Intro
Learn about the proper dose for hydrocodone, a potent opioid pain reliever, and understand its usage, side effects, and interactions to ensure safe consumption and minimize risks of addiction and overdose.
Hydrocodone is a powerful opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is often prescribed in combination with other medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to enhance its pain-relieving effects. However, the dosage of hydrocodone must be carefully managed to minimize the risk of side effects, dependence, and overdose.
The importance of proper dosing cannot be overstated, as hydrocodone can be habit-forming and may lead to addiction if not used as directed. Moreover, taking too much hydrocodone can cause respiratory depression, which can be life-threatening. Therefore, it is essential to understand the recommended dosage, potential interactions, and warning signs of overdose to ensure safe and effective use.
The use of hydrocodone has been a topic of discussion in recent years, with concerns about its potential for abuse and the opioid epidemic. As a result, healthcare providers are now more cautious when prescribing hydrocodone, and patients are encouraged to be more mindful of their medication use. By understanding the proper dosage and potential risks associated with hydrocodone, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Dosage Guidelines for Hydrocodone
The dosage of hydrocodone varies depending on the individual's medical condition, age, and response to treatment. The typical dosage range for hydrocodone is between 2.5 and 10 milligrams, taken every 4 to 6 hours as needed. However, the maximum daily dose should not exceed 40 milligrams. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and not to take more than the recommended amount, as this can increase the risk of side effects and dependence.
For patients who are new to hydrocodone, it is recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed and under medical supervision. This approach helps to minimize the risk of adverse effects and allows the individual to develop tolerance to the medication. Additionally, patients should be aware of the potential interactions between hydrocodone and other medications, such as sedatives, tranquilizers, and antidepressants, which can increase the risk of side effects.
Factors Affecting Hydrocodone Dosage
The dosage of hydrocodone can be affected by several factors, including the individual's weight, age, and medical condition. For example, older adults or those with liver or kidney disease may require lower doses due to decreased metabolism and increased sensitivity to the medication. On the other hand, individuals with a history of substance abuse or those taking other medications that interact with hydrocodone may require closer monitoring and adjusted dosing.Other factors that can influence hydrocodone dosage include the type of pain being treated, the individual's pain tolerance, and the presence of other medical conditions, such as respiratory disease or gastrointestinal disorders. By considering these factors, healthcare providers can tailor the dosage to the individual's specific needs and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Types of Hydrocodone Formulations

Hydrocodone is available in various formulations, including tablets, capsules, and liquid solutions. The choice of formulation depends on the individual's preferences, the severity of their pain, and the presence of other medical conditions. For example, extended-release formulations may be suitable for individuals with chronic pain, while immediate-release formulations may be preferred for those with acute pain.
Some common hydrocodone formulations include:
- Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets (e.g., Vicodin)
- Hydrocodone bitartrate and ibuprofen tablets (e.g., Vicoprofen)
- Hydrocodone bitartrate and aspirin tablets (e.g., Lortab)
- Hydrocodone liquid solution (e.g., Hycodan)
Each formulation has its own unique characteristics, and the dosage may vary depending on the specific product. Therefore, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions for use to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Warning Signs of Overdose
Taking too much hydrocodone can lead to overdose, which can be life-threatening. Warning signs of overdose include:- Respiratory depression (slow or shallow breathing)
- Drowsiness or unresponsiveness
- Confusion or disorientation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Seizures or convulsions
If you suspect an overdose, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Call emergency services or go to the nearest hospital, and provide as much information as possible about the overdose, including the amount and type of medication taken.
Potential Interactions with Hydrocodone

Hydrocodone can interact with other medications, increasing the risk of side effects and dependence. Some potential interactions include:
- Sedatives and tranquilizers (e.g., benzodiazepines, barbiturates)
- Antidepressants (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants)
- Muscle relaxants (e.g., cyclobenzaprine, carisoprodol)
- Antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine, loratadine)
- Other opioid medications (e.g., morphine, codeine)
To minimize the risk of interactions, it is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and supplements. By being aware of potential interactions, you can take steps to minimize the risk of adverse effects and ensure safe and effective treatment.
Managing Side Effects
Hydrocodone can cause a range of side effects, including:- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Drowsiness or fatigue
- Headache
- Dry mouth
To manage side effects, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions for use. Additionally, you can take steps to minimize the risk of side effects, such as:
- Taking hydrocodone with food to reduce nausea and vomiting
- Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated
- Avoiding activities that require alertness, such as driving or operating heavy machinery
- Getting regular exercise to improve overall health and well-being
By being aware of potential side effects and taking steps to manage them, you can minimize the risk of adverse effects and ensure safe and effective treatment.
Long-Term Use and Dependence

Long-term use of hydrocodone can lead to dependence, which can be challenging to overcome. Dependence occurs when the body adapts to the medication and requires increasingly higher doses to achieve the same effect. Warning signs of dependence include:
- Taking more hydrocodone than prescribed
- Using hydrocodone for longer than prescribed
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when stopping or reducing hydrocodone use
- Neglecting responsibilities or relationships due to hydrocodone use
- Continuing to use hydrocodone despite negative consequences
If you suspect dependence, it is essential to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider can help you develop a treatment plan to manage withdrawal symptoms and overcome dependence.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms can occur when stopping or reducing hydrocodone use. Common withdrawal symptoms include:- Anxiety or agitation
- Insomnia or restlessness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea or abdominal cramps
- Headache or fatigue
- Muscle or joint pain
To manage withdrawal symptoms, it is essential to work with a healthcare provider. They can help you develop a tapering schedule to gradually reduce hydrocodone use and minimize the risk of withdrawal symptoms.
Conclusion and Next Steps
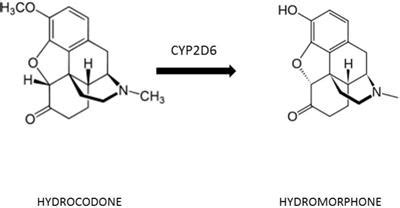
In conclusion, hydrocodone is a powerful opioid medication that requires careful management to minimize the risk of side effects, dependence, and overdose. By understanding the recommended dosage, potential interactions, and warning signs of overdose, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and ensure safe and effective use.
If you have any questions or concerns about hydrocodone, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They can help you develop a personalized treatment plan and provide guidance on managing side effects, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, we invite you to comment below and share your experiences with hydrocodone. By working together, we can promote safe and effective use of opioid medications and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
What is the recommended dosage for hydrocodone?
+The recommended dosage for hydrocodone varies depending on the individual's medical condition, age, and response to treatment. The typical dosage range is between 2.5 and 10 milligrams, taken every 4 to 6 hours as needed.
Can I take hydrocodone with other medications?
+Hydrocodone can interact with other medications, increasing the risk of side effects and dependence. It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and supplements.
How can I manage side effects of hydrocodone?
+To manage side effects, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions for use. Additionally, you can take steps to minimize the risk of side effects, such as taking hydrocodone with food, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding activities that require alertness.
