Intro
Learn about Elevated CO2 in Blood Levels, a condition linked to Respiratory Acidosis, Hypercapnia, and Carbon Dioxide Toxicity, affecting Oxygen Levels and pH Balance, requiring prompt Medical Attention and Treatment.
Elevated CO2 levels in the blood, also known as hypercapnia, can have significant effects on the human body. The importance of maintaining normal CO2 levels cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including respiration, circulation, and nervous system function. When CO2 levels become elevated, it can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and even life-threatening conditions if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the world of elevated CO2 levels, exploring the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available.
The human body is designed to maintain a delicate balance of gases, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. CO2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism, and its levels are tightly regulated by the respiratory and circulatory systems. When CO2 levels rise, it can lead to a range of problems, including respiratory acidosis, which can cause the blood to become more acidic. This, in turn, can lead to a range of symptoms, including shortness of breath, headaches, and confusion. In severe cases, elevated CO2 levels can lead to coma, seizures, and even death.
Elevated CO2 levels can be caused by a range of factors, including respiratory problems, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and asthma. Other causes include circulatory problems, such as heart failure, and neurological disorders, such as stroke and spinal cord injuries. Additionally, certain medications, such as sedatives and opioids, can also contribute to elevated CO2 levels. Understanding the causes of elevated CO2 levels is crucial in developing effective treatment strategies and preventing long-term damage to the body.
Causes of Elevated CO2 Levels
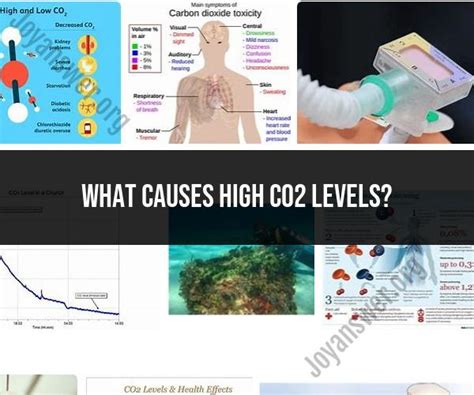
Respiratory Problems
Respiratory problems are a common cause of elevated CO2 levels. Conditions such as COPD, pneumonia, and asthma can lead to impaired gas exchange, resulting in elevated CO2 levels. These conditions can cause the lungs to become less efficient at removing CO2 from the blood, leading to a buildup of CO2. Other respiratory problems, such as cystic fibrosis and pulmonary embolism, can also contribute to elevated CO2 levels.Circulatory Problems
Circulatory problems, such as heart failure, can also lead to elevated CO2 levels. When the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, it can lead to a buildup of CO2 in the blood. Other circulatory problems, such as shock and cardiac arrest, can also contribute to elevated CO2 levels.Symptoms of Elevated CO2 Levels

Mild Symptoms
Mild cases of elevated CO2 levels may cause symptoms such as: * Shortness of breath * Headaches * Confusion * Dizziness * Nausea and vomitingSevere Symptoms
More severe cases of elevated CO2 levels can cause symptoms such as: * Seizures * Coma * Death * Respiratory failure * Cardiac arrestDiagnosis of Elevated CO2 Levels

Blood Gas Analysis
Blood gas analysis is a crucial test in diagnosing elevated CO2 levels. It measures the levels of oxygen and CO2 in the blood, as well as the pH level. This test can help identify respiratory acidosis, which is a common complication of elevated CO2 levels.Pulmonary Function Tests
Pulmonary function tests assess lung function and can help identify underlying respiratory problems that may be contributing to elevated CO2 levels. These tests measure lung volume, capacity, and flow rates.Treatment of Elevated CO2 Levels
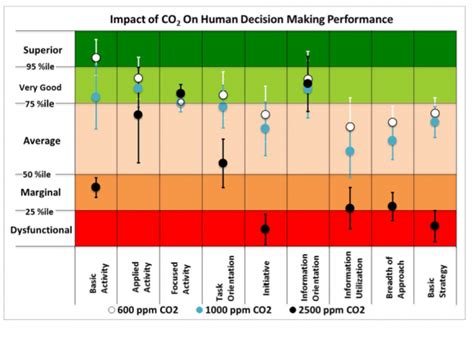
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms and address underlying conditions. These may include bronchodilators, which help open up airways, and diuretics, which help remove excess fluid from the body.Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy may be necessary to help increase oxygen levels in the blood. This can involve supplemental oxygen, which is delivered through a mask or nasal tube.Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to pollutants, can help reduce the risk of developing elevated CO2 levels. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can also help improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications.Prevention of Elevated CO2 Levels
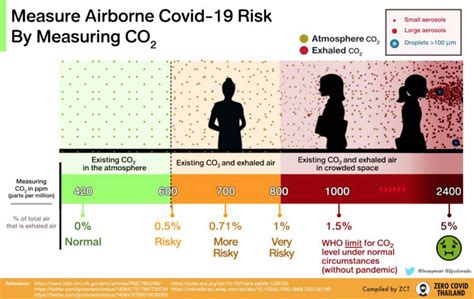
Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking is a crucial step in preventing elevated CO2 levels. Smoking can damage the lungs and increase the risk of developing respiratory problems, which can lead to elevated CO2 levels.Avoiding Exposure to Pollutants
Avoiding exposure to pollutants, such as air pollution and chemicals, can help reduce the risk of developing elevated CO2 levels. This may involve wearing a mask when outdoors, avoiding strong chemicals, and using air purifiers in the home.Regular Exercise and Healthy Diet
Engaging in regular exercise and eating a healthy diet can help improve overall health and reduce the risk of developing elevated CO2 levels. This may involve eating a balanced diet, engaging in aerobic exercise, and practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation and yoga.What are the symptoms of elevated CO2 levels?
+The symptoms of elevated CO2 levels can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but may include shortness of breath, headaches, confusion, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, seizures, coma, and even death.
How are elevated CO2 levels diagnosed?
+Elevated CO2 levels are diagnosed through a range of tests, including blood gas analysis, pulmonary function tests, and imaging studies, such as chest X-rays and CT scans.
How are elevated CO2 levels treated?
+Treating elevated CO2 levels involves addressing the underlying cause of the condition, which may include medications, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to pollutants, and engaging in regular exercise and a healthy diet.
Can elevated CO2 levels be prevented?
+Yes, elevated CO2 levels can be prevented by addressing underlying conditions and making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to pollutants, and engaging in regular exercise and a healthy diet.
What are the complications of elevated CO2 levels?
+The complications of elevated CO2 levels can include respiratory acidosis, respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and even death.
In conclusion, elevated CO2 levels can have significant effects on the human body, and it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available. By addressing underlying conditions and making lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing elevated CO2 levels and prevent long-term damage to the body. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with elevated CO2 levels in the comments section below and to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this important topic.
