Intro
Discover 5 ways an elevated sedimentation rate affects health, including inflammation, infection, and autoimmune disorders, and learn how to lower ESR levels naturally through diet and lifestyle changes.
Elevated sedimentation rate, also known as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The test is used to detect and monitor various inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis, and to monitor the effectiveness of treatments. An elevated ESR can indicate the presence of inflammation, infection, or other conditions that require medical attention. In this article, we will explore five ways elevated sedimentation rates can impact an individual's health and discuss the importance of understanding and managing this condition.
The sedimentation rate is influenced by several factors, including the presence of inflammatory proteins, the concentration of red blood cells, and the overall health of the individual. When the body is experiencing inflammation, the liver produces more inflammatory proteins, which cause red blood cells to clump together and settle more quickly. This results in an elevated ESR. Inflammation can be caused by various factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and injuries. It is essential to identify and address the underlying cause of elevated ESR to prevent long-term damage and complications.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system, but chronic inflammation can lead to various health problems. Elevated sedimentation rates can be an indication of underlying conditions that require medical attention. For instance, an elevated ESR can be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, as inflammation in the blood vessels can lead to the formation of plaques and narrowed arteries. Additionally, elevated ESR has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Understanding the causes and consequences of elevated sedimentation rates can help individuals take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of complications.
Understanding Elevated Sedimentation Rate
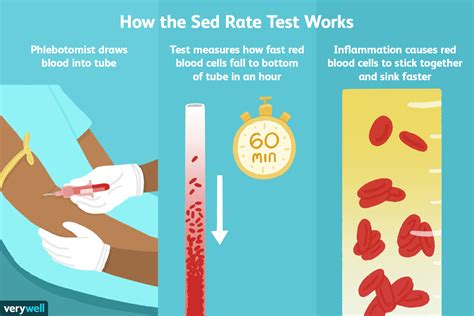
Causes of Elevated Sedimentation Rate
There are several causes of elevated sedimentation rate, including: * Infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis * Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus * Inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis * Cancer, such as lymphoma or multiple myeloma * Injuries or trauma, such as fractures or surgery It is crucial to identify the underlying cause of elevated ESR to provide appropriate treatment and management.Health Implications of Elevated Sedimentation Rate

Managing Elevated Sedimentation Rate
Managing elevated sedimentation rate requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying cause of inflammation. This may involve: * Medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids, to reduce inflammation * Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, to reduce inflammation and promote overall health * Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or meditation, to reduce stress and promote relaxation It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan that addresses the underlying cause of elevated ESR.5 Ways Elevated Sedimentation Rate Can Impact Health

Importance of Monitoring Elevated Sedimentation Rate
Monitoring elevated sedimentation rate is crucial to managing inflammation and preventing long-term damage. Regular ESR tests can help healthcare providers: * Monitor the effectiveness of treatments * Identify potential complications or comorbidities * Adjust treatment plans as needed It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized monitoring plan that addresses the underlying cause of elevated ESR.Practical Tips for Managing Elevated Sedimentation Rate

Conclusion and Next Steps
Elevated sedimentation rate is a non-specific indicator of inflammation that requires further investigation to determine the underlying cause. Managing elevated ESR requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying cause of inflammation. By understanding the causes and consequences of elevated sedimentation rate, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of complications. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan that addresses the underlying cause of elevated ESR.What is an elevated sedimentation rate?
+An elevated sedimentation rate is a non-specific indicator of inflammation, meaning that it can be elevated in various conditions.
What are the causes of elevated sedimentation rate?
+The causes of elevated sedimentation rate include infections, autoimmune disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, cancer, and injuries or trauma.
How can elevated sedimentation rate be managed?
+Elevated sedimentation rate can be managed through medications, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or meditation.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of elevated sedimentation rate and its impact on health. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about elevated sedimentation rate and its management. Take the first step towards managing your health and reducing the risk of complications by consulting with a healthcare provider today.
