Intro
Discover the 5 coronary risk factors, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, to reduce heart disease risk with lifestyle changes and medical management.
Coronary heart disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and understanding its risk factors is crucial for prevention and management. Over the years, research has identified several key risk factors that contribute to the development of coronary heart disease. These risk factors can be broadly categorized into modifiable and non-modifiable factors. Modifiable risk factors are those that can be changed or controlled through lifestyle modifications or medical interventions, while non-modifiable risk factors are those that cannot be changed, such as age or family history. In this article, we will delve into the 5 coronary risk factors that are widely recognized and explore their implications for cardiovascular health.
The importance of understanding coronary risk factors cannot be overstated. By identifying and addressing these risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing coronary heart disease and its associated complications, such as heart attacks, strokes, and cardiac arrhythmias. Moreover, recognizing the risk factors can help healthcare professionals develop targeted interventions and treatment plans to mitigate their impact. The 5 coronary risk factors that will be discussed in this article are high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and obesity. These factors are interconnected and can have a cumulative effect on cardiovascular health, making it essential to address them comprehensively.
The relationship between these risk factors and coronary heart disease is complex and multifaceted. For instance, high blood pressure can damage the blood vessels, making them more susceptible to blockages, while high cholesterol can contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries. Smoking, on the other hand, can damage the inner lining of the blood vessels, making them more prone to narrowing and blockages. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease, while obesity can contribute to the development of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Understanding these relationships is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Introduction to Coronary Risk Factors
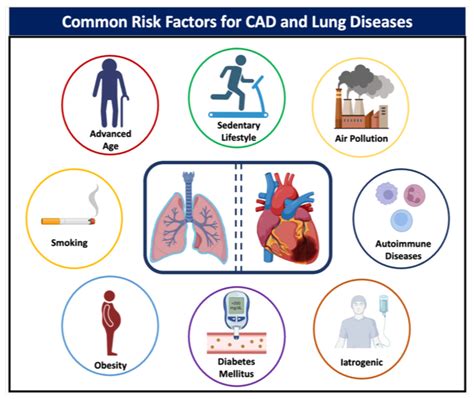
Modifiable vs. Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Modifiable risk factors are those that can be changed or controlled through lifestyle modifications or medical interventions. These factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and obesity. Non-modifiable risk factors, on the other hand, are those that cannot be changed, such as age, family history, or genetics. While non-modifiable risk factors cannot be changed, understanding their impact can help individuals and healthcare professionals develop targeted interventions to mitigate their effects.High Blood Pressure as a Coronary Risk Factor
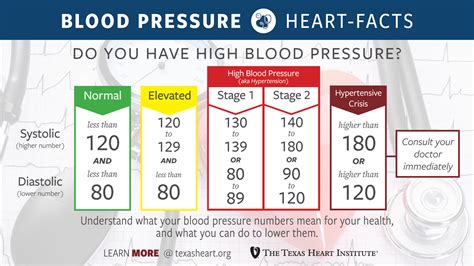
Causes and Consequences of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, stress, and lifestyle. A diet high in sodium, sugar, and saturated fats can contribute to high blood pressure, as can a lack of physical activity and chronic stress. If left unmanaged, high blood pressure can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Managing high blood pressure through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can help reduce the risk of these complications.High Cholesterol as a Coronary Risk Factor

Causes and Consequences of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, and lifestyle. A diet high in saturated fats and cholesterol can contribute to high cholesterol, as can a lack of physical activity and obesity. If left unmanaged, high cholesterol can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Managing high cholesterol through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can help reduce the risk of these complications.Smoking as a Coronary Risk Factor

Causes and Consequences of Smoking
Smoking can be caused by a variety of factors, including addiction, stress, and social pressures. Nicotine, the primary psychoactive substance in tobacco, can lead to physical dependence and addiction. If left unmanaged, smoking can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, and lung cancer. Quitting smoking through lifestyle modifications, such as counseling and nicotine replacement therapy, can help reduce the risk of these complications.Diabetes as a Coronary Risk Factor

Causes and Consequences of Diabetes
Diabetes can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, and lifestyle. A diet high in sugar and saturated fats can contribute to diabetes, as can a lack of physical activity and obesity. If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Managing diabetes through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can help reduce the risk of these complications.Obesity as a Coronary Risk Factor

Causes and Consequences of Obesity
Obesity can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, and lifestyle. A diet high in sugar and saturated fats can contribute to obesity, as can a lack of physical activity and sedentary behavior. If left unmanaged, obesity can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Managing obesity through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can help reduce the risk of these complications.In conclusion, the 5 coronary risk factors discussed in this article are major contributors to the development of coronary heart disease. By understanding these risk factors and taking targeted interventions to mitigate their effects, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing coronary heart disease and its associated complications. It is essential to recognize the interconnectedness of these risk factors and address them comprehensively to achieve optimal cardiovascular health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on coronary risk factors in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Together, we can work towards reducing the burden of coronary heart disease and promoting cardiovascular health.
What are the 5 coronary risk factors?
+The 5 coronary risk factors are high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and obesity.
Can coronary risk factors be managed?
+Yes, coronary risk factors can be managed through lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction, as well as medical interventions.
What are the consequences of unmanaged coronary risk factors?
+Unmanaged coronary risk factors can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
How can I reduce my risk of coronary heart disease?
+You can reduce your risk of coronary heart disease by managing your coronary risk factors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and obesity, through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions.
What is the importance of understanding coronary risk factors?
+Understanding coronary risk factors is essential for developing targeted interventions and treatment plans to mitigate their impact and reduce the risk of coronary heart disease.
