Intro
Discover how enlarged glands impact overall health, causing swelling, pain, and infection, affecting lymph nodes, salivary, and thyroid glands, leading to discomfort and potential complications, explore 5 ways enlarged glands hurt and their symptoms.
The human body is made up of various systems, each playing a crucial role in maintaining overall health. One such system is the lymphatic system, which comprises lymph nodes, spleen, and lymphoid tissues. Lymph nodes, also known as glands, are small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph fluid, trapping bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances. However, when these glands become enlarged, it can be a sign of an underlying issue. Enlarged glands, also known as swollen lymph nodes, can be painful and may indicate a range of health problems. In this article, we will delve into the world of enlarged glands, exploring the various ways they can hurt and what it might mean for your health.
Enlarged glands can be a cause for concern, as they often signal that the body is fighting an infection or disease. The swelling can be due to various reasons, including viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, or even cancer. When glands become enlarged, they can put pressure on surrounding tissues and nerves, leading to discomfort, pain, and other complications. It is essential to understand the causes and effects of enlarged glands to seek proper medical attention and prevent further complications.
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in maintaining the body's immune system, and when it is compromised, it can lead to a range of health issues. Enlarged glands can be a symptom of a more significant problem, and it is crucial to identify the underlying cause to receive appropriate treatment. In some cases, enlarged glands may be a sign of a minor infection that can be treated with antibiotics or other medications. However, in other cases, it may indicate a more severe condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Understanding Enlarged Glands
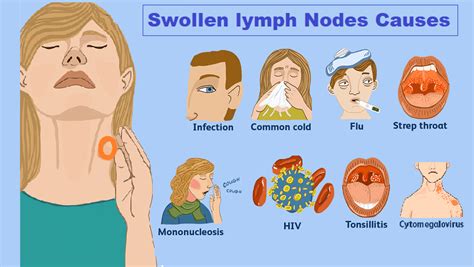
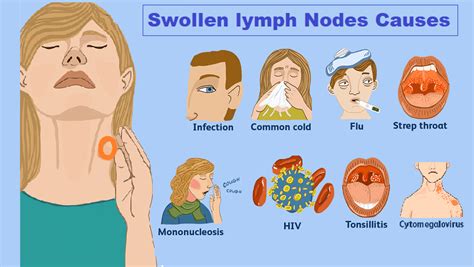
Causes of Enlarged Glands
There are several reasons why glands can become enlarged. Some of the most common causes include: * Viral or bacterial infections, such as the common cold, flu, or strep throat * Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus * Cancer, including lymphoma or leukemia * Infections, such as tuberculosis or cat-scratch disease * Allergic reactions, such as hay fever or allergic contact dermatitis5 Ways Enlarged Glands Can Hurt
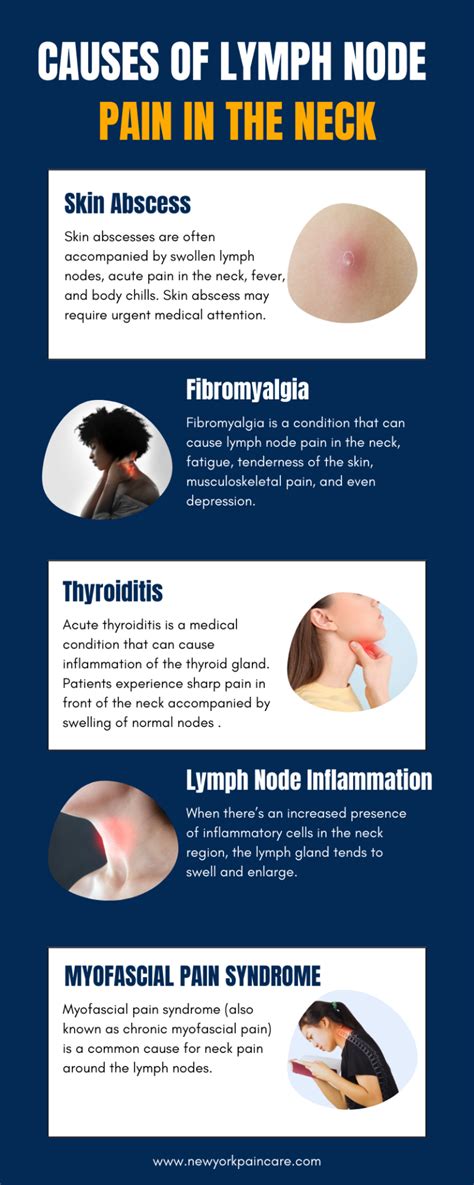
Treatment Options
Treatment for enlarged glands depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, antibiotics or other medications may be prescribed to treat the underlying infection. In other cases, surgery or radiation therapy may be necessary to treat cancer or other conditions. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of enlarged glands, as early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further complications.Diagnosing Enlarged Glands

Prevention and Self-Care
Preventing enlarged glands requires maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, can also help prevent infections. Self-care measures, such as applying warm compresses or taking over-the-counter pain medications, can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.Living with Enlarged Glands
Coping with Emotional Distress
Coping with emotional distress caused by enlarged glands requires a supportive network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals. Seeking counseling or therapy can help individuals cope with anxiety, stress, and depression. Joining support groups or online forums can also provide a sense of community and connection with others who are experiencing similar challenges.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with enlarged glands in the comments section below. Your input can help others who may be going through similar challenges. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
What are the common causes of enlarged glands?
+Common causes of enlarged glands include viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, cancer, and allergic reactions.
How are enlarged glands diagnosed?
+Diagnosing enlarged glands typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging studies, or biopsies.
What are the treatment options for enlarged glands?
+Treatment options for enlarged glands depend on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics, surgery, radiation therapy, or other medications.
Can enlarged glands be prevented?
+While enlarged glands cannot be completely prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing good hygiene, and seeking medical attention early on can help prevent further complications.
What are the emotional effects of living with enlarged glands?
+Living with enlarged glands can cause emotional distress, including anxiety, stress, and depression. Seeking counseling or therapy and joining support groups can help individuals cope with these emotions.
