Intro
Identify 5 Sjögrens warning signs, including dry eyes and mouth, fatigue, and joint pain, to detect this autoimmune disorder early, managing symptoms like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis overlaps, for timely treatment and relief.
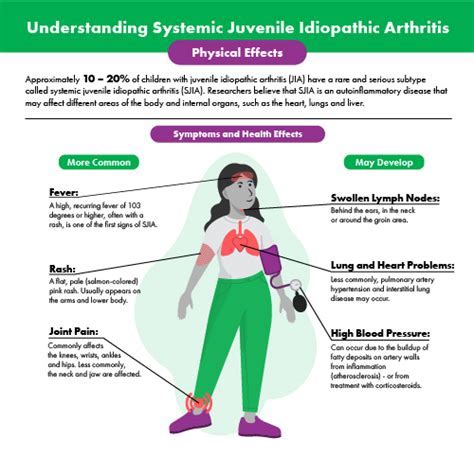
Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (sJIA) is a rare and chronic autoimmune disease that affects children under the age of 16. It is characterized by inflammation in the joints, skin, and internal organs, and can be a challenging condition to diagnose and manage. Recognizing the warning signs of sJIA is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve the quality of life for affected children. In this article, we will delve into the 5 SJS warning signs, exploring the symptoms, causes, and management of this complex condition.
The importance of early recognition and diagnosis of sJIA cannot be overstated. If left untreated, sJIA can lead to serious complications, including joint damage, growth retardation, and even life-threatening conditions such as macrophage activation syndrome (MAS). MAS is a rare but potentially fatal complication of sJIA, characterized by excessive activation of the immune system, which can lead to organ failure. Therefore, it is essential for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to be aware of the warning signs of sJIA and seek medical attention promptly if they suspect that a child may be affected.
The diagnosis of sJIA can be challenging, as the symptoms can be non-specific and similar to those of other conditions. However, by being aware of the common warning signs and seeking medical attention early, it is possible to diagnose and manage sJIA effectively. In this article, we will explore the 5 SJS warning signs, including fever, rash, joint pain and swelling, eye inflammation, and lymphadenopathy. We will also discuss the causes, management, and treatment options for sJIA, as well as provide practical advice and support for families affected by this condition.
Introduction to sJIA
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of sJIA is unknown, but it is believed to be a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing sJIA, and environmental triggers such as infections or trauma may also play a role. Additionally, sJIA is more common in children with a family history of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.Warning Sign 1: Fever

Managing Fever in sJIA
Managing fever in sJIA requires a comprehensive approach, including medication, rest, and hydration. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce fever and alleviate pain. Additionally, corticosteroids such as prednisone may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.Warning Sign 2: Rash

Managing Rash in sJIA
Managing rash in sJIA requires a gentle and comprehensive approach, including topical creams, ointments, and medications. Topical corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone can help reduce inflammation and alleviate itching. Additionally, oral medications such as antihistamines or corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.Warning Sign 3: Joint Pain and Swelling

Managing Joint Pain and Swelling in sJIA
Managing joint pain and swelling in sJIA requires a comprehensive approach, including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. Additionally, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression.Warning Sign 4: Eye Inflammation

Managing Eye Inflammation in sJIA
Managing eye inflammation in sJIA requires a comprehensive approach, including medication, rest, and hydration. Topical corticosteroids such as prednisolone can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Additionally, oral medications such as corticosteroids or DMARDs may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.Warning Sign 5: Lymphadenopathy
Managing Lymphadenopathy in sJIA
Managing lymphadenopathy in sJIA requires a comprehensive approach, including medication, rest, and hydration. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. Additionally, corticosteroids such as prednisone may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.What is the prognosis for children with sJIA?
+The prognosis for children with sJIA varies depending on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. With early diagnosis and aggressive treatment, many children with sJIA can achieve remission and lead active, healthy lives.
How is sJIA diagnosed?
+sJIA is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The diagnosis is typically made by a pediatric rheumatologist, who will perform a thorough physical examination, take a complete medical history, and order laboratory tests such as blood work and imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for sJIA?
+The treatment options for sJIA include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Medications such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and DMARDs can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Physical therapy can help improve mobility and strength, while lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and a healthy diet can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
Can sJIA be prevented?
+There is currently no known way to prevent sJIA, as the exact cause of the disease is unknown. However, early recognition and diagnosis of the disease can help improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
What is the role of the family in managing sJIA?
+The family plays a critical role in managing sJIA, as they can provide emotional support, help with medication management, and assist with lifestyle modifications. Families can also work with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan and make informed decisions about their child's care.
In conclusion, recognizing the warning signs of sJIA is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve the quality of life for affected children. By being aware of the common warning signs, including fever, rash, joint pain and swelling, eye inflammation, and lymphadenopathy, parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals can work together to diagnose and manage sJIA effectively. We encourage readers to share this article with others, and to comment below with any questions or concerns about sJIA. Together, we can raise awareness and improve outcomes for children affected by this complex and challenging condition.
