Intro
Discover Clindamycin uses for treating bacterial infections, acne, skin infections, and respiratory issues, with its antibiotic properties and benefits, and learn about its applications and side effects.
Clindamycin is a type of antibiotic that has been widely used to treat various bacterial infections. It belongs to the class of lincosamide antibiotics and works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. The importance of clindamycin lies in its ability to combat infections that are resistant to other types of antibiotics, making it a valuable treatment option for many patients. With its broad spectrum of activity, clindamycin has become a staple in the treatment of various bacterial infections, and its uses continue to expand as research uncovers its potential benefits.
Clindamycin has been used to treat a range of infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, respiratory tract infections, and infections of the bones and joints. Its effectiveness in treating these types of infections has made it a popular choice among healthcare professionals. Additionally, clindamycin has been used to treat infections caused by anaerobic bacteria, which are bacteria that thrive in environments with low oxygen levels. This makes it an essential treatment option for infections that occur in areas with limited oxygen supply, such as the digestive tract or the female reproductive system.
The versatility of clindamycin has led to its use in various medical specialties, including dermatology, orthopedics, and obstetrics and gynecology. Its ability to penetrate deep into tissues and reach high concentrations at the site of infection makes it an effective treatment option for infections that are difficult to reach with other antibiotics. Furthermore, clindamycin has been used in combination with other antibiotics to treat complex infections, highlighting its potential as a valuable component of combination therapy regimens.
Clindamycin Uses

Clindamycin Mechanism of Action
Clindamycin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, which is responsible for protein synthesis. This binding prevents the formation of peptides, which are essential for bacterial growth and survival. As a result, clindamycin is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Clindamycin Benefits

Clindamycin Side Effects
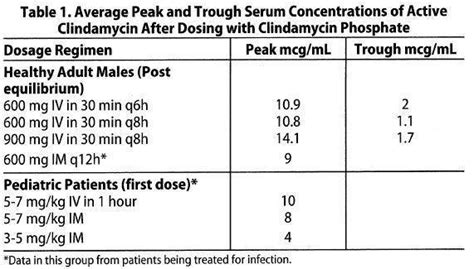
Like all antibiotics, clindamycin can cause side effects, including: * Gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea * Allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, and difficulty breathing * Increased risk of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection * Increased risk of antibiotic resistanceClindamycin Dosage
Clindamycin Interactions
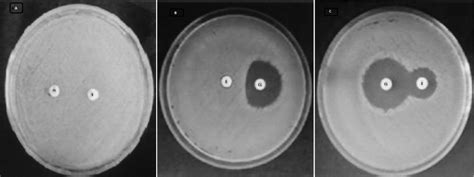
Clindamycin can interact with other medications, including: * Erythromycin, which can increase the risk of side effects * Warfarin, which can increase the risk of bleeding * Neuromuscular blockers, which can increase the risk of respiratory depressionClindamycin Resistance
Clindamycin Alternatives
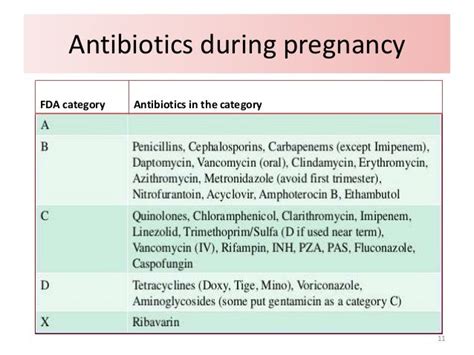
Alternatives to clindamycin include: * Other lincosamide antibiotics, such as lincomycin * Macrolide antibiotics, such as erythromycin and azithromycin * Fluoroquinolone antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin * Cephalosporin antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone and cefepimeClindamycin and Pregnancy
Clindamycin and Breastfeeding
Clindamycin is excreted in breast milk, and its use during breastfeeding should be approached with caution. The benefits of using clindamycin during breastfeeding should be weighed against the potential risks, and alternative treatments should be considered if possible.Clindamycin and Children

Clindamycin and Elderly
Clindamycin can be used in elderly patients, but the dosage and formulation should be adjusted according to the patient's age and health status. The use of clindamycin in elderly patients should be approached with caution, and alternative treatments should be considered if possible.What is clindamycin used for?
+Clindamycin is used to treat a range of bacterial infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, respiratory tract infections, and infections of the bones and joints.
How does clindamycin work?
+Clindamycin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, which is responsible for protein synthesis.
What are the side effects of clindamycin?
+The side effects of clindamycin include gastrointestinal side effects, allergic reactions, increased risk of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection, and increased risk of antibiotic resistance.
Can clindamycin be used during pregnancy?
+Clindamycin is generally considered safe to use during pregnancy, but it should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Can clindamycin be used in children?
+Clindamycin can be used in children, but the dosage and formulation should be adjusted according to the child's age and weight.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of clindamycin uses and its benefits. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with clindamycin, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
