Intro
Learn Deep Thrombosis In Leg Symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Identify blood clot signs, leg pain, swelling, and DVT risks to prevent pulmonary embolism.
Deep thrombosis in the leg, also known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the leg. This condition can be life-threatening if the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of deep thrombosis in the leg to seek medical attention promptly. The importance of early detection and treatment cannot be overstated, as it can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term complications.
The symptoms of deep thrombosis in the leg can vary from person to person, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all. However, common signs and symptoms include pain, swelling, and discoloration of the affected leg. The pain may feel like a cramp or soreness in the calf or thigh, and it may worsen when standing or walking. Swelling in the leg or ankle is another common symptom, and the skin may become red, purple, or blue due to inadequate blood flow. In some cases, the skin may feel warm or tender to the touch.
Recognizing the symptoms of deep thrombosis in the leg is crucial, as prompt medical attention can help prevent serious complications. If left untreated, DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism, which can be fatal. Furthermore, DVT can cause long-term damage to the veins, leading to chronic venous insufficiency and post-thrombotic syndrome. These conditions can cause persistent pain, swelling, and skin ulcers, significantly impacting a person's quality of life. Therefore, it is vital to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Causes and Risk Factors of Deep Thrombosis
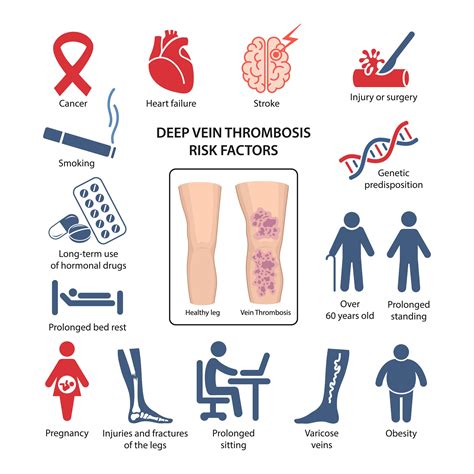
Deep thrombosis in the leg is often caused by a combination of factors that contribute to the formation of blood clots. These factors include blood flow changes, hypercoagulability, and endothelial injury. Blood flow changes, such as those that occur during surgery or prolonged bed rest, can lead to stagnation of blood in the deep veins, increasing the risk of clot formation. Hypercoagulability, which can be caused by genetic disorders or certain medications, can also increase the risk of blood clots. Endothelial injury, such as that caused by trauma or infection, can damage the lining of the blood vessels, making them more susceptible to clot formation.
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing deep thrombosis in the leg. These risk factors include age, family history, obesity, and smoking. Age is a significant risk factor, as the risk of DVT increases with age. A family history of DVT or other blood clotting disorders can also increase the risk. Obesity and smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots. Other risk factors include pregnancy, cancer, and certain medical conditions, such as heart failure or respiratory disease.
Types of Blood Clots
There are two main types of blood clots that can form in the deep veins of the leg: arterial and venous. Arterial clots form in the arteries and can cause damage to the surrounding tissue. Venous clots, on the other hand, form in the veins and can cause swelling and pain. Deep thrombosis in the leg is a type of venous clot that forms in the deep veins of the leg.Symptoms of Deep Thrombosis
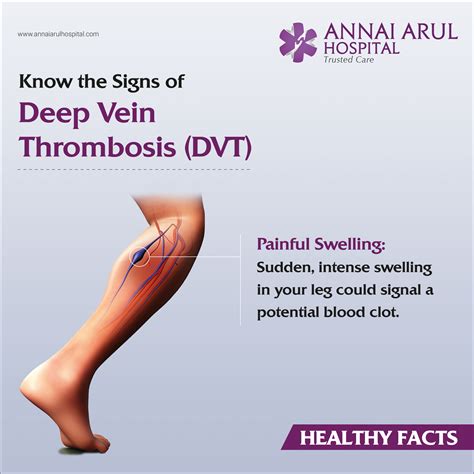
The symptoms of deep thrombosis in the leg can vary from person to person, but common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness in the leg, which may feel like a cramp or soreness in the calf or thigh
- Swelling in the leg or ankle
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- Warmth or tenderness of the skin
- Weakness or fatigue in the leg
- Difficulty walking or standing
In some cases, people may not experience any symptoms at all. However, if symptoms persist or worsen over time, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosing Deep Thrombosis
Diagnosing deep thrombosis in the leg typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. A physical examination may reveal swelling, redness, or warmth in the affected leg. A medical history may help identify risk factors, such as recent surgery or prolonged bed rest. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, can help confirm the presence of a blood clot.Treatment Options for Deep Thrombosis
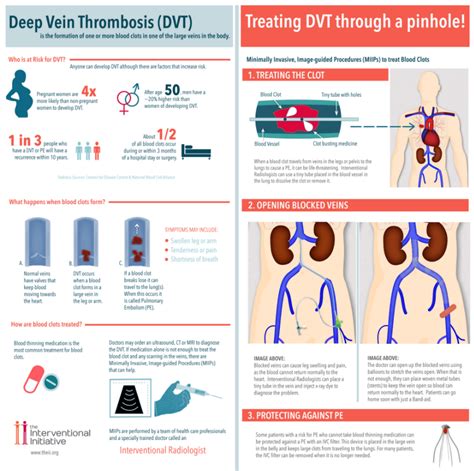
Treatment options for deep thrombosis in the leg typically involve anticoagulation therapy, which helps prevent the clot from growing and causing further complications. Anticoagulant medications, such as heparin or warfarin, can help thin the blood and reduce the risk of clot formation. In some cases, thrombolytic therapy may be used to dissolve the clot.
Other treatment options may include:
- Compression stockings to help reduce swelling
- Elevation of the affected leg to improve blood flow
- Pain relief medications to manage discomfort
- Surgery to remove the clot or repair damaged blood vessels
Preventing Deep Thrombosis
Preventing deep thrombosis in the leg involves reducing the risk of blood clots and promoting healthy blood flow. This can be achieved by: * Staying active and mobile, especially during long periods of travel or bed rest * Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products * Maintaining a healthy weight and diet * Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing * Wearing compression stockings or socksComplications of Deep Thrombosis

Deep thrombosis in the leg can cause serious complications if left untreated. These complications include:
- Pulmonary embolism, which can be fatal
- Chronic venous insufficiency, which can cause persistent pain and swelling
- Post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause skin ulcers and discoloration
- Long-term damage to the blood vessels, which can increase the risk of future blood clots
Managing Deep Thrombosis
Managing deep thrombosis in the leg involves working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan. This plan may include anticoagulation therapy, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress.It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms persist or worsen over time. With prompt treatment and proper management, people with deep thrombosis in the leg can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, deep thrombosis in the leg is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By recognizing the symptoms and risk factors, people can take steps to reduce their risk of developing DVT. With proper management and treatment, people with deep thrombosis in the leg can improve their overall health and well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with deep thrombosis in the leg. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with DVT? What steps have you taken to manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications? Share your story in the comments below, and let's work together to raise awareness and promote education about this important health topic.
What are the symptoms of deep thrombosis in the leg?
+The symptoms of deep thrombosis in the leg include pain, swelling, and discoloration of the affected leg. The pain may feel like a cramp or soreness in the calf or thigh, and it may worsen when standing or walking.
What are the risk factors for deep thrombosis in the leg?
+Risk factors for deep thrombosis in the leg include age, family history, obesity, and smoking. Other risk factors include pregnancy, cancer, and certain medical conditions, such as heart failure or respiratory disease.
How is deep thrombosis in the leg diagnosed?
+Diagnosing deep thrombosis in the leg typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans.
What are the treatment options for deep thrombosis in the leg?
+Treatment options for deep thrombosis in the leg include anticoagulation therapy, compression stockings, elevation of the affected leg, and pain relief medications. In some cases, thrombolytic therapy or surgery may be necessary.
How can I prevent deep thrombosis in the leg?
+Preventing deep thrombosis in the leg involves reducing the risk of blood clots and promoting healthy blood flow. This can be achieved by staying active and mobile, quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight and diet, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing.
