Intro
Discover the ultimate Lisinopril Dosing Guide, covering dosage recommendations, administration tips, and interactions, to ensure safe and effective blood pressure management with this ACE inhibitor medication.
Lisinopril is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. It is primarily used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. The medication works by relaxing blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood. Lisinopril is also used to protect the kidneys from damage due to diabetes. With its widespread use, understanding the correct dosing of lisinopril is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients to ensure the medication's effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.
The importance of proper dosing cannot be overstated. Incorrect dosing can lead to reduced efficacy or increased risk of side effects. Healthcare providers consider several factors when determining the appropriate dose of lisinopril, including the patient's age, kidney function, and the presence of other health conditions. For individuals with high blood pressure, the goal of treatment is to lower blood pressure to a level that reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke. For those with heart failure, the aim is to improve symptoms and enhance survival.
Lisinopril's effectiveness and safety profile make it a preferred choice for many patients. However, like all medications, it must be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Patients should be aware of the potential side effects, drug interactions, and the importance of regular monitoring of blood pressure and kidney function. By understanding how lisinopril works and how it should be dosed, patients can better manage their condition and improve their overall health outcomes.
Lisinopril Mechanism of Action

Benefits of Lisinopril
The benefits of lisinopril include its ability to lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke, and protect the kidneys from damage. It is also effective in managing heart failure by improving symptoms and enhancing survival. Lisinopril is generally well-tolerated, with common side effects being mild and temporary.Lisinopril Dosing Recommendations
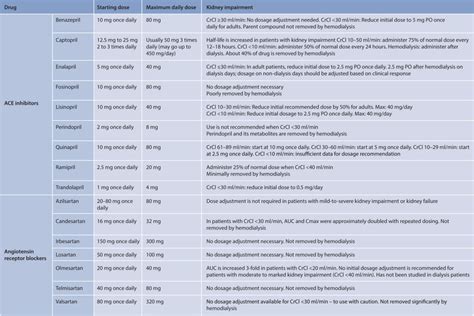
Key Considerations for Dosing
- **Kidney Function:** Lisinopril is excreted by the kidneys, so dosing adjustments are necessary in patients with kidney disease. - **Age:** Elderly patients may require lower doses due to decreased kidney function and potential sensitivity to the medication. - **Combination Therapy:** When used in combination with other blood pressure medications, the dose of lisinopril may need to be adjusted.Potential Side Effects and Interactions
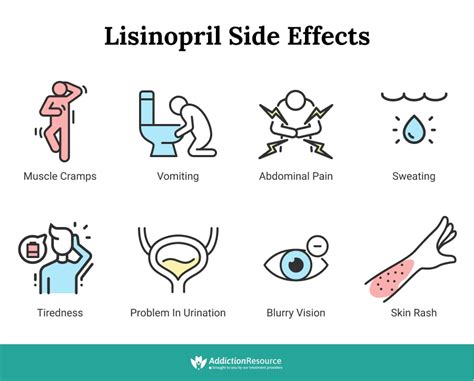
Managing Side Effects
- **Monitoring:** Regular monitoring of blood pressure, kidney function, and potassium levels is crucial. - **Lifestyle Changes:** Dietary changes, such as reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium-rich foods, can help manage blood pressure. - **Medication Adjustment:** The healthcare provider may adjust the dose or switch to a different medication if side effects are severe.Practical Tips for Patients
Enhancing Adherence
- **Simplifying Regimens:** Using a pill box or setting reminders can help patients remember to take their medication. - **Education:** Understanding the importance of the medication and how it works can improve adherence. - **Support:** Family and friends can provide support and encouragement.Future Directions and Research

Emerging Trends
- **Precision Medicine:** Tailoring treatment to the individual based on genetic and other factors. - **Combination Therapies:** Investigating the benefits of combining lisinopril with other medications for enhanced efficacy. - **Digital Health:** Utilizing digital tools for monitoring and managing blood pressure.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite readers to share their experiences with lisinopril, ask questions, or provide insights that could help others. Your engagement can contribute to a better understanding of this medication and its role in managing cardiovascular health. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with someone who might benefit from the information provided.
What is the primary use of lisinopril?
+Lisinopril is primarily used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure.
How does lisinopril work?
+Lisinopril works by inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, leading to a decrease in blood pressure and a reduction in the heart's workload.
What are the common side effects of lisinopril?
+Common side effects include cough, dizziness, and increased potassium levels. Serious side effects can include kidney problems and angioedema.
