Intro
Discover the ultimate guide to combination birth control pills, exploring types, benefits, and side effects, including hormonal balance, menstrual regulation, and contraceptive efficacy, to make informed decisions about your reproductive health and fertility management.
The use of combination birth control pills has been a cornerstone in reproductive health for decades, offering women a reliable method to prevent pregnancy while also providing other health benefits. Understanding how these pills work, their benefits, and potential side effects is crucial for anyone considering this form of contraception. With the vast array of options available, navigating the world of combination birth control pills can seem daunting, but with the right information, individuals can make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
The importance of birth control cannot be overstated, as it allows individuals to plan their families, pursue education and career goals without the burden of unintended pregnancies, and maintain control over their bodies and lives. Combination birth control pills, which contain both estrogen and progestin, are one of the most popular forms of birth control due to their effectiveness and additional health benefits. However, like any medication, they come with potential side effects and may not be suitable for everyone. It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best birth control method based on individual health needs and preferences.
For many women, combination birth control pills are more than just a means of preventing pregnancy; they also offer relief from menstrual cramps, reduce the risk of certain cancers, and can even improve acne. The mechanism behind these pills involves altering the body's hormonal balance to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus to block sperm, and thin the uterine lining to prevent implantation of a fertilized egg. This multifaceted approach makes combination birth control pills highly effective when taken correctly. Despite their benefits, it's crucial to weigh these against potential side effects, such as nausea, breast tenderness, and mood changes, to ensure that this form of contraception aligns with one's health and lifestyle.
Introduction to Combination Birth Control Pills
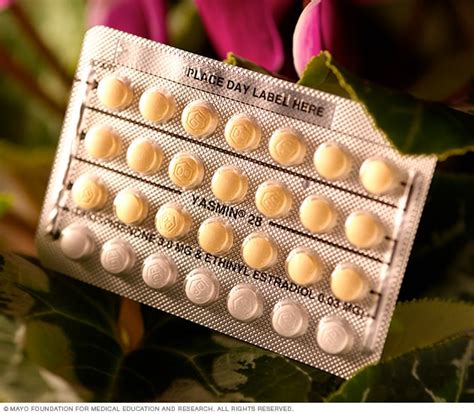
Types of Combination Birth Control Pills
There are several types of combination birth control pills, each with its unique formulation and benefits. Monophasic pills contain the same amount of estrogen and progestin in each active pill, providing a consistent dose of hormones throughout the cycle. Biphasic and triphasic pills, on the other hand, contain different levels of hormones in each active pill, mimicking the natural hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle. Extended-cycle pills allow for fewer periods per year, and continuous-cycle pills can stop menstruation altogether. Understanding the differences between these types can help individuals choose the pill that best suits their needs.Benefits of Combination Birth Control Pills
Non-Contraceptive Benefits
The non-contraceptive benefits of combination birth control pills are numerous and well-documented. These benefits include: - Reduction in menstrual cramps and heavy bleeding - Improvement in acne - Regulation of menstrual cycles - Decrease in the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancer - Reduction in the risk of ectopic pregnancy - Decrease in the severity of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms These benefits make combination birth control pills a valuable option for women seeking to manage their reproductive health beyond just preventing pregnancy.Potential Side Effects

Minimizing Side Effects
To minimize side effects, it's crucial to follow the prescribed regimen carefully and attend follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider. This allows for the monitoring of any side effects and the adjustment of the pill formulation if necessary. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help mitigate some side effects. Staying hydrated, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can also contribute to a smoother experience with combination birth control pills.Choosing the Right Combination Birth Control Pill
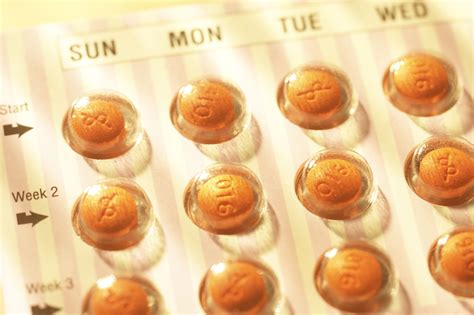
Consultation with a Healthcare Provider
A consultation with a healthcare provider is a critical step in choosing the right combination birth control pill. During this consultation, women should discuss their medical history, including any current medications, allergies, and previous experiences with birth control. The healthcare provider can then recommend the most suitable pill formulation based on this information, ensuring that the selected pill aligns with the individual's health needs and minimizes the risk of side effects.Effectiveness and Convenience
Adherence and Missed Pills
Adhering to the prescribed regimen is crucial for the effectiveness of combination birth control pills. Missing pills can increase the risk of ovulation and, consequently, pregnancy. If a pill is missed, women should follow the instructions provided with their pill pack or consult their healthcare provider for guidance. In some cases, an additional form of contraception, such as condoms, may be recommended until the next menstrual period to ensure protection against pregnancy.Comparison with Other Contraceptive Methods
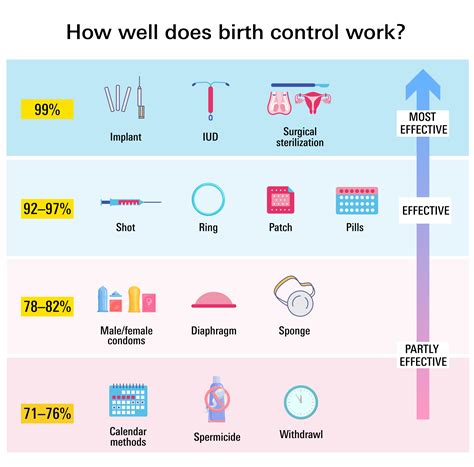
Long-Acting Reversible Contraceptives (LARCs)
LARCs, including IUDs and implants, are gaining popularity due to their high effectiveness and convenience. These methods are particularly appealing to women who desire a long-term contraceptive solution without the daily commitment of taking a pill. However, they may not offer the same non-contraceptive benefits as combination birth control pills, such as regulation of menstrual cycles or improvement in acne. Discussing the options with a healthcare provider can help determine the most suitable contraceptive method based on individual preferences and health needs.Future of Combination Birth Control Pills
Emerging Trends and Technologies
Emerging trends in contraception include the development of non-hormonal methods, such as contraceptive gels or patches, and the use of technology to enhance adherence and effectiveness. Mobile apps that track menstrual cycles and remind users to take their pills can improve adherence, while telemedicine services can increase access to contraceptive care. These advancements hold the potential to make contraception more accessible, effective, and appealing to a wider range of individuals.As we conclude our comprehensive guide to combination birth control pills, it's clear that these medications offer a reliable and effective means of preventing pregnancy, along with several non-contraceptive benefits. However, they may not be the best fit for everyone due to potential side effects and individual health considerations. By understanding how combination birth control pills work, their benefits, and their limitations, individuals can make informed decisions about their reproductive health. Whether you're considering starting combination birth control pills or are already using them, we invite you to share your experiences, ask questions, or seek further information in the comments below. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping others navigate the world of reproductive health.
What are the most common side effects of combination birth control pills?
+Common side effects include nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, and headaches. Less common but more serious side effects can include blood clots, stroke, and heart attack.
How effective are combination birth control pills in preventing pregnancy?
+Combination birth control pills are highly effective when taken correctly, with a failure rate of less than 1% for perfect use. However, typical use can result in a higher failure rate due to missed pills or incorrect usage.
Can combination birth control pills be used for purposes other than preventing pregnancy?
+Yes, combination birth control pills can be used to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce the risk of certain cancers, improve acne, and decrease the severity of menstrual cramps and heavy bleeding.
