Intro
Clopidogrel treats heart conditions like coronary artery disease, preventing blood clots and strokes, with antiplatelet therapy, cardiovascular benefits, and reduced cardiac risk.
The use of medications to manage and prevent heart conditions has become a cornerstone of modern medicine. Among the various drugs available, clopidogrel has emerged as a crucial component in the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases. This medication, commonly known by its brand name Plavix, has been widely used to reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes in patients with certain heart conditions. The importance of clopidogrel lies in its ability to prevent platelets from clumping together and forming blood clots, which can block arteries and lead to severe cardiovascular events.
Clopidogrel is particularly beneficial for patients who have experienced a heart attack or stroke, as well as those with peripheral artery disease. By inhibiting platelet activation, clopidogrel reduces the risk of subsequent cardiovascular events, thereby improving the patient's quality of life and increasing their chances of survival. Furthermore, clopidogrel is often used in combination with other medications, such as aspirin, to enhance its effectiveness in preventing blood clots. The combination of clopidogrel and aspirin has been shown to be particularly effective in reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes in patients with acute coronary syndrome.
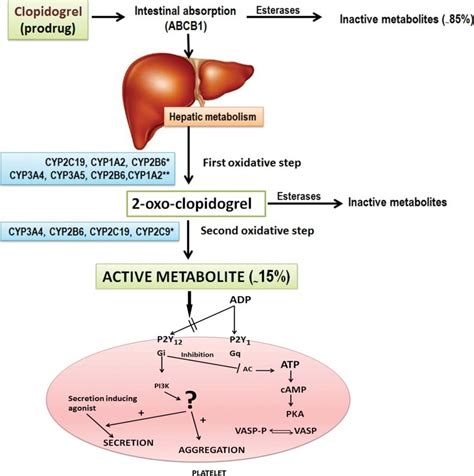
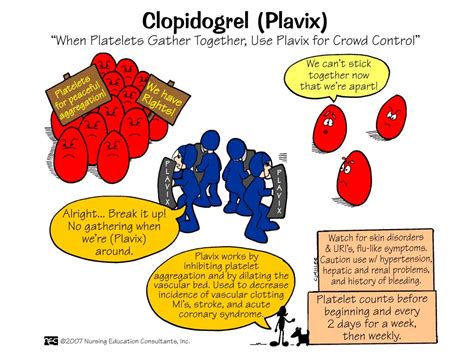
The mechanism of action of clopidogrel is complex and involves the inhibition of the P2Y12 receptor on platelets. By blocking this receptor, clopidogrel prevents adenosine diphosphate (ADP) from binding to the receptor, which in turn prevents platelet activation and aggregation. This antiplatelet effect is essential in preventing the formation of blood clots that can cause heart attacks and strokes. In addition to its use in preventing cardiovascular events, clopidogrel has also been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of stent thrombosis in patients who have undergone percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Clopidogrel Mechanism of Action
Clopidogrel Benefits
The benefits of clopidogrel in preventing cardiovascular events are numerous. Some of the key benefits include: * Reduced risk of heart attacks and strokes * Reduced risk of stent thrombosis in patients who have undergone PCI * Improved survival rates in patients with acute coronary syndrome * Reduced need for repeat revascularization procedures * Improved quality of life in patients with cardiovascular diseaseClopidogrel Side Effects
Clopidogrel Interactions
Clopidogrel can interact with several medications, including: * Aspirin: increases the risk of bleeding complications * Warfarin: increases the risk of bleeding complications * Ibuprofen: increases the risk of bleeding complications * Omeprazole: reduces the effectiveness of clopidogrel * Fluoxetine: increases the risk of bleeding complicationsClopidogrel Dosage
Clopidogrel Contraindications
Clopidogrel is contraindicated in patients with: * Active bleeding complications * Bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia * Severe liver disease * Pregnancy and breastfeedingClopidogrel Warnings and Precautions

Clopidogrel Storage and Handling
Clopidogrel should be stored at room temperature, away from light and moisture. The medication should be kept out of reach of children and pets, and should not be disposed of in the toilet or sink.Clopidogrel Overdose

Clopidogrel Toxicity
The toxicity of clopidogrel is generally low, but high doses of the medication can cause several adverse effects. The LD50 of clopidogrel is approximately 2000 mg/kg in rats, and the medication has been shown to be well-tolerated in clinical trials.Clopidogrel Clinical Trials
Clopidogrel Future Directions
The future of clopidogrel looks promising, with several ongoing clinical trials evaluating its efficacy and safety in various patient populations. The medication has been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with certain genetic disorders, and its use in combination with other medications, such as aspirin and prasugrel, may provide additional benefits.Clopidogrel Patient Education
Clopidogrel Healthcare Provider Education
Healthcare providers should be educated about the benefits and risks of clopidogrel, as well as its proper use in various patient populations. Healthcare providers should be aware of the potential interactions between clopidogrel and other medications, and should monitor patients closely for signs of bleeding complications.What is clopidogrel used for?
+Clopidogrel is used to prevent blood clots that cause heart attacks and strokes. It is also used to prevent stent thrombosis in patients who have undergone percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
How does clopidogrel work?
+Clopidogrel works by inhibiting the P2Y12 receptor on platelets, which prevents platelet activation and aggregation. This antiplatelet effect reduces the risk of blood clots that can cause heart attacks and strokes.
What are the common side effects of clopidogrel?
+The common side effects of clopidogrel include bleeding complications, gastrointestinal upset, headache, and dizziness. Patients should report any signs of bleeding, such as bruising or nosebleeds, to their healthcare provider immediately.
Can clopidogrel be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, clopidogrel can be used in combination with other medications, such as aspirin and prasugrel. However, patients should be aware of the potential interactions between clopidogrel and other medications, and should monitor themselves closely for signs of bleeding complications.
What should patients do if they miss a dose of clopidogrel?
+Patients should take the missed dose as soon as they remember. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, patients should skip the missed dose and take the next dose as scheduled. Patients should not take a double dose of clopidogrel to make up for a missed dose.
In conclusion, clopidogrel is a crucial medication in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Its ability to prevent platelet activation and aggregation reduces the risk of blood clots that can cause heart attacks and strokes. Patients should be educated about the benefits and risks of clopidogrel, and healthcare providers should be aware of its proper use in various patient populations. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with clopidogrel, and to ask any questions they may have about this important medication. By working together, we can improve our understanding of clopidogrel and its role in preventing cardiovascular events.
