Intro
Unlock the secrets of CRP blood test results, exploring C-Reactive Protein levels, inflammation markers, and health implications, to understand your bodys response to infection, disease, and injury, and discover the significance of high or low CRP levels.
The C-Reactive Protein (CRP) blood test is a commonly used diagnostic tool to measure the levels of C-Reactive Protein in the blood. CRP is a protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation, infection, or injury. High levels of CRP in the blood can indicate a range of health issues, from infections and autoimmune disorders to cardiovascular disease and cancer. In this article, we will delve into the world of CRP blood test results, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and what steps you can take to manage your CRP levels.
The importance of understanding CRP blood test results cannot be overstated. By grasping the significance of CRP levels, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Furthermore, CRP blood tests can help healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other autoimmune disorders. With the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, it is essential to understand the role of CRP in maintaining overall health and wellbeing.
CRP blood tests are relatively simple and non-invasive, involving a blood sample drawn from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the levels of CRP are measured. The results are typically available within a few hours or days, depending on the laboratory and the testing methods used. Once the results are available, healthcare professionals can interpret them to determine the presence and severity of inflammation or infection.
Understanding CRP Blood Test Results
CRP blood test results are measured in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The normal range for CRP levels is typically considered to be below 10 mg/L or 1 mg/dL. However, the exact normal range may vary depending on the laboratory and the testing methods used. Elevated CRP levels can indicate a range of health issues, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease.
Interpreting CRP Blood Test Results
CRP blood test results can be interpreted in different ways, depending on the underlying condition or disease being diagnosed or monitored. For example, high CRP levels may indicate a bacterial or viral infection, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis. In contrast, low CRP levels may indicate a non-inflammatory condition, such as a viral infection or a allergic reaction.What Do High CRP Levels Mean?
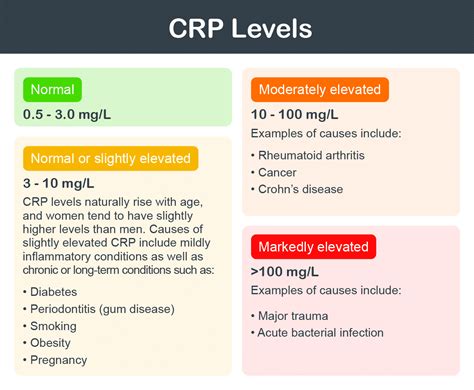
High CRP levels can indicate a range of health issues, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease. For example, CRP levels above 10 mg/L or 1 mg/dL may indicate a bacterial or viral infection, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis. CRP levels above 50 mg/L or 5 mg/dL may indicate a severe infection or inflammation, such as sepsis or rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes of High CRP Levels
There are several causes of high CRP levels, including: * Infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis * Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus * Cardiovascular disease, such as heart disease or stroke * Cancer, such as lymphoma or lung cancer * Inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitisWhat Do Low CRP Levels Mean?

Low CRP levels can indicate a range of health issues, including non-inflammatory conditions, such as viral infections or allergic reactions. For example, CRP levels below 1 mg/L or 0.1 mg/dL may indicate a non-inflammatory condition, such as a viral infection or a allergic reaction.
Causes of Low CRP Levels
There are several causes of low CRP levels, including: * Non-inflammatory conditions, such as viral infections or allergic reactions * Hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or menopause * Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) * Nutritional deficiencies, such as vitamin D or omega-3 fatty acid deficiencyManaging CRP Levels

Managing CRP levels is crucial to reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. There are several ways to manage CRP levels, including:
- Maintaining a healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking or swimming
- Managing stress, through techniques such as meditation or yoga
- Getting enough sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per night
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce CRP Levels
There are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce CRP levels, including: * Losing weight, if overweight or obese * Increasing physical activity, such as walking or swimming * Reducing stress, through techniques such as meditation or yoga * Getting enough sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per night * Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumptionCRP Blood Tests and Chronic Diseases
CRP blood tests can play a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. For example, high CRP levels may indicate an increased risk of heart disease or stroke. In contrast, low CRP levels may indicate a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
CRP Blood Tests and Cardiovascular Disease
CRP blood tests can help diagnose and monitor cardiovascular disease, such as heart disease or stroke. For example, high CRP levels may indicate an increased risk of heart disease or stroke. In contrast, low CRP levels may indicate a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, CRP blood test results can provide valuable insights into overall health and wellbeing. By understanding the significance of CRP levels, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. If you have concerns about your CRP levels or overall health, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help interpret your CRP blood test results and provide guidance on managing your CRP levels and reducing your risk of chronic diseases.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about CRP blood test results in the comments section below. Your feedback and engagement are crucial to creating a supportive and informative community. Please feel free to share this article with friends and family who may benefit from understanding CRP blood test results.
What is the normal range for CRP levels?
+The normal range for CRP levels is typically considered to be below 10 mg/L or 1 mg/dL. However, the exact normal range may vary depending on the laboratory and the testing methods used.
What do high CRP levels indicate?
+High CRP levels can indicate a range of health issues, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease. For example, CRP levels above 10 mg/L or 1 mg/dL may indicate a bacterial or viral infection, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis.
How can I manage my CRP levels?
+Managing CRP levels is crucial to reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. There are several ways to manage CRP levels, including maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and getting enough sleep.
