Intro
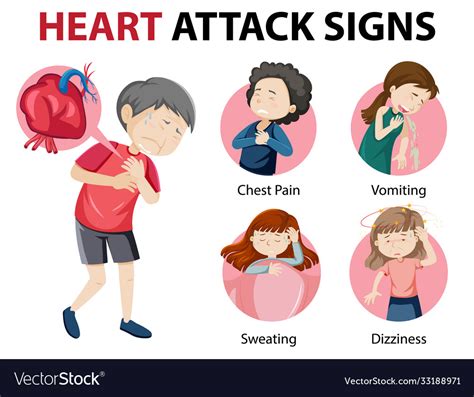
Identify early signs of heart attack, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue, to prevent cardiac arrest and coronary disease, and learn symptoms, risks, and treatment options for a healthy heart.
Recognizing the early signs of a heart attack is crucial for prompt medical attention and treatment. A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. The early detection of a heart attack can significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. In this article, we will delve into the importance of identifying early signs of a heart attack and provide valuable information on the symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
The importance of recognizing early signs of a heart attack cannot be overstated. According to the American Heart Association, approximately 735,000 Americans suffer a heart attack each year, and about 120,000 of these individuals die as a result. The key to reducing this mortality rate lies in prompt recognition and treatment of heart attack symptoms. By being aware of the early warning signs, individuals can seek medical attention immediately, reducing the risk of long-term damage and improving their chances of survival.
Heart attacks can occur suddenly, but they often develop over time, with subtle symptoms that may be easily overlooked. It is essential to be aware of these early signs to take prompt action and prevent further damage. Some common early signs of a heart attack include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, and fatigue. These symptoms can be mild or severe and may come and go, making it challenging to diagnose a heart attack. However, by understanding the causes and risk factors associated with heart attacks, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and recognize the early warning signs.
Understanding Heart Attack Symptoms
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of a heart attack are complex and multifaceted. Some of the most common causes include: * Coronary artery disease: This occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart. * Blood clots: A blood clot can form in the coronary arteries, blocking blood flow to the heart. * Spontaneous coronary artery dissection: This occurs when the inner layer of the coronary artery tears, causing a blockage. * Heart conditions: Certain heart conditions, such as cardiomyopathy or heart valve problems, can increase the risk of a heart attack.Diagnosing a Heart Attack

Treatment Options
The treatment options for a heart attack depend on the severity of the attack and the individual's overall health. Some common treatment options include: * Medications: Medications such as aspirin, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors can help reduce the risk of further complications. * Angioplasty: This procedure involves inserting a catheter into the blocked artery to restore blood flow to the heart. * Thrombolytic therapy: This treatment involves administering medications to dissolve blood clots that are blocking the coronary arteries. * Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): This surgery involves bypassing the blocked artery to restore blood flow to the heart.Prevention and Lifestyle Changes

Managing Risk Factors
Managing risk factors is essential for preventing a heart attack. Some common risk factors include: * High blood pressure: High blood pressure can increase the risk of heart disease, and managing it through lifestyle changes and medications can help reduce this risk. * High cholesterol: High cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease, and managing it through lifestyle changes and medications can help reduce this risk. * Diabetes: Diabetes can increase the risk of heart disease, and managing it through lifestyle changes and medications can help reduce this risk.Conclusion and Next Steps

We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, please seek medical attention immediately. By raising awareness and promoting education, we can work together to reduce the risk of heart attacks and improve treatment outcomes.
What are the most common symptoms of a heart attack?
+The most common symptoms of a heart attack include chest discomfort or pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Other symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, as well as lightheadedness or dizziness.
How can I reduce my risk of a heart attack?
+Reducing your risk of a heart attack requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Quitting smoking, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and managing stress can all help reduce your risk. Additionally, managing risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes can also help reduce your risk.
What should I do if I think I am having a heart attack?
+If you think you are having a heart attack, call emergency services immediately. Symptoms of a heart attack can be mild or severe, and it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Do not drive yourself to the hospital, as this can increase your risk of complications.
