Intro
Identify 5 key Ecoli symptoms, including diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, to recognize the signs of Ecoli infection, food poisoning, and urinary tract infections, and learn how to prevent and treat this bacterial illness effectively.
The presence of E. coli in the human body can lead to a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. It is essential to understand these symptoms to seek medical attention promptly. E. coli, or Escherichia coli, is a type of bacteria commonly found in the environment, foods, and the intestines of humans and animals. While many strains of E. coli are harmless, some can cause serious food poisoning and infections. Recognizing the symptoms of E. coli infection is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
E. coli infections can manifest differently in different people, but there are common symptoms that many individuals experience. The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary depending on the strain of E. coli, the amount of bacteria ingested, and the individual's overall health. It's also important to note that some people may not show any symptoms at all, even if they are infected with E. coli.
Understanding E. coli symptoms is the first step in managing and treating the infection. By being aware of the signs and symptoms, individuals can take the necessary steps to prevent the spread of the infection and seek medical help if needed. E. coli infections can sometimes lead to severe complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. Therefore, it is vital to take any suspected E. coli infection seriously and consult a healthcare professional.
Introduction to E. coli Symptoms

Common E. coli Symptoms
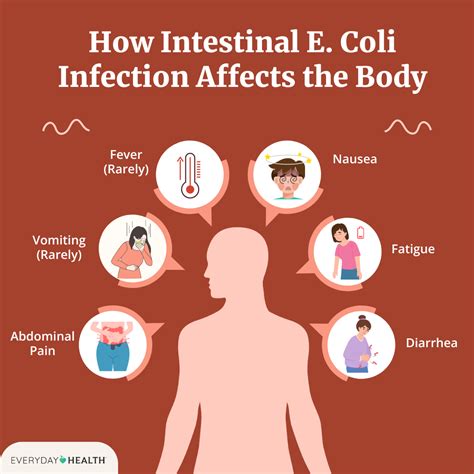
Diarrhea as a Symptom
Diarrhea is one of the most common symptoms of E. coli infection. It can range from mild, watery stools to severe, bloody diarrhea. The presence of blood in the stool is a sign of a more severe infection and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Diarrhea can lead to dehydration, especially in vulnerable populations, so it's essential to drink plenty of fluids to replace lost electrolytes and water.Severe E. coli Symptoms

Complications of E. coli Infections
Complications of E. coli infections can be severe and long-lasting. One of the most significant complications is the development of hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), which is characterized by the destruction of red blood cells, low platelet count, and kidney failure. HUS can lead to permanent kidney damage and requires intensive medical care. Other complications may include neurological problems, such as seizures and stroke, due to the toxins produced by the bacteria.Diagnosing E. coli Infections
Treatment Options for E. coli Infections
Treatment for E. coli infections usually focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. For mild cases, treatment may involve: - Rest and hydration to replace lost fluids and electrolytes - Over-the-counter medications to manage diarrhea and abdominal pain - Dietary changes to help manage symptoms For severe cases or those with significant complications, hospitalization may be necessary to provide: - Intravenous fluids and electrolytes - Medications to manage symptoms and prevent further complications - Close monitoring for signs of severe complicationsPreventing E. coli Infections

Public Health Measures
Public health measures play a crucial role in preventing and controlling E. coli outbreaks. These measures may include: - Surveillance and monitoring of E. coli cases and outbreaks - Investigation of outbreaks to identify sources of infection - Implementation of control measures, such as recalling contaminated food products - Education and awareness campaigns to inform the public about E. coli risks and prevention strategiesConclusion and Next Steps

As you consider the information provided, we invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about E. coli symptoms and prevention in the comments below. Your engagement can help others understand the importance of this topic and encourage further discussion on public health issues.
What are the common symptoms of E. coli infection?
+The common symptoms of E. coli infection include diarrhea, abdominal cramping, vomiting, and fever. In severe cases, symptoms can include bloody diarrhea, significant abdominal pain, and signs of dehydration.
How is E. coli infection diagnosed?
+E. coli infection is typically diagnosed through a stool test that checks for the presence of E. coli bacteria. Additional tests, such as blood tests or imaging studies, may be necessary in some cases to rule out other conditions or evaluate the extent of the infection.
What are the prevention strategies for E. coli infections?
+Prevention strategies for E. coli infections include practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, avoiding undercooked or raw ground beef, unpasteurized juices, and raw sprouts, and ensuring that water used for drinking, cooking, and personal hygiene is safe and not contaminated.
What are the complications of E. coli infections?
+The complications of E. coli infections can be severe and include hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), a type of kidney failure, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), a blood disorder, and septicemia, or bacteria in the blood. These complications can lead to long-term health issues and require intensive medical care.
How can I reduce my risk of getting an E. coli infection?
+You can reduce your risk of getting an E. coli infection by following safe food handling practices, avoiding contaminated water, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding close contact with anyone who has an E. coli infection. Staying informed about E. coli outbreaks and taking preventive measures can also help reduce your risk.
