Intro
Learn proper dog bite wound care to prevent infection. Discover treatment, symptoms, and first aid for animal bites, including wound cleaning and antibiotic ointment application.
Dog bite wounds can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, especially if left untreated or not properly cared for. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 4.5 million dog bites occur each year in the United States, resulting in an estimated 20-30 fatalities. It is essential to understand the importance of proper wound care and management to prevent infection, promote healing, and minimize the risk of long-term complications.
Dog bites can range from minor scratches to severe lacerations, and the severity of the wound often depends on the size and breed of the dog, as well as the location and depth of the bite. In some cases, dog bites can also transmit diseases such as rabies, tetanus, and capnocytophaga. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know has been bitten by a dog.
The first step in treating a dog bite wound is to stop the bleeding and clean the area to prevent infection. This can be done by applying gentle pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage and rinsing the area with cool or lukewarm water. It is also important to remove any debris or dirt from the wound to promote healing and prevent infection. In this article, we will discuss the importance of proper dog bite wound care, the benefits of seeking medical attention, and the steps you can take to prevent infection and promote healing.
Dog Bite Wound Care and Management

Proper wound care and management are critical in preventing infection and promoting healing. The first step in treating a dog bite wound is to stop the bleeding and clean the area. This can be done by applying gentle pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage and rinsing the area with cool or lukewarm water. It is also essential to remove any debris or dirt from the wound to promote healing and prevent infection.
Benefits of Seeking Medical Attention
Seeking medical attention immediately after a dog bite is crucial in preventing infection and promoting healing. A medical professional can assess the severity of the wound and provide proper treatment, including antibiotics, tetanus shots, and rabies prophylaxis if necessary. Additionally, a medical professional can also provide guidance on proper wound care and management, including how to clean and dress the wound, and how to monitor for signs of infection.Preventing Infection and Promoting Healing
Preventing infection and promoting healing are critical in the treatment of dog bite wounds. This can be achieved by keeping the wound clean and dry, applying topical antibiotics, and taking oral antibiotics as prescribed by a medical professional. It is also essential to monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, and increased pain.
Steps to Prevent Infection
To prevent infection and promote healing, it is essential to follow these steps: * Keep the wound clean and dry * Apply topical antibiotics as prescribed by a medical professional * Take oral antibiotics as prescribed by a medical professional * Monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, and increased pain * Seek medical attention immediately if you notice any signs of infectionRabies and Tetanus Prophylaxis

Rabies and tetanus prophylaxis are critical in the treatment of dog bite wounds. Rabies is a viral disease that can be transmitted through the saliva of an infected animal, and tetanus is a bacterial disease that can be transmitted through contaminated wounds. A medical professional can provide guidance on whether rabies or tetanus prophylaxis is necessary, based on the severity of the wound and the vaccination status of the dog.
Rabies Prophylaxis
Rabies prophylaxis typically involves a series of injections, including: * Immediate washing of the wound with soap and water * Administration of rabies immune globulin * Administration of a rabies vaccine seriesTetanus Prophylaxis
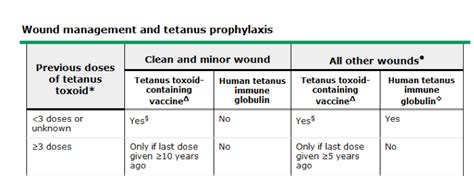
Tetanus prophylaxis typically involves a tetanus shot, which is administered to prevent tetanus infection. The tetanus shot is usually given immediately after the wound is cleaned and dressed, and a booster shot may be given if the wound is severe or if the individual has not received a tetanus shot in the past 10 years.
Benefits of Tetanus Prophylaxis
The benefits of tetanus prophylaxis include: * Prevention of tetanus infection * Prevention of serious complications, such as lockjaw and respiratory failure * Promotion of wound healing and recoveryWound Healing and Recovery
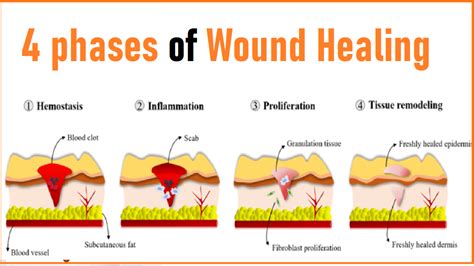
Wound healing and recovery are critical in the treatment of dog bite wounds. Proper wound care and management, including keeping the wound clean and dry, applying topical antibiotics, and taking oral antibiotics as prescribed, can promote wound healing and recovery.
Factors that Affect Wound Healing
Several factors can affect wound healing, including: * Age and overall health of the individual * Severity of the wound * Presence of underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or poor circulation * Use of tobacco or other substances that can impair wound healingLong-Term Complications

Long-term complications can occur if dog bite wounds are not properly treated or managed. These complications can include:
- Infection and sepsis
- Tetanus and rabies
- Scarring and disfigurement
- Nerve damage and numbness
- Chronic pain and disability
Prevention of Long-Term Complications
Prevention of long-term complications can be achieved by: * Seeking medical attention immediately after a dog bite * Following proper wound care and management * Taking antibiotics as prescribed by a medical professional * Monitoring the wound for signs of infection and seeking medical attention if necessaryWhat should I do immediately after a dog bite?
+Immediately after a dog bite, stop the bleeding and clean the area with cool or lukewarm water. Remove any debris or dirt from the wound and apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth or bandage. Seek medical attention immediately to prevent infection and promote healing.
How can I prevent infection after a dog bite?
+To prevent infection after a dog bite, keep the wound clean and dry, apply topical antibiotics as prescribed by a medical professional, and take oral antibiotics as prescribed. Monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, and increased pain, and seek medical attention immediately if you notice any of these symptoms.
What are the long-term complications of dog bite wounds?
+In final thoughts, dog bite wound care and management are critical in preventing infection and promoting healing. By understanding the importance of proper wound care and management, seeking medical attention immediately after a dog bite, and following the steps outlined in this article, you can minimize the risk of long-term complications and promote optimal recovery. If you or someone you know has been bitten by a dog, remember to stay calm, stop the bleeding, and seek medical attention immediately. Share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of dog bite wound care and management, and don't hesitate to comment below with any questions or concerns.
