Intro
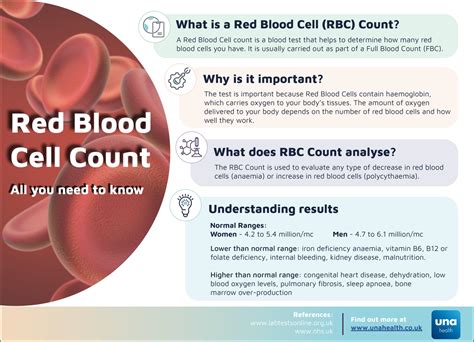
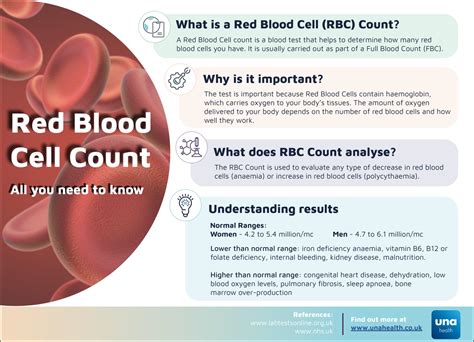
Discover the Red Blood Cell Count Definition, understanding its significance in diagnosing anemia, blood disorders, and hematological conditions, with related terms like hemoglobin, erythrocytes, and blood test results.
The human body is made up of various cells, each with its unique functions and characteristics. One of the most essential types of cells is the red blood cell, which plays a crucial role in transporting oxygen throughout the body. A red blood cell count is a test used to measure the number of red blood cells in the blood, and it is an essential aspect of diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of red blood cells, exploring their definition, functions, and the importance of red blood cell count in maintaining overall health.
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, are the most abundant type of cell in the blood, making up approximately 45% of its total content. These cells are produced in the bone marrow and have a lifespan of around 120 days. Their primary function is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and organs, as well as to transport carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs. Red blood cells contain a protein called hemoglobin, which binds to oxygen and allows it to be transported throughout the body.
The importance of red blood cells cannot be overstated, as they are essential for maintaining the body's overall health and function. A decrease in red blood cell count can lead to a range of health problems, including anemia, fatigue, and shortness of breath. On the other hand, an increase in red blood cell count can be a sign of dehydration, polycythemia, or other underlying health conditions. Therefore, it is essential to maintain a healthy red blood cell count, and this is where the red blood cell count test comes in.
What is Red Blood Cell Count?
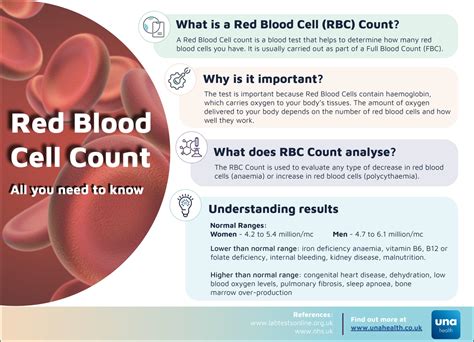
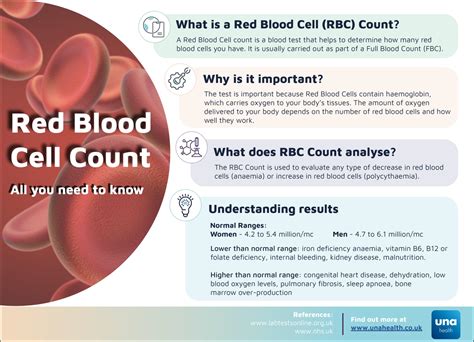
The normal range for red blood cell count varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. For adult men, the normal range is typically between 4.32 and 5.72 million cells per microliter (µL) of blood. For adult women, the normal range is typically between 3.90 and 5.03 million cells per µL. Children and infants have a higher red blood cell count due to their smaller blood volume.
How is Red Blood Cell Count Measured?
The red blood cell count is typically measured using a automated hematology analyzer, which uses a small sample of blood to perform the test. The test is usually performed in a laboratory or hospital setting, and the results are available within a few hours. The test measures the number of red blood cells in a specific volume of blood, usually 1 µL.The red blood cell count can also be measured manually using a microscope and a hemocytometer. This method is less accurate than automated analyzers but can be used in situations where automated equipment is not available.
Importance of Red Blood Cell Count
On the other hand, an increase in red blood cell count can be a sign of dehydration, polycythemia, or other underlying health conditions. Polycythemia is a condition characterized by an overproduction of red blood cells, which can increase the risk of blood clots and other cardiovascular problems.
The red blood cell count is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for various health conditions. For example, in patients with anemia, the red blood cell count can be used to monitor the response to iron supplements or blood transfusions.
Benefits of Red Blood Cell Count
The red blood cell count has several benefits, including:- Diagnosing and monitoring anemia and other blood disorders
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatments for various health conditions
- Identifying underlying health conditions, such as dehydration and polycythemia
- Providing information about the body's overall health and function
The red blood cell count is a simple and non-invasive test that can provide valuable information about the body's overall health and function. It is an essential aspect of diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions, and it can help healthcare professionals develop effective treatment plans.
Red Blood Cell Count and Health Conditions
- Anemia: a condition characterized by a decrease in red blood cell count, which can be caused by iron deficiency, vitamin deficiency, and chronic diseases such as kidney disease and cancer.
- Polycythemia: a condition characterized by an overproduction of red blood cells, which can increase the risk of blood clots and other cardiovascular problems.
- Dehydration: a condition characterized by a decrease in blood volume, which can cause an increase in red blood cell count.
- Blood disorders: such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia, which can affect the production and function of red blood cells.
The red blood cell count can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for various health conditions. For example, in patients with anemia, the red blood cell count can be used to monitor the response to iron supplements or blood transfusions.
Red Blood Cell Count and Age
The red blood cell count can vary depending on age. Children and infants have a higher red blood cell count due to their smaller blood volume. The normal range for red blood cell count in children and infants is typically higher than in adults.As people age, the red blood cell count can decrease, which can increase the risk of anemia and other blood disorders. Older adults may be at increased risk of anemia due to chronic diseases such as kidney disease and cancer, as well as age-related declines in physical function and mobility.
How to Improve Red Blood Cell Count
- Eating a healthy diet: rich in iron, vitamins, and minerals
- Taking iron supplements: to treat iron deficiency anemia
- Avoiding dehydration: by drinking plenty of water and other fluids
- Managing chronic diseases: such as kidney disease and cancer
- Getting regular exercise: to improve overall health and function
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements or making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine.
Red Blood Cell Count and Nutrition
A healthy diet rich in iron, vitamins, and minerals is essential for maintaining a healthy red blood cell count. Foods that are rich in iron include:- Red meat
- Poultry
- Fish
- Beans
- Lentils
- Fortified cereals
Foods that are rich in vitamins and minerals include:
- Leafy green vegetables
- Fruits
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Whole grains
Adequate nutrition is essential for maintaining a healthy red blood cell count, and a healthcare professional can provide personalized dietary recommendations.
Red Blood Cell Count and Exercise
However, intense or prolonged exercise can also cause dehydration, which can lead to an increase in red blood cell count. It is essential to stay hydrated during exercise by drinking plenty of water and other fluids.
Red Blood Cell Count and Stress
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on red blood cell count, as it can cause inflammation and oxidative stress. Stress can also lead to poor nutrition, dehydration, and lack of sleep, all of which can negatively impact red blood cell count.Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress and promote overall health and well-being.
Red Blood Cell Count and Sleep
Getting 7-9 hours of sleep per night is essential for maintaining overall health and function, including a healthy red blood cell count.
Red Blood Cell Count and Overall Health
The red blood cell count is an essential aspect of overall health and function. Maintaining a healthy red blood cell count can help prevent anemia, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.A healthcare professional can provide personalized recommendations for maintaining a healthy red blood cell count, including dietary changes, exercise routines, and stress-reducing activities.
What is the normal range for red blood cell count?
+The normal range for red blood cell count varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. For adult men, the normal range is typically between 4.32 and 5.72 million cells per microliter (µL) of blood. For adult women, the normal range is typically between 3.90 and 5.03 million cells per µL.
What are the benefits of red blood cell count?
+The benefits of red blood cell count include diagnosing and monitoring anemia and other blood disorders, monitoring the effectiveness of treatments, identifying underlying health conditions, and providing information about the body's overall health and function.
How can I improve my red blood cell count?
+There are several ways to improve red blood cell count, including eating a healthy diet rich in iron, vitamins, and minerals, taking iron supplements, avoiding dehydration, managing chronic diseases, and getting regular exercise.
What are the risks of an abnormal red blood cell count?
+An abnormal red blood cell count can increase the risk of anemia, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic health conditions. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your red blood cell count.
How often should I get my red blood cell count checked?
+The frequency of red blood cell count checks depends on individual factors, such as age, health status, and medical history. A healthcare professional can provide personalized recommendations for red blood cell count checks.
In conclusion, the red blood cell count is an essential aspect of diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. Maintaining a healthy red blood cell count can help prevent anemia, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. By understanding the importance of red blood cell count and taking steps to maintain a healthy count, individuals can promote overall health and well-being. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with red blood cell count in the comments below and to consult with a healthcare professional if they have concerns about their red blood cell count.
