Intro
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly affects the body's ability to function properly. The normal range for fasting sugar, also known as fasting blood glucose, is a key indicator of how well the body is managing its blood sugar levels. Understanding the importance of fasting sugar levels and their normal range can help individuals take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and preventing potential complications.
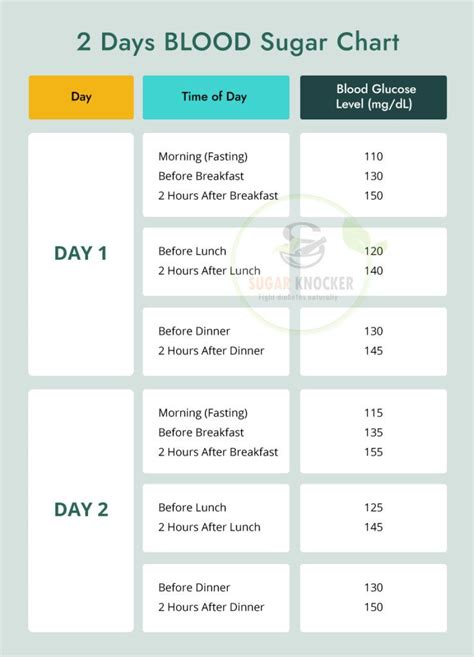
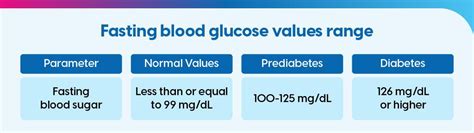
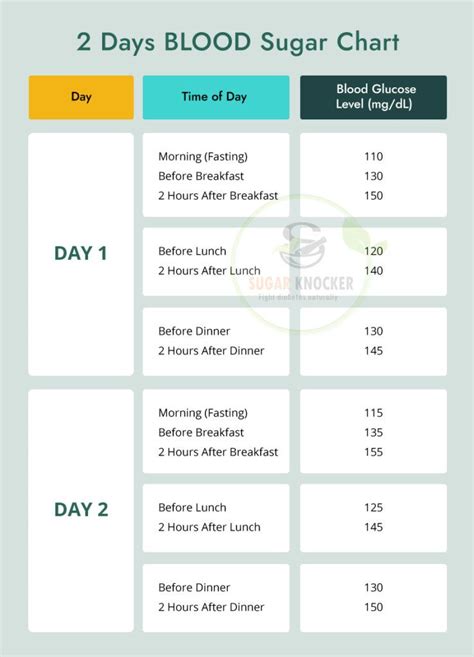
Fasting sugar levels are typically measured after an overnight fast, usually between 8 to 12 hours without food or drink, except for water. This test provides a baseline measurement of blood glucose levels, giving insight into how the body regulates blood sugar when it's not being influenced by recent food consumption. The normal range for fasting blood glucose is generally considered to be between 70 and 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) for people without diabetes. However, these values can slightly vary depending on the laboratory and the specific testing methods used.
The significance of maintaining fasting sugar levels within the normal range cannot be overstated. Elevated fasting glucose levels can indicate impaired fasting glucose or diabetes, conditions that, if left unmanaged, can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Therefore, it's essential for individuals to be aware of their fasting sugar levels and to understand the factors that can influence these levels, such as diet, physical activity, and certain medications.
Understanding Fasting Sugar Levels
Understanding fasting sugar levels involves recognizing the body's natural fluctuations in blood glucose throughout the day. After eating, blood glucose levels rise, and the body releases insulin to help cells absorb glucose for energy. During fasting periods, such as overnight, the body relies on stored glucose (glycogen) and produces glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis to maintain blood sugar levels within a normal range.
Factors Influencing Fasting Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence fasting sugar levels, including: - **Diet:** Consumption of high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods before fasting can elevate fasting glucose levels. - **Physical Activity:** Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, helping to lower fasting glucose levels. - **Sleep:** Poor sleep quality or duration can disrupt hormones that regulate blood sugar, leading to higher fasting glucose levels. - **Stress:** Chronic stress can increase cortisol levels, which can contribute to higher blood sugar levels. - **Medications:** Certain medications, such as steroids and some psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels.Normal Range for Fasting Sugar
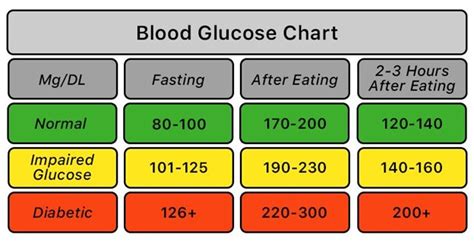
The normal range for fasting sugar is generally considered to be between 70 and 99 mg/dL. Levels within this range indicate that the body is effectively regulating blood glucose levels. However, levels outside this range may indicate potential health issues:
- Levels below 70 mg/dL may indicate hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which can be caused by too much insulin, certain medications, or other medical conditions.
- Levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL are considered impaired fasting glucose, a condition that increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Levels of 126 mg/dL or higher are typically diagnostic of diabetes, indicating that the body is not effectively managing blood sugar levels.
Importance of Monitoring Fasting Sugar Levels
Monitoring fasting sugar levels is crucial for early detection and management of diabetes and prediabetes. Regular monitoring can help individuals: - Identify potential issues before they become severe - Adjust diet and exercise routines to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism - Work with healthcare providers to develop a personalized management planManaging Fasting Sugar Levels
Effective management of fasting sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medication. Key strategies include:
- Dietary Changes: Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, along with muscle-strengthening activities, can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Stress Reduction: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels, which in turn can help regulate blood sugar.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a critical role in helping individuals manage their fasting sugar levels. They can: - Conduct regular blood glucose tests to monitor levels - Provide personalized dietary and exercise advice - Prescribe medications when necessary to help regulate blood sugar - Offer support and resources for lifestyle changes and disease managementFasting Sugar Levels and Overall Health
Maintaining healthy fasting sugar levels is integral to overall health. Elevated fasting glucose levels are associated with an increased risk of several health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Kidney Disease: Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney failure, as high blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys over time.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): High blood sugar can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
- Vision Problems: High blood sugar levels can cause swelling in the lens of the eye, leading to blurred vision, and if left untreated, can cause more severe vision problems.
Prevention and Early Intervention
Preventing elevated fasting sugar levels or intervening early in their development is crucial. Strategies for prevention include: - Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine - Managing stress effectively - Getting enough sleep - Regular health check-ups to monitor blood glucose levelsConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding and managing fasting sugar levels is vital for maintaining overall health and preventing serious health complications. By recognizing the factors that influence fasting glucose, making informed lifestyle choices, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can effectively manage their fasting sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing diabetes and related conditions.
For those looking to take the next step in managing their health, consider the following actions:
- Schedule a health check-up to discuss fasting sugar levels with a healthcare provider
- Start making dietary changes to focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods
- Incorporate regular physical activity into daily routines
- Explore stress reduction techniques to improve overall well-being
What is the normal range for fasting blood glucose?
+The normal range for fasting blood glucose is generally considered to be between 70 and 99 mg/dL.
What can influence fasting sugar levels?
+Factors such as diet, physical activity, sleep, stress, and certain medications can influence fasting sugar levels.
Why is it important to monitor fasting sugar levels?
+Monitoring fasting sugar levels is crucial for early detection and management of diabetes and prediabetes, and for preventing serious health complications.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about fasting sugar levels in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards better health and wellness by understanding and managing fasting sugar levels effectively.
