Intro
Manage diabetic blood sugar levels with our comprehensive guide, covering normal ranges, monitoring, and control techniques to prevent complications, including hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and managing blood sugar levels is key to preventing complications and improving quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of diabetic blood sugar levels, exploring the importance of monitoring and controlling blood sugar, the benefits of maintaining healthy levels, and providing practical tips and guidelines for managing diabetes.
The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. When blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Furthermore, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can increase the risk of developing other health conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and stroke. By monitoring and controlling blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing these complications and improve their overall health and well-being.
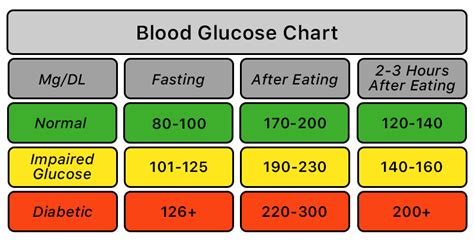
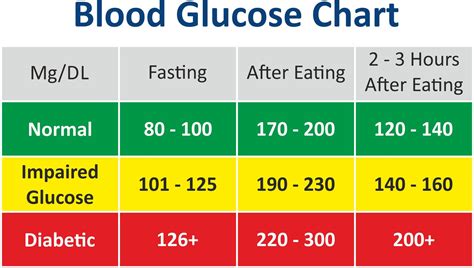
For individuals with diabetes, understanding blood sugar levels is essential for managing the condition. Blood sugar levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and are typically checked using a blood glucose meter. The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with diabetes aim for the following blood sugar levels: between 70 and 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals. By maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing complications and improve their overall health and well-being.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels

Understanding blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes. Blood sugar levels are affected by a variety of factors, including diet, physical activity, stress, and medication. When blood sugar levels are too high, it can lead to a range of health complications, including ketoacidosis, a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. On the other hand, when blood sugar levels are too low, it can lead to hypoglycemia, a condition that can cause confusion, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness.
Factors That Affect Blood Sugar Levels
There are several factors that can affect blood sugar levels, including: * Diet: The type and amount of food consumed can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, can cause blood sugar levels to rise. * Physical activity: Regular physical activity can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. * Stress: Stress can cause blood sugar levels to rise, as the body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase blood sugar levels. * Medication: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can increase blood sugar levels.Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
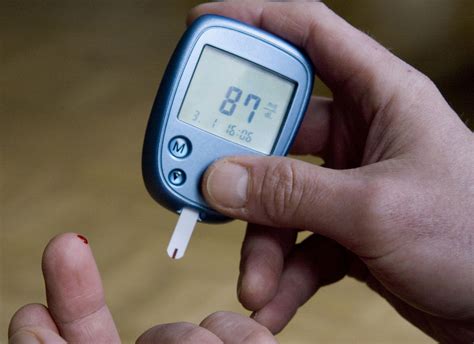
Monitoring blood sugar levels is an essential part of managing diabetes. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including:
- Blood glucose meters: These are small devices that measure the level of glucose in the blood.
- Continuous glucose monitors: These are small devices that are inserted under the skin and provide continuous readings of blood sugar levels.
- Urine tests: These tests measure the level of ketones in the urine, which can indicate high blood sugar levels.
Tips for Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Here are some tips for monitoring blood sugar levels: * Test blood sugar levels regularly, ideally before meals and before bed. * Keep a record of blood sugar levels to track progress and identify patterns. * Use a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor to get accurate readings. * Test for ketones if blood sugar levels are high or if symptoms of ketoacidosis occur.Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Here are some tips for managing blood sugar levels:
- Eat a healthy diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Take medication as prescribed: If medication is prescribed, take it as directed to help control blood sugar levels.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels can have numerous benefits, including: * Reducing the risk of complications: By maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. * Improving overall health: Managing blood sugar levels can improve overall health and well-being, reducing the risk of other health conditions, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol. * Increasing energy: Managing blood sugar levels can increase energy levels and improve physical function.Diabetic Blood Sugar Levels Guide
This guide provides an overview of diabetic blood sugar levels, including the importance of monitoring and controlling blood sugar levels, the benefits of maintaining healthy levels, and practical tips and guidelines for managing diabetes. By following this guide, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing complications and improve their overall health and well-being.
Practical Tips for Managing Diabetes
Here are some practical tips for managing diabetes: * Keep a record of blood sugar levels to track progress and identify patterns. * Use a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor to get accurate readings. * Test for ketones if blood sugar levels are high or if symptoms of ketoacidosis occur. * Eat a healthy diet, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods. * Exercise regularly, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, managing diabetic blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing complications and improving quality of life. By understanding blood sugar levels, monitoring and controlling levels, and making lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing complications and improve their overall health and well-being. We encourage readers to take the next step in managing their diabetes by consulting with a healthcare provider, making lifestyle changes, and staying informed about the latest research and developments in diabetes management.
What are the normal blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes?
+Normal blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes are between 70 and 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals.
How often should individuals with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels?
+Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, ideally before meals and before bed.
What are the benefits of managing blood sugar levels?
+Managing blood sugar levels can reduce the risk of complications, improve overall health and well-being, and increase energy levels.
We invite readers to share their experiences and tips for managing diabetic blood sugar levels in the comments below. By working together and staying informed, we can improve our understanding of diabetes and develop effective strategies for managing the condition.
