Intro
Learn about 5 current flu symptoms, including fever, cough, and fatigue. Discover related LSI keywords like influenza signs, flu season warnings, and respiratory illness treatments to stay informed and protected.
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the influenza virus. It can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status, and can lead to serious complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with certain chronic health conditions. The flu season typically runs from October to May, with the peak season usually occurring between December and February. Understanding the current flu symptoms is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of the spread of the disease.
The flu is a significant public health concern, and its impact can be substantial. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the flu affects millions of people in the United States each year, resulting in thousands of hospitalizations and deaths. The economic burden of the flu is also significant, with estimated costs ranging from $10 billion to $20 billion annually. Furthermore, the flu can have a profound impact on individuals, families, and communities, causing missed work or school days, decreased productivity, and increased stress.
The flu virus is highly contagious and can spread quickly through respiratory droplets, contact with contaminated surfaces, and close contact with an infected person. The virus can also mutate, leading to new strains and making it challenging to develop effective vaccines. Despite these challenges, there are many ways to prevent and treat the flu, including vaccination, antiviral medications, and good hygiene practices. By understanding the current flu symptoms and taking proactive steps, individuals can reduce their risk of getting the flu and help prevent the spread of the disease.
Introduction to Current Flu Symptoms
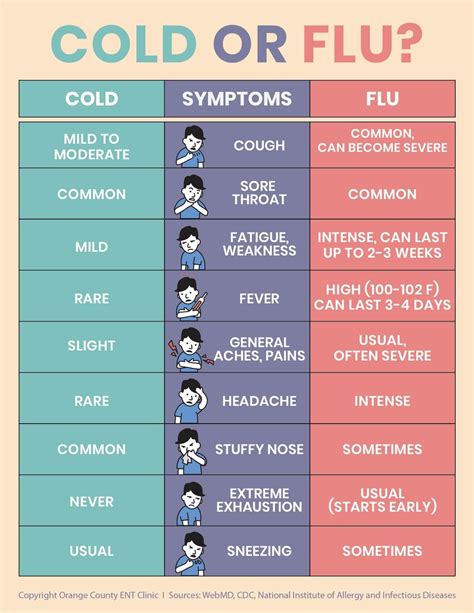
Types of Flu Viruses

Subtypes of Influenza A Virus
The influenza A virus can be further divided into subtypes based on their surface proteins, including hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N). Some common subtypes of influenza A virus include H1N1, H3N2, and H5N1. These subtypes can vary in their severity and ability to spread from person to person.Current Flu Symptoms in Adults
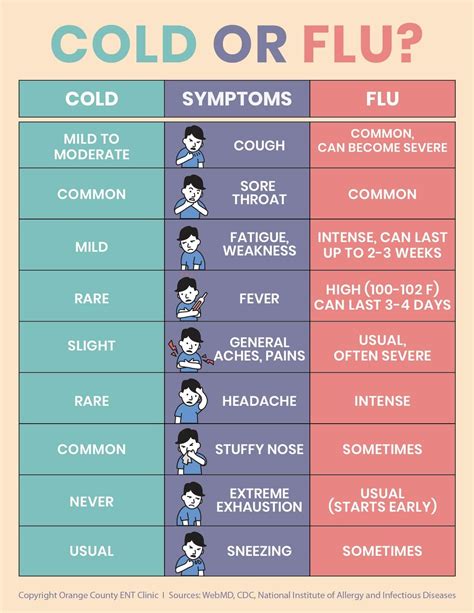
Treatment Options for Adults
Treatment options for adults with the flu may include antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza), which can help shorten the duration and severity of symptoms. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers and decongestants, can also help manage symptoms.Current Flu Symptoms in Children

Prevention Strategies for Children
Prevention strategies for children include vaccination, good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with anyone who is sick.Current Flu Symptoms in Older Adults

Complications in Older Adults
Complications in older adults can include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and exacerbation of underlying health conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes. It's essential for older adults to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any symptoms of the flu.Prevention and Treatment

Good Hygiene Practices
Good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with anyone who is sick, can also help prevent the spread of the flu.What are the most common symptoms of the flu?
+The most common symptoms of the flu include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, fatigue, and muscle or body aches.
How can I prevent getting the flu?
+You can prevent getting the flu by getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with anyone who is sick.
What are the complications of the flu?
+Complications of the flu can include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and exacerbation of underlying health conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes.
How long does the flu last?
+The flu typically lasts for 5-7 days, but some people may experience symptoms for up to 2 weeks.
Can I take antibiotics to treat the flu?
+No, antibiotics are not effective against the flu virus. Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza), can help treat the flu and reduce the risk of complications.
In conclusion, understanding the current flu symptoms is essential for early detection, treatment, and prevention of the spread of the disease. By recognizing the symptoms, taking proactive steps, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of getting the flu and help prevent the spread of the disease. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the flu in the comments section below. If you found this article helpful, please share it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of flu prevention and treatment.
