Intro
Learn about Closed Head Injury Symptoms, including concussion, traumatic brain injury, and mild TBI signs, to recognize and treat head trauma, brain damage, and neurological disorders effectively.
Closed head injuries can have a profound impact on an individual's life, affecting not only their physical health but also their emotional and cognitive well-being. These types of injuries occur when the head is struck or hits something, causing damage to the brain without penetrating the skull. The symptoms of a closed head injury can vary widely, depending on the severity of the injury and the area of the brain that is affected. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for providing proper care and support to individuals who have suffered a closed head injury.
The importance of recognizing the symptoms of a closed head injury cannot be overstated. Prompt medical attention is essential for preventing further damage and promoting the best possible recovery. Moreover, being aware of the potential symptoms can help individuals take preventive measures to avoid such injuries in the first place. Whether it's wearing protective gear during sports, ensuring a safe living environment, or practicing cautious behavior in potentially hazardous situations, knowledge is key to mitigating the risks associated with closed head injuries.
In the following sections, we will delve into the specifics of closed head injury symptoms, exploring the various manifestations, their underlying causes, and what they might indicate about the injury's severity. This comprehensive overview aims to educate readers on the complexities of closed head injuries, fostering a deeper understanding and empathy for those affected by these conditions.
Closed Head Injury Symptoms Overview
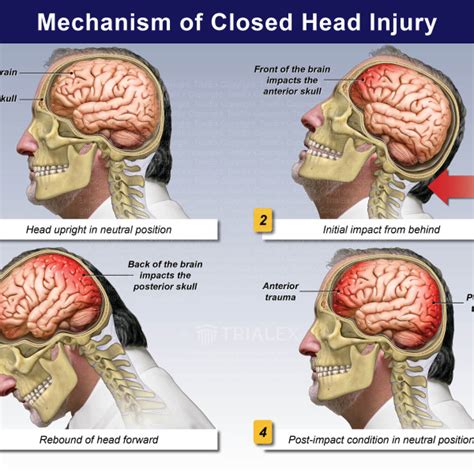
Physical Symptoms of Closed Head Injuries
Physical symptoms are often the first indicators of a closed head injury. They can be immediate or delayed, depending on the injury's severity and the individual's overall health. Common physical symptoms include: - Headaches: These can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent. - Dizziness or Loss of Balance: Individuals may feel lightheaded or have trouble walking. - Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can occur immediately after the injury or develop over time. - Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired or lacking energy is a common complaint. - Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty sleeping or sleeping too much can be a symptom of a closed head injury. - Blurred Vision or Double Vision: Problems with vision can indicate damage to parts of the brain responsible for visual processing.Cognitive Symptoms of Closed Head Injuries
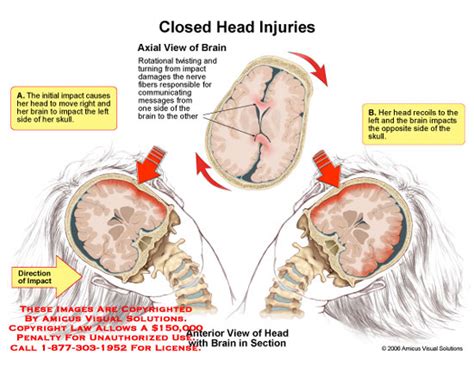
Emotional and Psychological Symptoms
The emotional and psychological impact of a closed head injury should not be underestimated. These symptoms can be just as debilitating as physical or cognitive symptoms and often require specialized care. Common emotional and psychological symptoms include: - Mood Swings: Rapid changes in mood, irritability, or emotional reactivity are frequent complaints. - Anxiety and Depression: These conditions can develop as a direct result of the injury or as a response to the challenges posed by other symptoms. - Personality Changes: Friends and family may notice significant changes in personality, such as increased aggression or passivity. - Emotional Regulation Difficulties: Managing emotions in a healthy way can become challenging, leading to outbursts or inappropriate emotional responses.Treatment and Recovery

Prevention Strategies
Preventing closed head injuries is a critical aspect of public health. Simple yet effective measures include: - Wearing helmets during sports, biking, or any activity that poses a risk of head injury. - Ensuring home safety by removing tripping hazards and installing handrails. - Practicing safe driving habits, such as wearing seatbelts and avoiding distracted driving. - Encouraging a culture of safety in workplaces and public spaces.Support and Resources

Future Perspectives
Research into closed head injuries is ongoing, with scientists and medical professionals seeking to understand better the mechanisms of these injuries and to develop more effective treatments. Advances in neuroimaging, neuroplasticity, and rehabilitation techniques hold promise for improving outcomes for those affected. Moreover, public awareness campaigns can play a vital role in preventing injuries and fostering a supportive community for those recovering from closed head injuries.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, or seek resources related to closed head injuries in the comments below. Your engagement can help foster a community of support and understanding, contributing to a broader discussion on this critical health issue.
What are the immediate symptoms of a closed head injury?
+Immediate symptoms can include headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. In severe cases, there may be loss of consciousness, confusion, or difficulty with coordination and balance.
How are closed head injuries diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examinations, patient history, and imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs to assess the extent of the injury.
What is the prognosis for recovery from a closed head injury?
+The prognosis varies widely depending on the severity of the injury, the promptness and quality of medical care, and the individual's overall health. Mild injuries may result in full recovery, while severe injuries can lead to permanent disabilities.
