Intro
Elevated glucose levels impact overall health, causing diabetes, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, affecting cardiovascular, kidney, and nerve function, and increasing risk of complications like heart disease and stroke.
Elevated glucose levels can have a significant impact on overall health, affecting various bodily systems and increasing the risk of developing chronic diseases. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the primary source of energy for cells, and its regulation is crucial for maintaining proper bodily functions. When glucose levels become elevated, either due to diabetes, insulin resistance, or other factors, it can lead to a range of health complications. In this article, we will delve into the effects of elevated glucose on health, exploring the mechanisms, symptoms, and long-term consequences of high glucose levels.
The importance of maintaining healthy glucose levels cannot be overstated. Elevated glucose can affect not only physical health but also mental well-being, quality of life, and life expectancy. The good news is that many cases of elevated glucose can be managed through lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress reduction. By understanding the impact of elevated glucose on health, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or mitigate its effects, reducing the risk of developing related health issues.
Elevated glucose levels can have far-reaching consequences, from mild symptoms like fatigue and thirst to severe complications like organ damage and increased risk of infections. The effects of high glucose can be both immediate and long-term, making it essential to address the issue promptly. Whether you are at risk of developing diabetes, are already living with the condition, or simply want to maintain optimal health, understanding the implications of elevated glucose is crucial. This knowledge can empower you to make informed decisions about your health, lifestyle, and the steps you can take to prevent or manage elevated glucose levels.
Introduction to Elevated Glucose
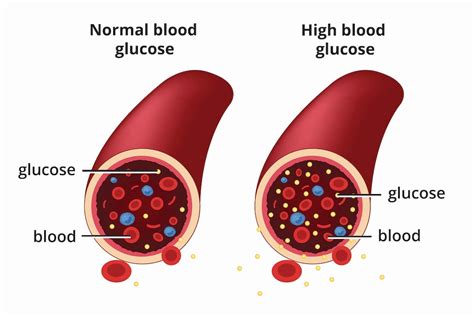
Causes of Elevated Glucose
The causes of elevated glucose can be broadly categorized into two main types: type 1 diabetes, where the body's immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, and type 2 diabetes, where the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance. Other factors, such as gestational diabetes during pregnancy, certain medications, and hormonal imbalances, can also lead to elevated glucose levels. Recognizing these causes can help in the early detection and management of elevated glucose.Effects of Elevated Glucose on Organs
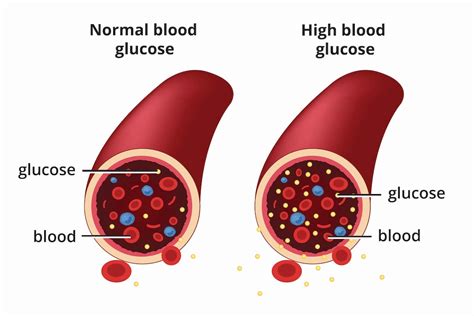
Cardiovascular Risks
One of the most significant risks associated with elevated glucose is the increased likelihood of cardiovascular disease. High glucose levels can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart, leading to atherosclerosis, heart failure, and stroke. The risk of cardiovascular disease is further compounded by other factors often associated with diabetes, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and obesity. Managing elevated glucose, therefore, requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication to control these associated risk factors.Managing Elevated Glucose

Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are at the heart of managing elevated glucose. This includes quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga. Getting enough sleep and maintaining a healthy weight are also critical, as excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can increase insulin resistance. By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing complications associated with elevated glucose.Technological Advances in Glucose Monitoring
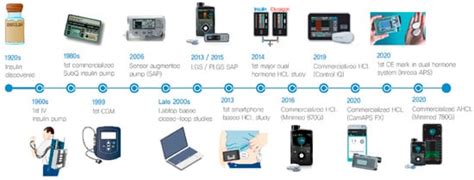
Future Directions
The future of glucose management holds much promise, with ongoing research into new technologies and treatments. The development of artificial pancreas systems, which can automatically adjust insulin doses based on real-time glucose levels, is a significant area of research. Furthermore, advances in diabetes education and support are helping individuals better manage their condition, improving health outcomes and quality of life. As our understanding of diabetes and elevated glucose grows, so too will the array of effective management strategies and treatments.Conclusion and Next Steps

Call to Action
If you or someone you know is living with elevated glucose or diabetes, it is essential to take proactive steps towards management and prevention of complications. This includes scheduling regular health check-ups, adhering to medication regimens, and incorporating healthy lifestyle habits. By taking control of your health and staying informed about the latest developments in glucose management, you can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risks associated with elevated glucose.What are the symptoms of elevated glucose?
+Common symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How can I manage elevated glucose through diet?
+Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats but high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate glucose levels.
What role does physical activity play in managing elevated glucose?
+Regular physical activity, such as walking, can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and helping to manage elevated glucose levels.
