Intro
Learn about Ezetimibe 10mg Tablets, a cholesterol-lowering medication, and its uses, benefits, and side effects, including hypercholesterolemia treatment and lipid management.
Ezetimibe 10mg tablets have become a crucial medication in the management of high cholesterol levels, a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. High cholesterol, or hypercholesterolemia, affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to serious health issues, including heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. The importance of managing cholesterol levels cannot be overstated, and medications like ezetimibe play a vital role in this process. Understanding how ezetimibe works, its benefits, and its potential side effects is essential for individuals considering this treatment option.
The management of high cholesterol involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication. Lifestyle modifications include dietary changes, increased physical activity, weight management, and quitting smoking. However, for many individuals, these changes alone are not sufficient to achieve desirable cholesterol levels, and that's where medications like ezetimibe come into play. Ezetimibe is particularly useful because it works through a different mechanism than statins, which are the most commonly prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs. This makes it an excellent option for individuals who cannot tolerate statins due to side effects or for those whose cholesterol levels are not adequately controlled by statins alone.
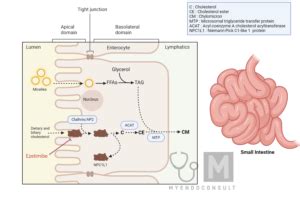
Ezetimibe's role in cholesterol management is unique and valuable. It is a selective inhibitor of intestinal cholesterol absorption, meaning it works by reducing the amount of cholesterol absorbed from the intestine into the bloodstream. By decreasing the absorption of cholesterol, ezetimibe helps lower the levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, which is a major contributor to the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. The effectiveness of ezetimibe in lowering LDL-C levels, combined with its relatively favorable side effect profile, makes it a valuable treatment option for many patients.
Ezetimibe Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Ezetimibe
The benefits of ezetimibe are multifaceted, making it a valuable addition to the arsenal of cholesterol-lowering medications. Some of the key benefits include: - **Effective LDL-C Reduction**: Ezetimibe has been shown to significantly reduce LDL-C levels, which is crucial for reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. - **Complementary to Statins**: Ezetimibe works through a different mechanism than statins, making it an excellent option for use in combination with statins for patients who require additional LDL-C lowering. - **Favorable Safety Profile**: Ezetimibe is generally well-tolerated, with a safety profile that is comparable to placebo in many studies. - **Convenience**: Ezetimibe is administered once daily, which can improve adherence to treatment.Ezetimibe Dosage and Administration

Potential Side Effects
While ezetimibe is generally well-tolerated, like all medications, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include: - Headache - Dizziness - Fatigue - Diarrhea - Abdominal pain - Muscle pain It's essential for patients to discuss any side effects they experience with their healthcare provider, as adjustments to treatment may be necessary.Ezetimibe Interactions and Contraindications

Special Considerations
Special considerations must be taken into account when prescribing ezetimibe, particularly in certain patient populations. For example: - **Pregnancy and Lactation**: Ezetimibe should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as there is limited data on its safety in these populations. - **Pediatric Use**: The safety and efficacy of ezetimibe in pediatric patients have not been established for all indications. - **Geriatric Use**: Ezetimibe is generally well-tolerated in elderly patients, but dose adjustments may be necessary based on renal function.Ezetimibe and Cardiovascular Outcomes

Real-World Evidence
Real-world evidence and observational studies have provided valuable insights into the effectiveness and safety of ezetimibe in diverse patient populations. These studies have generally supported the findings from clinical trials, demonstrating that ezetimibe is effective in lowering LDL-C levels and reducing cardiovascular risk in a broad range of patients.Future Directions and Emerging Therapies

Personalized Medicine
The concept of personalized medicine is becoming increasingly relevant in the field of cholesterol management. With the advent of genetic testing and the identification of specific genetic variants that influence an individual's response to certain medications, healthcare providers can make more informed treatment decisions. This personalized approach may involve the use of ezetimibe in combination with other medications or the selection of ezetimibe as a first-line treatment based on an individual's genetic profile.What is the primary mechanism of action of ezetimibe?
+Ezetimibe works by selectively inhibiting the intestinal absorption of cholesterol, primarily through the inhibition of the Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) protein.
Can ezetimibe be used in combination with statins?
+Yes, ezetimibe can be used in combination with statins. This combination is often used to achieve greater reductions in LDL-C levels than can be achieved with either medication alone.
What are the common side effects of ezetimibe?
+Common side effects of ezetimibe include headache, dizziness, fatigue, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and muscle pain. These side effects are generally mild and temporary.
In conclusion, ezetimibe 10mg tablets represent a valuable treatment option for individuals with high cholesterol, offering a unique mechanism of action and a favorable safety profile. As the field of cholesterol management continues to evolve, the role of ezetimibe is likely to remain significant, particularly in the context of combination therapy and personalized medicine approaches. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with ezetimibe and cholesterol management, and we encourage healthcare providers to consider the benefits of ezetimibe in their treatment strategies for patients with hypercholesterolemia. By working together, we can better manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, improving the health and well-being of individuals worldwide.
