Intro
Doxycycline side effects can be severe, including antibiotic resistance, stomach issues, and photosensitivity. Learn about common and rare doxycycline effects, interactions, and warnings to minimize risks.
The importance of understanding the potential side effects of doxycycline, a commonly prescribed antibiotic, cannot be overstated. As a medication that is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, from acne and respiratory tract infections to Lyme disease and cholera, its impact on public health is significant. However, like all medications, doxycycline can cause side effects, some of which can be severe. It is crucial for patients to be aware of these potential side effects to ensure they can make informed decisions about their treatment and to seek medical attention if necessary.
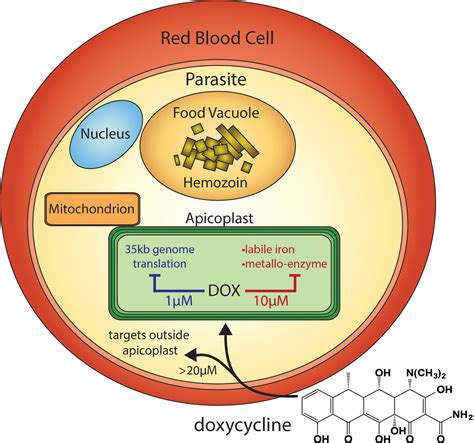
Doxycycline belongs to the class of antibiotics known as tetracyclines, which work by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, thereby preventing the growth and spread of the infection. While doxycycline is generally well-tolerated, its side effects can vary from mild to severe and can affect different systems of the body. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, which can often be managed with dietary changes or over-the-counter medications. However, more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions, liver damage, and increased sensitivity to sunlight, can have significant implications for a patient's health and quality of life.
The potential for side effects to impact a patient's adherence to their treatment regimen and overall health outcomes underscores the need for careful consideration and monitoring when prescribing doxycycline. Healthcare providers must weigh the benefits of using doxycycline against the potential risks and consider alternative treatments if necessary. Furthermore, patients should be empowered with knowledge about the potential side effects of doxycycline, how to manage them, and when to seek medical attention. By fostering a collaborative approach to healthcare, where patients and healthcare providers work together to manage treatment and side effects, we can optimize the use of doxycycline and other antibiotics, ensuring they remain effective tools in the fight against bacterial infections.
Doxycycline Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Doxycycline
The benefits of doxycycline are numerous and well-documented. Its broad-spectrum activity makes it effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Doxycycline is also known for its ability to penetrate into tissues and cells, allowing it to reach the site of infection effectively. This property, combined with its long half-life, means that doxycycline can be administered less frequently than some other antibiotics, improving patient compliance. Additionally, doxycycline has anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial in treating conditions like acne and rosacea.Doxycycline Side Effects Overview
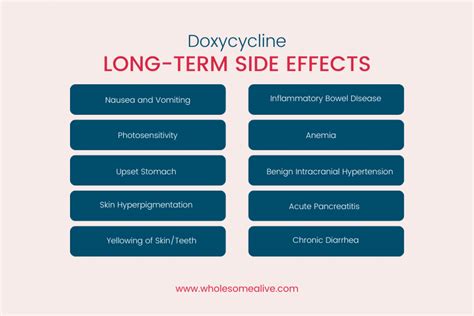
Common Side Effects of Doxycycline
Some of the most common side effects of doxycycline include: - Nausea and vomiting - Diarrhea - Abdominal pain - Photosensitivity (increased sensitivity to sunlight) - Headache - Dizziness - Fatigue These side effects are often mild and may resolve on their own or with minor adjustments to the treatment regimen. However, if they persist or worsen, patients should consult their healthcare provider.Severe Side Effects of Doxycycline
Managing Doxycycline Side Effects
Managing side effects of doxycycline often involves a combination of patient education, lifestyle adjustments, and, in some cases, additional medications. For example, taking doxycycline with food can help minimize gastrointestinal upset, while avoiding sun exposure and using protective measures such as sunscreen and clothing can reduce the risk of photosensitivity. In cases where side effects are severe or persistent, healthcare providers may need to adjust the treatment regimen or consider alternative antibiotics.Doxycycline Interactions and Precautions
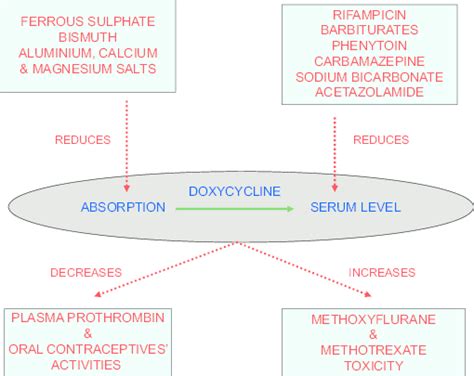
Patient Considerations
Certain patient populations may require special consideration when taking doxycycline. These include: - Pregnant women: Doxycycline is generally contraindicated in pregnancy due to the risk of inhibiting bone growth and causing tooth discoloration in the fetus. - Nursing mothers: While doxycycline is excreted in breast milk, the risk to the infant is considered low, but breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider. - Children: The use of doxycycline in children under 8 years old is typically avoided due to the risk of tooth discoloration and inhibition of bone growth.Doxycycline Resistance and Stewardship
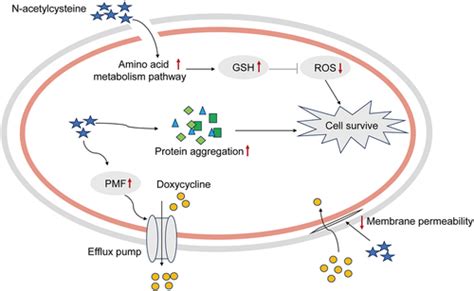
Future Directions
The future of doxycycline and other antibiotics hinges on our ability to balance their use with the need to combat antibiotic resistance. This involves ongoing research into new antibiotics and alternative treatments, as well as public health initiatives to reduce the spread of infections and promote antibiotic stewardship. By working together, healthcare providers, patients, and policymakers can ensure that doxycycline remains a valuable tool in the fight against bacterial infections.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with doxycycline in the comments below. Have you taken doxycycline for a bacterial infection? What were your experiences with side effects, and how did you manage them? Your insights can help others who may be considering doxycycline as a treatment option. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information.
What are the most common side effects of doxycycline?
+The most common side effects of doxycycline include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, photosensitivity, headache, dizziness, and fatigue.
Can doxycycline cause allergic reactions?
+Yes, doxycycline can cause allergic reactions, ranging from mild skin rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis. If you experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction, seek medical attention immediately.
How can I minimize the risk of side effects when taking doxycycline?
+To minimize the risk of side effects, take doxycycline with food, avoid sun exposure, and stay hydrated. Also, inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and vitamins you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
