Intro
Discover the 5 uses of Dexamethasone, a potent corticosteroid, for treating inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and cancer, with applications in immunosuppression, anti-inflammatory, and palliative care, offering therapeutic benefits and symptom relief.
The importance of understanding the various applications of medications cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to drugs like dexamethasone. Dexamethasone is a synthetic corticosteroid with potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties, making it a versatile medication in the medical field. Its uses span across various medical specialties, from emergency medicine to oncology, and its effectiveness has saved countless lives and improved the quality of life for many patients. The significance of dexamethasone lies in its ability to manage and treat a wide range of conditions, making it a crucial component of modern healthcare.
Dexamethasone's mechanism of action involves the suppression of the immune system, which can be beneficial in conditions where the body's immune response is harmful. This suppression can lead to a reduction in inflammation, making it an effective treatment for various inflammatory conditions. Moreover, dexamethasone can influence the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, further expanding its therapeutic applications. The drug's potency and long-lasting effects compared to other corticosteroids have made it a preferred choice in many clinical scenarios.
The applications of dexamethasone are diverse and continue to evolve as medical research advances. From treating life-threatening conditions to managing chronic diseases, the role of dexamethasone in healthcare is multifaceted. Its use in emergency situations, such as severe allergic reactions or asthma exacerbations, highlights its critical role in saving lives. Additionally, dexamethasone's application in palliative care to improve the quality of life for patients with terminal illnesses underscores its importance in comprehensive patient care.
Introduction to Dexamethasone

Dexamethasone is a long-acting corticosteroid that is synthesized from prednisolone. Its chemical structure and pharmacological properties allow it to have a higher potency and longer biological half-life compared to cortisol, the naturally occurring corticosteroid in the human body. This synthetic corticosteroid can be administered orally, intravenously, or via other routes, depending on the clinical scenario and the desired onset of action. The versatility in administration routes, combined with its potent effects, makes dexamethasone a valuable asset in clinical practice.
Clinical Applications of Dexamethasone
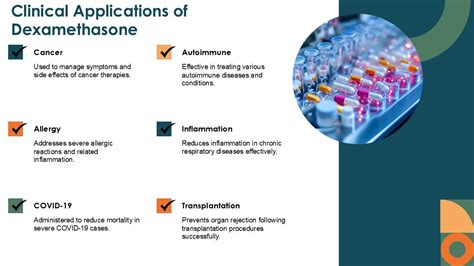
The clinical applications of dexamethasone are broad, reflecting its anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, and metabolic effects. Some of the key uses of dexamethasone include:
- Emergency Medicine: Dexamethasone is used in the management of severe allergic reactions, anaphylaxis, and status asthmaticus due to its rapid and potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Oncology: It is utilized in the treatment of certain types of cancer, such as leukemia and lymphoma, due to its ability to suppress the immune system and reduce tumor size.
- Neurology: Dexamethasone can be used to reduce cerebral edema associated with brain tumors or after neurosurgery.
- Rheumatology: It is effective in managing inflammatory arthritis and other rheumatologic conditions by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system.
- Palliative Care: Dexamethasone is used to improve the quality of life for patients with terminal illnesses by reducing inflammation, improving appetite, and enhancing the sense of well-being.
Benefits and Mechanisms
The benefits of dexamethasone stem from its pharmacological properties, including its high potency, long duration of action, and versatility in administration. Its mechanisms of action involve: - Suppressing the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent tissue damage. - Influencing carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism, which can be beneficial in certain clinical conditions. - Reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other mediators of inflammation.Administration and Dosage

The administration and dosage of dexamethasone depend on the clinical scenario, the severity of the condition being treated, and the patient's response to the medication. Dexamethasone can be administered:
- Orally: Tablets or liquid formulations are available for oral administration.
- Intravenously: For rapid effects, especially in emergency situations.
- Intramuscularly: For situations where oral administration is not feasible.
- Topically: For localized skin conditions.
The dosage of dexamethasone varies widely, from a few milligrams for minor conditions to much higher doses for severe or life-threatening conditions. The dosage regimen may involve a single dose, intermittent dosing, or continuous administration, depending on the clinical context.
Side Effects and Precautions
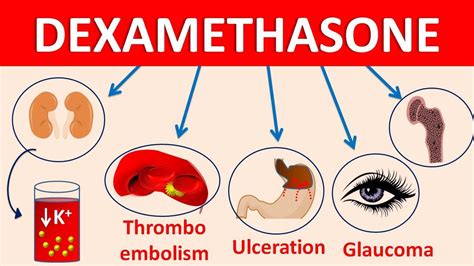
While dexamethasone is a valuable medication, its use is not without potential side effects and risks. Common side effects include:
- Weight gain
- Mood changes
- Increased appetite
- Insomnia
- Increased blood sugar levels
Long-term use of dexamethasone can lead to more serious side effects, such as:
- Osteoporosis
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
- Adrenal suppression
- Increased risk of infections
Precautions should be taken when using dexamethasone, especially in patients with a history of diabetes, osteoporosis, or those who are prone to infections. Monitoring of blood sugar levels, bone density, and eye pressure may be necessary during long-term therapy.
Special Considerations
Special considerations are necessary when prescribing dexamethasone to certain patient populations, including: - **Pregnant Women:** Dexamethasone can be used during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the risks, but it should be used with caution. - **Breastfeeding Mothers:** Dexamethasone is excreted in breast milk, and its use during breastfeeding should be carefully considered. - **Children:** The use of dexamethasone in children requires careful monitoring due to the potential for growth suppression and other side effects.Alternatives and Future Directions

While dexamethasone remains a cornerstone in the management of various conditions, research into alternative corticosteroids and non-steroidal treatments continues. The development of drugs with fewer side effects and more targeted mechanisms of action could potentially replace or complement dexamethasone in certain clinical scenarios. Future directions may include the use of dexamethasone in combination with other medications to enhance efficacy or reduce side effects.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, dexamethasone is a powerful and versatile medication with a wide range of applications in healthcare. Its potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects make it an invaluable tool in the management of acute and chronic conditions. However, its use requires careful consideration of potential side effects and interactions. As medical research advances, the role of dexamethasone will continue to evolve, and its applications may expand into new areas of healthcare.What is dexamethasone used for?
+Dexamethasone is used for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties in various medical conditions, including severe allergic reactions, asthma, cancer, and rheumatologic diseases.
How is dexamethasone administered?
+Dexamethasone can be administered orally, intravenously, intramuscularly, or topically, depending on the clinical scenario and desired onset of action.
What are the potential side effects of dexamethasone?
+Potential side effects include weight gain, mood changes, increased appetite, insomnia, and increased blood sugar levels. Long-term use can lead to more serious side effects such as osteoporosis, cataracts, and adrenal suppression.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with dexamethasone in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most accurate and helpful content possible.
