Intro
Unlock the secrets of CO2 blood work results, understanding carbon dioxide levels, bicarbonate, and pH balance in your body, and how they relate to respiratory and metabolic health, with expert explanations and insights.
The importance of understanding CO2 blood work results cannot be overstated, as it provides crucial information about the body's acid-base balance and respiratory function. CO2, or carbon dioxide, is a byproduct of cellular metabolism and is transported in the blood to the lungs, where it is exhaled. Abnormal CO2 levels can indicate a range of health issues, from respiratory problems to kidney disease. In this article, we will delve into the world of CO2 blood work results, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and what factors can influence them.
Understanding CO2 blood work results is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it enables the diagnosis and monitoring of various medical conditions. CO2 levels are typically measured as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) or an electrolyte panel, which includes other vital parameters such as sodium, potassium, and chloride. By analyzing CO2 blood work results, healthcare providers can identify potential issues, such as acid-base disturbances, and develop effective treatment plans to restore balance to the body.
The significance of CO2 blood work results extends beyond the diagnosis of respiratory and metabolic disorders. It also plays a critical role in monitoring patients with chronic conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and kidney disease. By regularly checking CO2 levels, healthcare providers can assess the effectiveness of treatment, identify potential complications, and make informed decisions about patient care. Furthermore, understanding CO2 blood work results can help patients take a more active role in their health, enabling them to make lifestyle changes and seek medical attention when necessary.
What is CO2 Blood Work?

CO2 blood work, also known as carbon dioxide testing, measures the level of CO2 in the blood. This test is usually performed as part of a routine medical examination or to diagnose and monitor various health conditions. CO2 blood work results are typically reported in units of milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The normal range for CO2 levels is typically between 23 and 29 mEq/L, although this may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and medical history.
How is CO2 Blood Work Performed?
CO2 blood work is a relatively simple and painless procedure. A healthcare professional will typically collect a blood sample from a vein in the arm, using a needle and syringe. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the CO2 level is measured using specialized equipment. The results are usually available within a few hours or days, depending on the laboratory's workload and testing procedures.Interpreting CO2 Blood Work Results
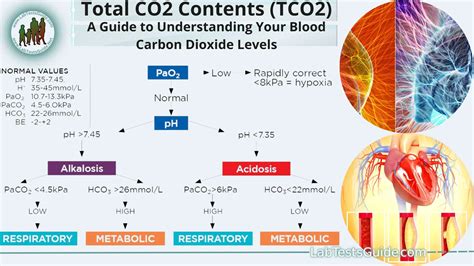
Interpreting CO2 blood work results requires a thorough understanding of the body's acid-base balance and the factors that influence CO2 levels. A high CO2 level, also known as hypercapnia, can indicate respiratory acidosis, which occurs when the lungs are unable to remove enough CO2 from the blood. This can be caused by a range of conditions, including COPD, pneumonia, and asthma. On the other hand, a low CO2 level, also known as hypocapnia, can indicate respiratory alkalosis, which occurs when the lungs remove too much CO2 from the blood. This can be caused by hyperventilation, anxiety, or other conditions that affect breathing.
Factors that Influence CO2 Blood Work Results
Several factors can influence CO2 blood work results, including: * Respiratory rate and depth: Changes in breathing patterns can affect CO2 levels, with rapid or deep breathing leading to hypocapnia and slow or shallow breathing leading to hypercapnia. * Metabolic rate: An increase in metabolic rate, such as during exercise or fever, can lead to an increase in CO2 production and subsequent hypercapnia. * Kidney function: The kidneys play a critical role in regulating acid-base balance, and impaired kidney function can lead to changes in CO2 levels. * Medications: Certain medications, such as sedatives and anesthetics, can affect breathing patterns and CO2 levels.CO2 Blood Work Results and Health Conditions
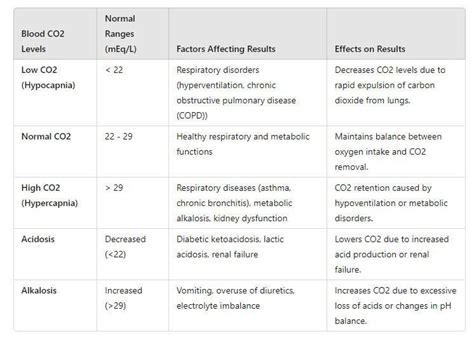
CO2 blood work results can be affected by a range of health conditions, including:
- Respiratory diseases: Conditions such as COPD, pneumonia, and asthma can lead to changes in CO2 levels.
- Kidney disease: Impaired kidney function can lead to changes in CO2 levels, as the kidneys are unable to regulate acid-base balance effectively.
- Metabolic disorders: Conditions such as diabetes and metabolic acidosis can lead to changes in CO2 levels.
- Cardiovascular disease: Conditions such as heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias can lead to changes in CO2 levels.
Managing CO2 Blood Work Results
Managing CO2 blood work results requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the underlying health condition, medical history, and lifestyle factors. This may involve: * Medications: Prescribed medications, such as bronchodilators and diuretics, can help manage CO2 levels and underlying health conditions. * Lifestyle changes: Changes to diet, exercise, and breathing patterns can help regulate CO2 levels and improve overall health. * Monitoring: Regular monitoring of CO2 blood work results can help healthcare providers track changes in CO2 levels and adjust treatment plans accordingly.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, understanding CO2 blood work results is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike. By interpreting CO2 blood work results in the context of the individual's medical history, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. As medical research continues to advance, it is likely that our understanding of CO2 blood work results will evolve, leading to new and innovative approaches to managing CO2 levels and related health conditions.
Final Thoughts
As we reflect on the importance of CO2 blood work results, it is clear that this simple yet powerful test has the potential to transform our understanding of human health and disease. By embracing the latest research and technologies, we can unlock new insights into the complex relationships between CO2 levels, acid-base balance, and overall health. As we move forward, it is essential that we prioritize patient education, awareness, and empowerment, enabling individuals to take a more active role in their health and well-being.What is the normal range for CO2 blood work results?
+The normal range for CO2 blood work results is typically between 23 and 29 mEq/L, although this may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and medical history.
What factors can influence CO2 blood work results?
+Several factors can influence CO2 blood work results, including respiratory rate and depth, metabolic rate, kidney function, and medications.
How are CO2 blood work results used to diagnose and monitor health conditions?
+CO2 blood work results are used to diagnose and monitor a range of health conditions, including respiratory diseases, kidney disease, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular disease. By analyzing CO2 levels, healthcare providers can identify potential issues, develop effective treatment plans, and track changes in CO2 levels over time.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of CO2 blood work results and their significance in human health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of CO2 blood work results, ultimately improving patient outcomes and advancing our knowledge of human health and disease.
