Intro
Discover 5 ways to define chronic pain, including persistent discomfort, neuropathic pain, and inflammatory responses, to better understand chronic pain management and relief strategies.
Chronic pain is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a major public health concern, with significant economic, social, and emotional impacts on individuals, families, and society as a whole. Despite its prevalence, chronic pain remains poorly understood, and its definition can be somewhat ambiguous. In this article, we will delve into the concept of chronic pain, its characteristics, and the various ways it can be defined.
The experience of chronic pain can vary greatly from person to person, and it can be influenced by a range of factors, including the underlying cause, individual tolerance, and emotional state. Some people may experience chronic pain as a constant, debilitating ache, while others may experience it as a recurring, episodic phenomenon. Regardless of its nature, chronic pain can have a profound impact on a person's quality of life, affecting their ability to work, maintain relationships, and engage in daily activities.
Chronic pain is often distinguished from acute pain, which is a normal, adaptive response to tissue damage or injury. Acute pain serves as a warning signal, alerting the individual to potential harm and prompting them to take action to prevent further injury. In contrast, chronic pain persists long after the initial injury has healed, and it can be resistant to treatment. The transition from acute to chronic pain is not always clear-cut, and it can be influenced by a range of factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and psychological state.
Introduction to Chronic Pain

Chronic pain can be defined in various ways, depending on the context and the criteria used. Some common definitions include the duration of pain, the intensity of pain, and the impact of pain on daily life. In general, chronic pain is characterized by its persistence, resistance to treatment, and significant impact on quality of life.
Characteristics of Chronic Pain
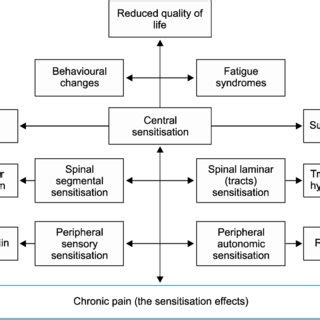
The characteristics of chronic pain can vary greatly from person to person, but some common features include:
- Persistence: Chronic pain persists over time, often for months or years.
- Resistance to treatment: Chronic pain can be resistant to treatment, and it may require a multidisciplinary approach to manage.
- Significant impact on quality of life: Chronic pain can have a profound impact on a person's quality of life, affecting their ability to work, maintain relationships, and engage in daily activities.
- Emotional and psychological components: Chronic pain often has emotional and psychological components, including anxiety, depression, and stress.
Types of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain can be categorized into different types, depending on the underlying cause and the characteristics of the pain. Some common types of chronic pain include: * Neuropathic pain: This type of pain is caused by damage to the nervous system, and it can be characterized by burning, shooting, or stabbing sensations. * Nociceptive pain: This type of pain is caused by tissue damage or inflammation, and it can be characterized by aching, throbbing, or stabbing sensations. * Psychogenic pain: This type of pain is caused by psychological or emotional factors, and it can be characterized by a range of symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and stress.Causes of Chronic Pain
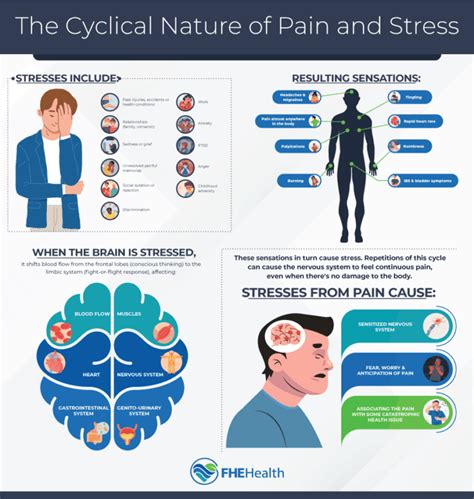
The causes of chronic pain can be complex and multifaceted, and they may involve a range of factors, including:
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to chronic pain due to their genetic makeup.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors, such as trauma, injury, or infection, can contribute to the development of chronic pain.
- Psychological factors: Psychological factors, such as anxiety, depression, and stress, can contribute to the development and maintenance of chronic pain.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and diabetes, can increase the risk of developing chronic pain.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Pain
The diagnosis and treatment of chronic pain can be challenging, and it often requires a multidisciplinary approach. Some common diagnostic tools include: * Medical history: A thorough medical history can help identify the underlying cause of chronic pain. * Physical examination: A physical examination can help identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to chronic pain. * Imaging studies: Imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans, can help identify any underlying structural abnormalities that may be contributing to chronic pain. * Psychological evaluation: A psychological evaluation can help identify any underlying psychological or emotional factors that may be contributing to chronic pain.Treatment Options for Chronic Pain

The treatment of chronic pain often requires a multidisciplinary approach, and it may involve a range of interventions, including:
- Medications: Medications, such as analgesics, anti-inflammatory agents, and antidepressants, can help manage chronic pain.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy, such as exercise, stretching, and massage, can help improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Psychological therapy: Psychological therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction, can help manage emotional and psychological factors that contribute to chronic pain.
- Alternative therapies: Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and herbal supplements, can help manage chronic pain.
Coping with Chronic Pain
Coping with chronic pain can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help. Some common coping strategies include: * Seeking support: Seeking support from family, friends, and support groups can help individuals cope with chronic pain. * Practicing self-care: Practicing self-care, such as getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in regular exercise, can help manage chronic pain. * Managing stress: Managing stress, through techniques such as meditation and deep breathing, can help reduce the emotional and psychological components of chronic pain. * Setting realistic goals: Setting realistic goals, such as taking regular breaks and prioritizing activities, can help individuals manage chronic pain and maintain a sense of control and purpose.Living with Chronic Pain

Living with chronic pain can be challenging, but it is possible to manage its impact and maintain a good quality of life. Some common strategies for living with chronic pain include:
- Creating a pain management plan: Creating a pain management plan, in consultation with a healthcare provider, can help individuals manage chronic pain and maintain a sense of control and purpose.
- Building a support network: Building a support network, including family, friends, and support groups, can help individuals cope with chronic pain.
- Practicing self-compassion: Practicing self-compassion, through techniques such as mindfulness and self-care, can help individuals manage the emotional and psychological components of chronic pain.
- Staying positive: Staying positive, through techniques such as gratitude and positive self-talk, can help individuals maintain a sense of hope and optimism, even in the face of chronic pain.
Future Directions in Chronic Pain Research
The field of chronic pain research is constantly evolving, and there are several future directions that hold promise for improving our understanding and management of chronic pain. Some common areas of research include: * Personalized medicine: Personalized medicine, which involves tailoring treatment to an individual's unique genetic and environmental profile, may help improve the effectiveness of chronic pain treatment. * Non-pharmacological interventions: Non-pharmacological interventions, such as mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral therapy, may help reduce the reliance on medications and improve the overall management of chronic pain. * Alternative therapies: Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal supplements, may provide additional options for managing chronic pain. * Technological advancements: Technological advancements, such as wearable devices and mobile apps, may help improve the monitoring and management of chronic pain.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, chronic pain is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Its definition can be somewhat ambiguous, but it is generally characterized by its persistence, resistance to treatment, and significant impact on quality of life. The causes of chronic pain can be complex and multifaceted, and they may involve a range of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, psychological factors, and medical conditions. The diagnosis and treatment of chronic pain can be challenging, and it often requires a multidisciplinary approach. By understanding the characteristics, causes, and treatment options for chronic pain, individuals can better manage its impact and maintain a good quality of life.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with chronic pain in the comments below. How do you manage your chronic pain? What strategies have you found to be most effective? By sharing your story, you can help others who may be struggling with chronic pain, and you can contribute to a greater understanding of this complex condition.
What is chronic pain?
+Chronic pain is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by its persistence, resistance to treatment, and significant impact on quality of life.
What are the causes of chronic pain?
+The causes of chronic pain can be complex and multifaceted, and they may involve a range of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, psychological factors, and medical conditions.
How is chronic pain diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of chronic pain often requires a multidisciplinary approach, and it may involve a range of diagnostic tools, including medical history, physical examination, imaging studies, and psychological evaluation.
What are the treatment options for chronic pain?
+The treatment of chronic pain often requires a multidisciplinary approach, and it may involve a range of interventions, including medications, physical therapy, psychological therapy, and alternative therapies.
How can I manage my chronic pain?
+Managing chronic pain can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help, including seeking support, practicing self-care, managing stress, and setting realistic goals.
