intro
Discover Chorionic Hematoma bleeding symptoms, causes, and treatment. Learn about placental abruption, maternal complications, and fetal distress related to this pregnancy condition.
The phenomenon of chorionic hematoma bleeding symptoms is a critical aspect of pregnancy that expectant mothers and healthcare providers must be aware of. Chorionic hematoma, also known as subchorionic hematoma, is a condition where blood accumulates between the placenta and the uterus, leading to potential complications. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and implications of chorionic hematoma bleeding is essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and preventing adverse outcomes.
Chorionic hematoma bleeding symptoms can be subtle, making it challenging for pregnant women to recognize the signs. However, being informed about the possible indicators can facilitate prompt medical attention and intervention. The symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and back pain, which can range from mild to severe. In some cases, women may experience no symptoms at all, making regular prenatal check-ups crucial for detecting any potential issues.
The importance of recognizing chorionic hematoma bleeding symptoms lies in the potential risks associated with this condition. If left untreated, chorionic hematoma can lead to miscarriage, preterm labor, and other complications that can affect the health of both the mother and the baby. Moreover, chorionic hematoma can increase the risk of placental abruption, a condition where the placenta separates from the uterus, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby. Therefore, it is essential to be aware of the symptoms and seek medical attention immediately if any concerns arise.
What is Chorionic Hematoma?
Chorionic hematoma is a condition characterized by the accumulation of blood between the placenta and the uterus. This blood accumulation can lead to the formation of a hematoma, which can cause symptoms such as vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and back pain. Chorionic hematoma can occur at any stage of pregnancy, but it is more common during the early stages. The exact cause of chorionic hematoma is still unknown, but several factors can increase the risk, including trauma, placental abruption, and underlying medical conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes and risk factors associated with chorionic hematoma are crucial in understanding the condition. While the exact cause is still unknown, several factors can increase the risk of developing chorionic hematoma. These include:- Trauma: Physical trauma, such as a fall or a car accident, can cause chorionic hematoma.
- Placental abruption: Placental abruption, a condition where the placenta separates from the uterus, can increase the risk of chorionic hematoma.
- Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and thyroid disorders, can increase the risk of chorionic hematoma.
- Multiple pregnancy: Women carrying multiple fetuses are at a higher risk of developing chorionic hematoma.
Symptoms of Chorionic Hematoma Bleeding
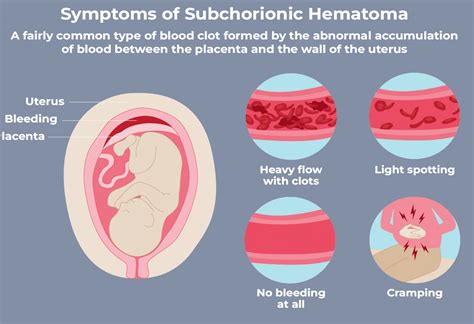
The symptoms of chorionic hematoma bleeding can vary from woman to woman. Some women may experience mild symptoms, while others may experience severe symptoms that require immediate medical attention. The symptoms may include:
- Vaginal bleeding: Vaginal bleeding is the most common symptom of chorionic hematoma bleeding. The bleeding can range from light to heavy and may be accompanied by clots.
- Abdominal pain: Abdominal pain is another common symptom of chorionic hematoma bleeding. The pain can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent.
- Back pain: Back pain is also a common symptom of chorionic hematoma bleeding. The pain can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent.
- Pelvic pressure: Some women may experience pelvic pressure or a feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing chorionic hematoma bleeding requires a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. The diagnostic tests may include:- Ultrasound: Ultrasound is the primary diagnostic tool for detecting chorionic hematoma. The test can help identify the presence of a hematoma and determine its size and location.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the hematoma.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to monitor the mother's blood count and detect any signs of infection.
The treatment for chorionic hematoma bleeding depends on the severity of the symptoms and the gestational age of the fetus. The treatment options may include:
- Bed rest: Bed rest is often recommended to reduce the risk of further bleeding and promote healing.
- Pain management: Pain management medications may be prescribed to manage abdominal pain and back pain.
- Monitoring: Close monitoring of the mother and the fetus is essential to detect any signs of complications.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the hematoma and prevent further complications.
Complications of Chorionic Hematoma Bleeding

Chorionic hematoma bleeding can lead to several complications, including:
- Miscarriage: Chorionic hematoma bleeding can increase the risk of miscarriage, especially if the bleeding is heavy and prolonged.
- Preterm labor: Chorionic hematoma bleeding can increase the risk of preterm labor, which can lead to premature birth and other complications.
- Placental abruption: Chorionic hematoma bleeding can increase the risk of placental abruption, a condition where the placenta separates from the uterus.
- Fetal growth restriction: Chorionic hematoma bleeding can reduce blood flow to the fetus, leading to fetal growth restriction and other complications.
Prevention and Management
Preventing chorionic hematoma bleeding requires a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. The prevention strategies may include:- Avoiding trauma: Avoiding physical trauma, such as falls and car accidents, can reduce the risk of chorionic hematoma bleeding.
- Managing underlying medical conditions: Managing underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes, can reduce the risk of chorionic hematoma bleeding.
- Avoiding strenuous activities: Avoiding strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting and bending, can reduce the risk of chorionic hematoma bleeding.
- Regular prenatal check-ups: Regular prenatal check-ups can help detect any signs of chorionic hematoma bleeding and prevent complications.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, chorionic hematoma bleeding symptoms are a critical aspect of pregnancy that requires prompt medical attention and intervention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and implications of chorionic hematoma bleeding is essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and preventing adverse outcomes. By being informed and taking preventive measures, pregnant women can reduce the risk of chorionic hematoma bleeding and promote a healthy pregnancy.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with chorionic hematoma bleeding symptoms in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to ask. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about chorionic hematoma bleeding symptoms and promote healthy pregnancies.
What is chorionic hematoma bleeding?
+Chorionic hematoma bleeding is a condition where blood accumulates between the placenta and the uterus, leading to potential complications.
What are the symptoms of chorionic hematoma bleeding?
+The symptoms of chorionic hematoma bleeding may include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, back pain, and pelvic pressure.
How is chorionic hematoma bleeding diagnosed?
+Chorionic hematoma bleeding is diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound and MRI.
What are the complications of chorionic hematoma bleeding?
+The complications of chorionic hematoma bleeding may include miscarriage, preterm labor, placental abruption, and fetal growth restriction.
How can chorionic hematoma bleeding be prevented?
+Chorionic hematoma bleeding can be prevented by avoiding trauma, managing underlying medical conditions, avoiding strenuous activities, and attending regular prenatal check-ups.
