Intro
Discover fascinating 5 Blood Facts, exploring blood types, donation, and circulation, revealing surprising blood pressure and hemoglobin insights, and shedding light on blood health and its vital functions.
The human body is a complex and fascinating machine, and one of its most vital components is blood. Blood is the fluid that circulates through our veins, arteries, and capillaries, delivering oxygen and nutrients to our cells and removing waste products. Despite its importance, many of us take blood for granted, unaware of its remarkable properties and functions. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood, exploring its composition, functions, and some fascinating facts that will leave you in awe.
Blood is often referred to as the "river of life" because of its crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. It is a specialized fluid that is composed of several components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Each of these components plays a vital role in maintaining our bodily functions, from transporting oxygen to fighting off infections. The unique composition of blood allows it to perform a wide range of functions, from regulating body temperature to maintaining healthy skin and muscles.
The study of blood is a fascinating field that has led to numerous breakthroughs in medical science. From the discovery of blood types to the development of blood transfusions, our understanding of blood has revolutionized the way we approach healthcare. Today, blood donations are a crucial part of medical care, with millions of people relying on donated blood to survive. Despite the importance of blood donations, many people are unaware of the process and the benefits it provides. In this article, we will explore the world of blood, discussing its composition, functions, and some fascinating facts that will leave you with a newfound appreciation for this vital fluid.
Blood Composition
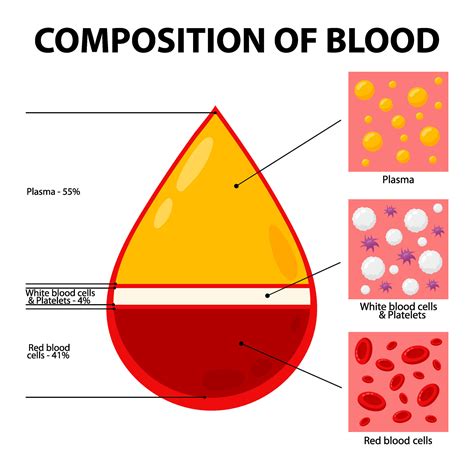
The composition of blood is carefully balanced to ensure that it can perform its various functions. The average adult has approximately 5 liters of blood, which is composed of 55% plasma and 45% blood cells. The plasma component of blood is mostly made up of water, with small amounts of proteins, nutrients, and hormones. The blood cells, on the other hand, are produced in the bone marrow and have a limited lifespan, ranging from a few days to several months.
Blood Functions
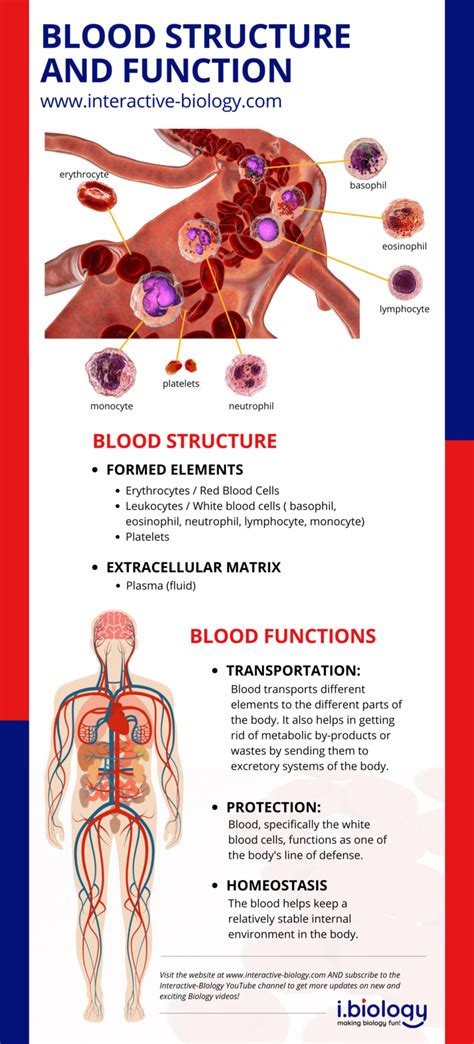
In addition to transporting oxygen, blood also plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature. The blood vessels near the surface of the skin constrict or dilate to conserve or release heat, helping to maintain a stable body temperature. Blood also helps to maintain healthy skin and muscles by transporting nutrients and oxygen to these tissues. The white blood cells in the blood help to fight off infections and diseases, while the platelets help to prevent excessive bleeding by forming blood clots.
Blood Types
Blood types are classified into four main groups: A, B, AB, and O. These blood types are determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. Antigens are substances that can trigger an immune response, and the immune system will attack any foreign substance that it recognizes as a threat. The ABO blood group system is the most important blood group system in transfusion medicine, as it determines the compatibility of blood transfusions.The Rh blood type system is another important blood group system that is used to classify blood types. The Rh system is based on the presence or absence of the RhD antigen on the surface of red blood cells. Individuals who have the RhD antigen are classified as Rh-positive, while those who do not have the antigen are classified as Rh-negative. The Rh blood type system is important in transfusion medicine, as it can help to prevent the transmission of Rh incompatibility, a condition that can occur when an Rh-negative individual is exposed to Rh-positive blood.
Blood Donation
The benefits of blood donation are numerous, not only for the recipients but also for the donors themselves. Donating blood can help to reduce the risk of heart disease and cancer, as it can help to lower the levels of iron in the blood. Donating blood can also help to improve cardiovascular health, as it can help to increase the production of new red blood cells. Additionally, donating blood can provide a sense of satisfaction and fulfillment, knowing that you are helping to save lives.
Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a medical procedure that involves transferring blood from a donor into the bloodstream of a recipient. Blood transfusions are used to treat a wide range of medical conditions, from anemia and cancer to surgery and trauma. The blood transfusion process is carefully monitored to ensure that the recipient receives the correct type and amount of blood.The risks associated with blood transfusions are relatively low, but they can include allergic reactions, transfusion-related acute lung injury, and transfusion-associated circulatory overload. To minimize these risks, blood banks and hospitals take numerous precautions, including testing the blood for infectious diseases and ensuring that the recipient receives the correct type and amount of blood.
Blood Disorders

Anemia is a condition characterized by a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood. This can lead to fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, are conditions that affect the blood's ability to clot, leading to excessive bleeding. Blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma, are conditions that affect the blood and blood-forming tissues, leading to an overproduction of abnormal blood cells.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the blood and its components. These tests can help to diagnose a wide range of medical conditions, from anemia and infection to cancer and bleeding disorders. Some common blood tests include complete blood counts, blood chemistry tests, and blood clotting tests.Complete blood counts are tests that measure the levels of different blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Blood chemistry tests are tests that measure the levels of various substances in the blood, including electrolytes, enzymes, and hormones. Blood clotting tests are tests that evaluate the blood's ability to clot, helping to diagnose bleeding disorders and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Blood and the Immune System
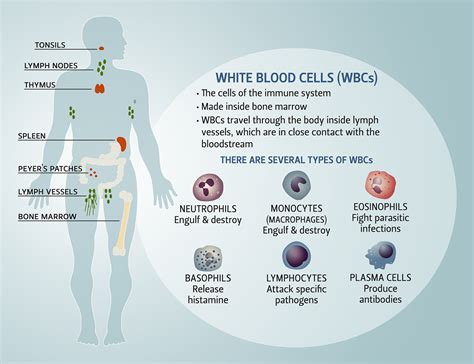
The immune system is made up of two main branches: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The innate immune system is the body's first line of defense, providing immediate protection against infection. The adaptive immune system is a more specific response, providing long-term protection against infection. Blood helps to support both branches of the immune system, providing the necessary cells, proteins, and nutrients to fight off infection and disease.
Immune System Disorders
Immune system disorders are conditions that affect the immune system, leading to an overactive or underactive response. Some common immune system disorders include autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency diseases, and allergic reactions. Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. Immunodeficiency diseases, such as HIV/AIDS, occur when the immune system is weakened, making it difficult for the body to fight off infection. Allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, occur when the immune system overreacts to a harmless substance.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We encourage you to share this article with others, helping to raise awareness about the importance of blood and blood donations. If you are eligible to donate blood, we encourage you to do so, as your donation can help to save lives. Additionally, we invite you to comment below, sharing your thoughts and experiences related to blood and blood donations.
What is the importance of blood in the human body?
+Blood is a vital component of the human body, playing a critical role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. It transports oxygen and nutrients to our cells, removes waste products, and helps to regulate body temperature.
What are the different components of blood?
+Blood is composed of several components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Each of these components plays a vital role in maintaining our bodily functions.
Why is blood donation important?
+Blood donation is important because it helps to save millions of lives each year. Donated blood is used to treat a wide range of medical conditions, from anemia and cancer to surgery and trauma.
What are the benefits of donating blood?
+The benefits of donating blood include reducing the risk of heart disease and cancer, improving cardiovascular health, and providing a sense of satisfaction and fulfillment.
How often can I donate blood?
+The frequency at which you can donate blood depends on several factors, including your age, weight, and medical history. Generally, you can donate blood every 56 days, but this may vary depending on your individual circumstances.
