Intro
Learn about Goiter Disease, a thyroid condition causing swelling, nodules, and hormonal imbalances, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options for hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Goiter disease, also known as goiter, is a condition characterized by the enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam's apple. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, it can cause a range of symptoms and health problems. In this article, we will delve into the world of goiter disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and more.
The thyroid gland is a vital part of the endocrine system, producing hormones that help regulate metabolism, energy production, and growth. When the thyroid gland is functioning properly, it produces the right amount of hormones to meet the body's needs. However, when the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, it can produce too much or too little of these hormones, leading to a range of health problems. Goiter disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including iodine deficiency, thyroid nodules, thyroiditis, and certain medications.
Causes of Goiter Disease
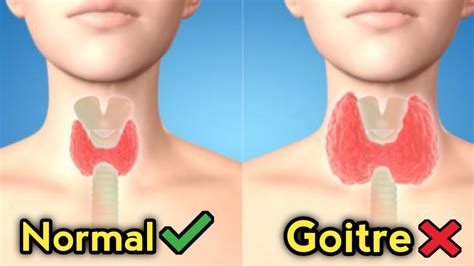
Types of Goiter Disease
There are several types of goiter disease, including simple goiter, toxic goiter, and endemic goiter. Simple goiter is the most common type of goiter disease and is characterized by an enlarged thyroid gland without any other symptoms. Toxic goiter, on the other hand, is a type of goiter disease that is caused by an overproduction of thyroid hormones. Endemic goiter is a type of goiter disease that is caused by iodine deficiency and is commonly found in areas where the soil and water are deficient in iodine.Symptoms of Goiter Disease

Diagnosis of Goiter Disease
The diagnosis of goiter disease typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and a range of diagnostic tests. During the physical examination, the doctor will check for any visible swelling in the neck and will also check the thyroid gland for any nodules or tenderness. The doctor will also take a medical history to determine if there are any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the goiter disease. Diagnostic tests such as thyroid function tests, ultrasound, and CT scans may also be used to diagnose goiter disease.Treatment Options for Goiter Disease
Prevention of Goiter Disease
Preventing goiter disease is possible by maintaining a healthy diet that includes foods that are rich in iodine, such as seaweed, dairy products, and bread. It is also important to avoid any foods that may interfere with thyroid function, such as soy products and cruciferous vegetables. Regular exercise and stress management can also help to prevent goiter disease. In areas where the soil and water are deficient in iodine, it may be necessary to take iodine supplements to prevent goiter disease.Complications of Goiter Disease
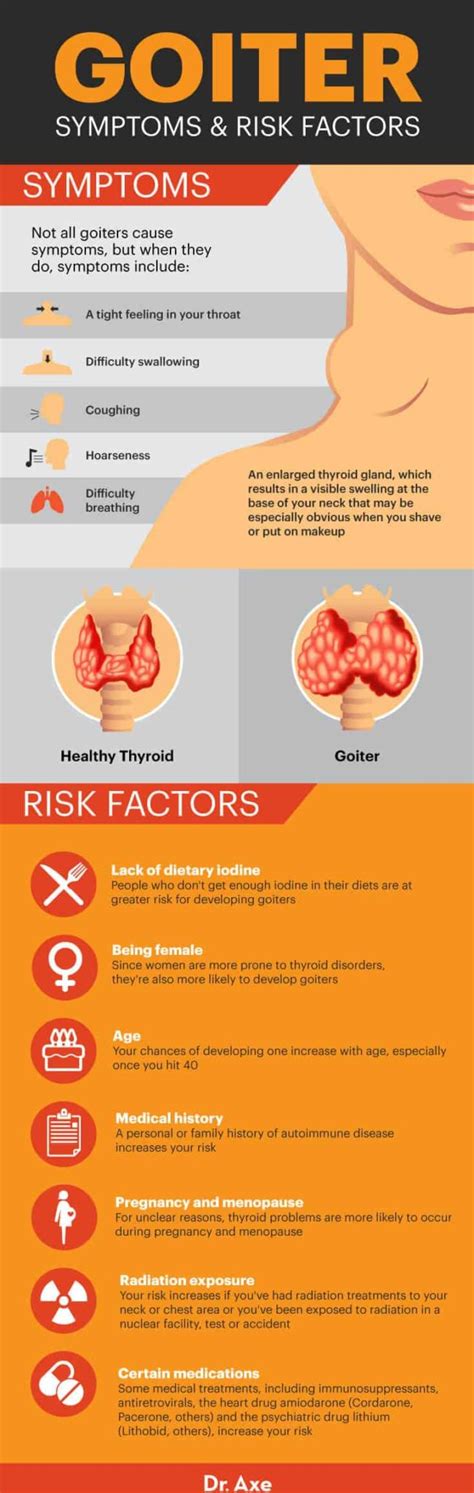
Living with Goiter Disease
Living with goiter disease can be challenging, particularly if the condition is severe or is causing symptoms. However, with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage the condition and prevent any complications. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that meets individual needs. Regular check-ups and monitoring can help to ensure that the condition is under control and that any complications are caught early.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

What is the main cause of goiter disease?
+The main cause of goiter disease is iodine deficiency, particularly in areas where the soil and water are deficient in iodine.
What are the symptoms of goiter disease?
+The symptoms of goiter disease can vary depending on the underlying cause of the condition, but common symptoms include a visible swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing, coughing, hoarseness, and shortness of breath.
How is goiter disease diagnosed?
+Goiter disease is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and a range of diagnostic tests, including thyroid function tests, ultrasound, and CT scans.
What are the treatment options for goiter disease?
+The treatment options for goiter disease depend on the underlying cause of the condition, but may include medications, surgery, and radioactive iodine therapy.
Can goiter disease be prevented?
+Yes, goiter disease can be prevented by maintaining a healthy diet that includes foods that are rich in iodine, avoiding any foods that may interfere with thyroid function, and taking iodine supplements if necessary.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with goiter disease in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about goiter disease, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. By working together, we can promote thyroid health and prevent goiter disease. Thank you for reading, and we look forward to hearing from you!
