Intro
Unlock the secrets of your 5 Crp Blood Report with expert tips, understanding CRP levels, inflammation markers, and health implications to make informed decisions about your well-being and disease prevention.
The importance of understanding blood reports cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to a Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) or a Complete Blood Count (CBC) like the CRP blood test. The CRP, or C-Reactive Protein test, is a crucial diagnostic tool that measures the levels of a specific protein in the blood, which is produced in the liver in response to inflammation. This protein is an acute-phase reactant, meaning its levels increase in response to inflammation throughout the body. Understanding the results of a CRP blood test can provide valuable insights into the body's inflammatory responses, helping to diagnose and monitor conditions such as infections, autoimmune diseases, and even heart disease.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system, designed to protect against harm, such as infections, injuries, and toxins. However, chronic or excessive inflammation can lead to various health issues, making the CRP test a vital tool for healthcare providers. By analyzing CRP levels, doctors can assess the severity of inflammation and monitor how well the body responds to treatment. It's essential for individuals to understand their CRP blood report to take proactive steps in managing their health. This understanding begins with knowing what the CRP test measures, how it's conducted, and what the results signify.
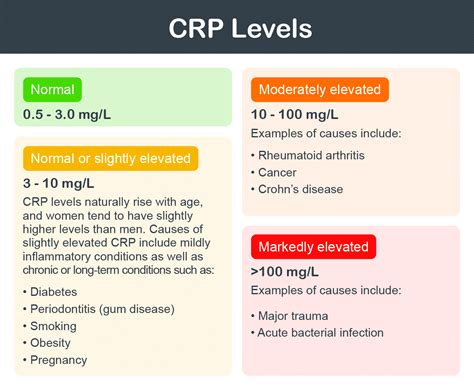
For individuals who have undergone a CRP blood test, interpreting the results can seem daunting. The test itself is straightforward, involving a simple blood draw from a vein, typically in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. However, deciphering the results requires some knowledge of what CRP levels indicate. High CRP levels are associated with inflammation, but the degree of elevation can suggest different conditions. For instance, significantly elevated CRP levels may indicate a severe infection or an acute inflammatory condition, while mildly elevated levels could suggest chronic inflammation or an early sign of cardiovascular disease.
Understanding CRP Blood Report Basics
Factors Influencing CRP Levels
Several factors can influence CRP levels, including but not limited to, the time of day, recent physical activity, dietary habits, and certain medications. For example, CRP levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day, typically peaking in the late afternoon and decreasing during sleep. Understanding these factors is essential for accurately interpreting CRP test results and for making informed decisions about health and lifestyle changes.Interpreting CRP Blood Test Results
CRP Levels and Health Conditions
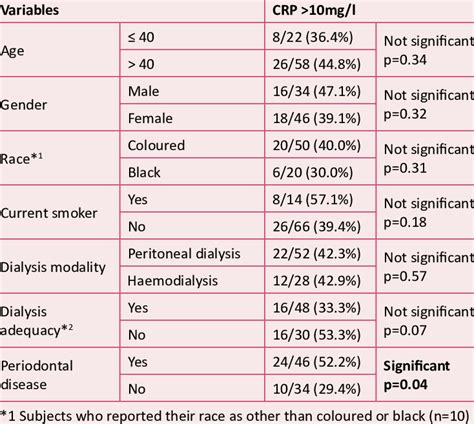
CRP levels are categorized into different ranges to help correlate them with various health conditions. Low sensitivity CRP (ls-CRP) tests are used to detect slightly elevated levels of CRP, which are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. High sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) tests, on the other hand, are more sensitive and can detect even minor elevations in CRP levels. This distinction is vital because the interpretation of CRP levels can significantly impact the diagnosis and management of conditions such as atherosclerosis, where chronic inflammation plays a central role.Managing Elevated CRP Levels
Lifestyle Changes for Reducing Inflammation
Making lifestyle changes is a critical component of managing and reducing chronic inflammation. This includes adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or more intense exercise, can also help reduce inflammation. Furthermore, managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga can have a positive impact on inflammatory markers, including CRP levels.CRP Blood Test and Cardiovascular Disease
Preventive Measures for Cardiovascular Health
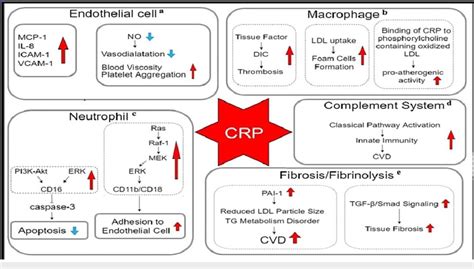
Preventing cardiovascular disease involves a multifaceted approach that includes maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, not smoking, and managing stress. Additionally, monitoring and managing other risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol levels is crucial. For some individuals, especially those with elevated CRP levels, preventive measures may also include taking statins or other medications to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.CRP Blood Test in Monitoring Disease Progression
Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups are essential for maintaining good health and catching potential issues early. These check-ups often include a range of tests, including blood work like the CRP test, to provide a comprehensive view of an individual's health status. By staying on top of health check-ups and being proactive about understanding test results, individuals can take a more active role in their health management and make informed decisions about their well-being.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about CRP blood tests and their role in health management. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide more informative and relevant content. If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from understanding their CRP blood reports. Together, we can work towards a healthier and more informed community.
What does a CRP blood test measure?
+A CRP blood test measures the levels of C-Reactive Protein in the blood, which is a marker of inflammation in the body.
What are normal CRP levels?
+Normal CRP levels are typically below 10 mg/L, but this can vary slightly between laboratories.
How can I reduce my CRP levels?
+Reducing CRP levels can be achieved through lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, not smoking, and managing stress.
