Intro
Discover the fasting test for diabetes, a diagnostic tool using blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and glucose tolerance to detect type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and metabolic syndrome, guiding treatment and prevention strategies.
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to a range of serious health complications if left untreated or poorly managed. One of the most common methods used to diagnose diabetes is the fasting test, also known as the fasting plasma glucose test. In this article, we will delve into the world of fasting tests for diabetes, exploring what they entail, how they work, and what the results mean.
The importance of diagnosing diabetes cannot be overstated. If left undiagnosed or untreated, diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and even blindness. The good news is that diabetes can be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle changes. The first step towards managing diabetes is to get an accurate diagnosis, which is where the fasting test comes in. The fasting test is a simple, non-invasive, and relatively inexpensive method that can help diagnose diabetes and prediabetes.
The fasting test is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as the oral glucose tolerance test and the hemoglobin A1c test. These tests can help healthcare providers determine whether a person has diabetes, prediabetes, or normal blood sugar levels. The fasting test is particularly useful for diagnosing type 2 diabetes, which is the most common form of the disease. Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, which means that the body's cells are unable to respond effectively to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels.
Fasting Test Procedure

How Fasting Test Works
Benefits of Fasting Test
The fasting test has several benefits, including: * It is a simple and non-invasive procedure * It is relatively inexpensive compared to other diagnostic tests * It can help diagnose diabetes and prediabetes * It can help healthcare providers monitor blood sugar levels over time * It can help people with diabetes manage their condition more effectivelyInterpreting Fasting Test Results

Risks and Limitations of Fasting Test

Preparation for Fasting Test
To prepare for the fasting test, people should: * Avoid eating and drinking for at least 8 hours before the test * Avoid strenuous exercise or physical activity before the test * Inform their healthcare provider about any medications or supplements they are taking * Come to the testing facility or healthcare provider's office after an overnight fastAlternative Diagnostic Tests
Managing Diabetes with Fasting Test Results
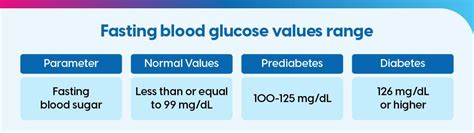
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the fasting test is a valuable diagnostic tool for diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes. By understanding how the test works, interpreting the results, and managing diabetes with the results, people can take control of their health and prevent serious complications. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes or prediabetes, it is essential to work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, people with diabetes can manage their condition effectively and live a long and healthy life.We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with diabetes and the fasting test in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. By working together, we can promote awareness and understanding of diabetes and improve the lives of people living with the condition.
What is the purpose of the fasting test?
+The purpose of the fasting test is to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes by measuring blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
How do I prepare for the fasting test?
+To prepare for the fasting test, avoid eating and drinking for at least 8 hours before the test, avoid strenuous exercise or physical activity, and inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking.
What are the risks and limitations of the fasting test?
+The risks and limitations of the fasting test include dehydration, hypoglycemia, inaccurate results, and limited sensitivity. It is essential to discuss these risks and limitations with your healthcare provider before undergoing the test.
