Intro
Discover comprehensive insights on Co Occurring Mental Health, including dual diagnosis, treatment options, and recovery strategies for individuals with concurrent mental health and substance use disorders, emphasizing integrated care and holistic approaches.
Mental health is a complex and multifaceted aspect of human well-being, and it is not uncommon for individuals to experience multiple mental health conditions simultaneously. This phenomenon is known as co-occurring mental health disorders, and it can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life. Co-occurring mental health disorders can involve a combination of mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, or substance use disorders and mental health conditions. The importance of understanding and addressing co-occurring mental health disorders cannot be overstated, as it is crucial for providing effective treatment and support to individuals who are struggling with these conditions.
The prevalence of co-occurring mental health disorders is a significant concern, as it can affect individuals from all walks of life. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately 50% of individuals with a mental health disorder also experience a substance use disorder, and vice versa. This highlights the need for comprehensive treatment approaches that address both mental health and substance use disorders simultaneously. Furthermore, co-occurring mental health disorders can have a profound impact on an individual's daily life, relationships, and overall well-being, making it essential to provide accessible and effective treatment options.
The complexity of co-occurring mental health disorders requires a nuanced understanding of the underlying causes and contributing factors. Research suggests that genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and traumatic experiences can all contribute to the development of co-occurring mental health disorders. Additionally, social and cultural factors, such as stigma and lack of access to healthcare, can exacerbate the challenges faced by individuals with co-occurring mental health disorders. By acknowledging the interplay between these factors, healthcare professionals can develop targeted treatment approaches that address the unique needs of each individual.
Understanding Co-Occurring Mental Health Disorders
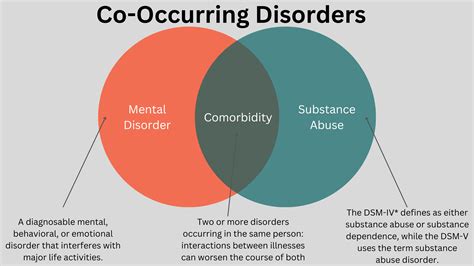
Co-occurring mental health disorders can involve a wide range of conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety disorders, personality disorders, and substance use disorders. The most common combinations of co-occurring mental health disorders include depression and anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and substance use disorder, and borderline personality disorder and substance use disorder. Understanding the specific characteristics and symptoms of each condition is essential for developing effective treatment plans. For instance, individuals with co-occurring depression and anxiety may require a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage their symptoms.
Types of Co-Occurring Mental Health Disorders
Co-occurring mental health disorders can be categorized into several types, including: * Mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder * Anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder * Personality disorders, such as borderline personality disorder and narcissistic personality disorder * Substance use disorders, such as alcohol use disorder and opioid use disorder * Trauma-related disorders, such as PTSD and complex trauma Each type of co-occurring mental health disorder requires a unique treatment approach, taking into account the individual's specific needs and circumstances.Causes and Risk Factors

The causes and risk factors of co-occurring mental health disorders are complex and multifaceted. Research suggests that genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and traumatic experiences can all contribute to the development of co-occurring mental health disorders. Additionally, social and cultural factors, such as stigma and lack of access to healthcare, can exacerbate the challenges faced by individuals with co-occurring mental health disorders. Some common risk factors include:
- Family history of mental health or substance use disorders
- Traumatic experiences, such as physical or emotional abuse
- Social and cultural factors, such as poverty and lack of access to healthcare
- Genetic predisposition to mental health or substance use disorders
- Brain chemistry and neurobiological factors, such as imbalances in neurotransmitters
Consequences of Untreated Co-Occurring Mental Health Disorders
The consequences of untreated co-occurring mental health disorders can be severe and far-reaching. Individuals with untreated co-occurring mental health disorders may experience: * Impaired daily functioning and relationships * Increased risk of suicide or self-harm * Worsening of symptoms and condition severity * Decreased quality of life and overall well-being * Increased risk of substance use disorders or other mental health conditions It is essential to provide accessible and effective treatment options to individuals with co-occurring mental health disorders to prevent these consequences and promote recovery.Treatment Approaches
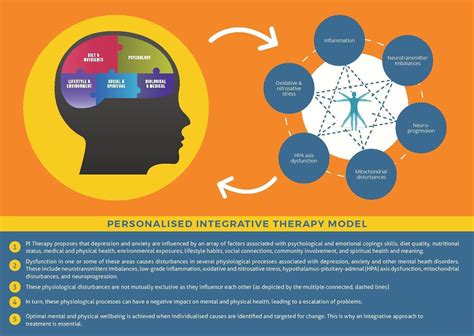
Treatment approaches for co-occurring mental health disorders typically involve a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. The most effective treatment approaches involve a comprehensive and integrated approach, addressing both mental health and substance use disorders simultaneously. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for substance use disorders
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for mental health conditions
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) for borderline personality disorder
- Family therapy and support groups for social and cultural factors
- Mindfulness-based therapies, such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR)
Benefits of Integrated Treatment
Integrated treatment approaches offer several benefits, including: * Improved treatment outcomes and reduced symptoms * Increased patient engagement and retention * Enhanced quality of life and overall well-being * Reduced risk of relapse and recidivism * Improved social and cultural functioning Integrated treatment approaches acknowledge the interplay between mental health and substance use disorders, providing a comprehensive and targeted treatment plan that addresses the unique needs of each individual.Recovery and Support

Recovery and support are essential components of treatment for co-occurring mental health disorders. Recovery involves a process of healing and growth, where individuals learn to manage their symptoms and develop coping strategies. Support can come in many forms, including family and friends, support groups, and mental health professionals. Some common support options include:
- 12-step programs, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA)
- Support groups, such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI)
- Online forums and communities, such as online support groups and forums
- Peer support specialists, who have personal experience with mental health or substance use disorders
- Family therapy and education, to promote understanding and support
Challenges and Barriers to Recovery
Recovery from co-occurring mental health disorders can be challenging, and individuals may face several barriers, including: * Stigma and shame, which can prevent individuals from seeking help * Lack of access to healthcare and treatment options * Financial constraints and limited resources * Social and cultural factors, such as poverty and lack of support * Trauma and adverse childhood experiences, which can impact recovery It is essential to address these challenges and barriers, providing accessible and effective treatment options to individuals with co-occurring mental health disorders.What are co-occurring mental health disorders?
+Co-occurring mental health disorders refer to the presence of two or more mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, or substance use disorders and mental health conditions, in an individual.
What are the most common types of co-occurring mental health disorders?
+The most common types of co-occurring mental health disorders include depression and anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and substance use disorder, and borderline personality disorder and substance use disorder.
How can co-occurring mental health disorders be treated?
+Co-occurring mental health disorders can be treated using a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. The most effective treatment approaches involve a comprehensive and integrated approach, addressing both mental health and substance use disorders simultaneously.
In conclusion, co-occurring mental health disorders are complex and multifaceted conditions that require a nuanced understanding and comprehensive treatment approach. By acknowledging the interplay between mental health and substance use disorders, healthcare professionals can develop targeted treatment plans that address the unique needs of each individual. It is essential to provide accessible and effective treatment options, as well as support and resources, to individuals with co-occurring mental health disorders. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with co-occurring mental health disorders, and to join the conversation on promoting recovery and support for individuals affected by these conditions.
