Intro
Understand FBS level in blood test, also known as fasting blood sugar, to diagnose diabetes, prediabetes, and monitor glucose control, with related terms like blood glucose, insulin resistance, and glycemic index.
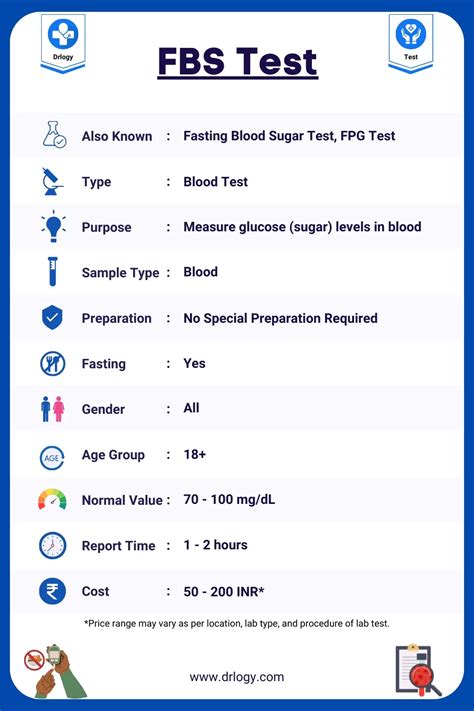
The FBS level in a blood test is a crucial indicator of an individual's health, particularly in relation to their blood sugar levels. FBS stands for Fasting Blood Sugar, which measures the amount of glucose present in the blood after a period of fasting, typically 8-12 hours. This test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor diabetes, as well as to assess the risk of developing the condition. In this article, we will delve into the importance of FBS levels, how they are measured, and what the results can indicate about an individual's health.
The FBS test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that involves drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm. The blood is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the glucose level is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The results of the FBS test can provide valuable insights into an individual's glucose metabolism and help healthcare professionals diagnose and manage diabetes.
FBS Level Ranges
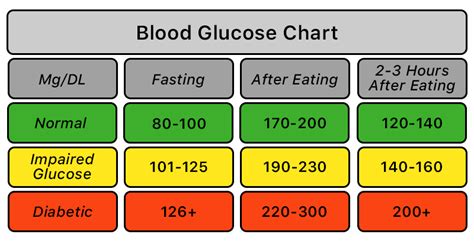
The FBS level ranges can vary depending on the individual and their health status. Generally, a normal FBS level is considered to be between 70-99 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L). Levels above 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) are typically indicative of diabetes, while levels between 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L) may indicate prediabetes or impaired glucose tolerance.
Importance of FBS Testing
FBS testing is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps diagnose and monitor diabetes, a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Secondly, it allows healthcare professionals to assess the risk of developing diabetes and take preventive measures. Finally, FBS testing can help individuals with diabetes manage their condition effectively, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall health outcomes.
Benefits of FBS Testing
The benefits of FBS testing include: * Early detection and diagnosis of diabetes * Monitoring of glucose levels in individuals with diabetes * Assessment of the risk of developing diabetes * Evaluation of the effectiveness of diabetes treatment * Identification of potential complications associated with diabetesFBS Level and Diabetes
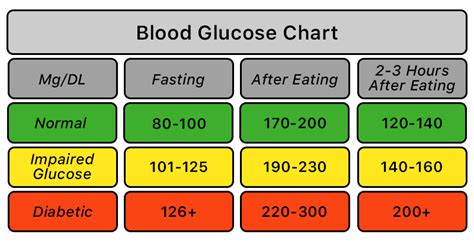
The FBS level is a critical indicator of diabetes. Individuals with diabetes typically have high FBS levels, which can indicate poor glucose control. The American Diabetes Association recommends the following FBS level targets for individuals with diabetes:
- Less than 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L) for adults with type 1 diabetes
- Less than 120 mg/dL (6.7 mmol/L) for adults with type 2 diabetes
- Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) for pregnant women with diabetes
Complications of High FBS Levels
High FBS levels can lead to several complications, including: * Nerve damage (neuropathy) * Kidney damage (nephropathy) * Eye damage (retinopathy) * Foot damage (ulcers and amputations) * Increased risk of heart disease and strokeFBS Level and Prediabetes
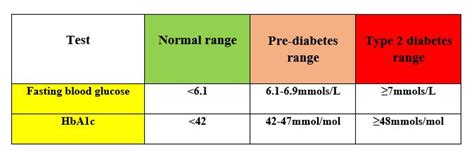
Prediabetes is a condition where the FBS level is higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Individuals with prediabetes are at increased risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The FBS level range for prediabetes is typically between 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L).
Risk Factors for Prediabetes
The risk factors for prediabetes include: * Obesity * Physical inactivity * Family history of diabetes * Age (45 years or older) * Ethnicity (African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, or Asian American)FBS Level and Pregnancy
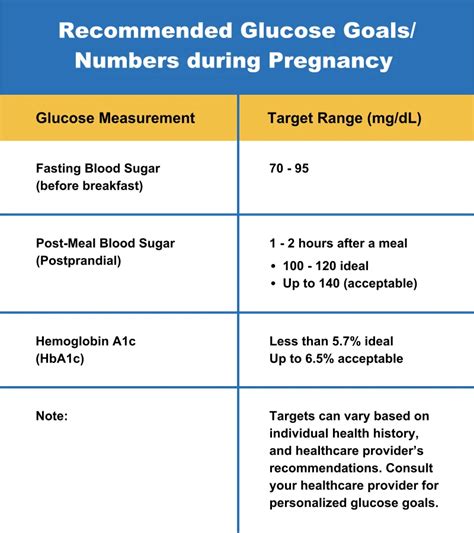
During pregnancy, the FBS level can be affected by hormonal changes and insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes is a condition that develops during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester. The FBS level range for gestational diabetes is typically between 92-153 mg/dL (5.1-8.5 mmol/L).
Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
The risk factors for gestational diabetes include: * Obesity * Family history of diabetes * Previous history of gestational diabetes * Age (35 years or older) * Ethnicity (African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, or Asian American)Managing FBS Levels
Managing FBS levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes or prediabetes. The following strategies can help:
- Healthy eating: focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and limiting sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates
- Regular physical activity: aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week
- Weight management: maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise
- Medication: taking medications as prescribed by a healthcare professional
- Monitoring: regularly monitoring FBS levels and adjusting treatment plans as needed
Benefits of Managing FBS Levels
The benefits of managing FBS levels include: * Improved glucose control * Reduced risk of complications * Enhanced overall health and well-being * Increased energy and productivity * Better quality of lifeWhat is the normal range for FBS levels?
+The normal range for FBS levels is between 70-99 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L).
What are the risk factors for prediabetes?
+The risk factors for prediabetes include obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, age (45 years or older), and ethnicity (African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, or Asian American).
How can I manage my FBS levels?
+Managing FBS levels involves healthy eating, regular physical activity, weight management, medication, and monitoring. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan.
In conclusion, the FBS level is a vital indicator of an individual's health, particularly in relation to their blood sugar levels. By understanding the importance of FBS testing, the benefits of managing FBS levels, and the risk factors for prediabetes and gestational diabetes, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their overall health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with FBS testing and management in the comments below. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns about FBS levels or diabetes, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support.
