Intro
Learn about flu symptoms, remedies, and treatments, including fever reduction, cough relief, and natural therapies to alleviate influenza, cold, and respiratory issues.
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness that affects millions of people worldwide every year. It is caused by the influenza virus, which can spread quickly from person to person through the air, by touching contaminated surfaces, or by coming into contact with someone who has the flu. The symptoms of the flu can be severe and debilitating, making it essential to understand the signs and symptoms of the illness and to know how to manage them effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of flu symptoms and remedies, exploring the best ways to prevent, treat, and recover from the flu.
The flu is a significant public health concern, and its impact can be felt across the globe. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the flu is responsible for up to 5 million cases of severe illness and up to 650,000 deaths worldwide each year. In the United States alone, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that the flu results in approximately 140,000 to 720,000 hospitalizations and 12,000 to 79,000 deaths annually. These statistics highlight the importance of taking the flu seriously and being proactive in preventing its spread.
Understanding the symptoms of the flu is crucial in recognizing when you or a loved one may be infected. The flu typically starts with a sudden onset of symptoms, which can include fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, fatigue, and diarrhea or vomiting. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can last for several days or even weeks. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following: difficulty breathing, chest pain or pressure, severe headache or confusion, or if you are at high risk for complications from the flu, such as older adults, young children, or people with certain chronic health conditions.
Causes And Risk Factors

The flu is caused by the influenza virus, which is spread through the air when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. The virus can also be spread by touching contaminated surfaces or by coming into contact with someone who has the flu. There are several risk factors that can increase your chances of getting the flu, including age, with older adults and young children being at higher risk, certain chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, or diabetes, a weakened immune system, and pregnancy. Understanding these risk factors can help you take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from the flu.
Types Of Flu
The flu comes in several different types, including influenza A, influenza B, and influenza C. Influenza A and B are the most common types of flu and are responsible for the seasonal flu outbreaks that occur every year. Influenza C is a milder form of the flu and is not typically associated with significant outbreaks. There are also several subtypes of influenza A, including H1N1 and H3N2, which can cause more severe illness. Knowing the type of flu you have can help your healthcare provider determine the best course of treatment.Symptoms And Diagnosis
The symptoms of the flu can vary from person to person, but they typically include fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, fatigue, and diarrhea or vomiting. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine if you have the flu. Your healthcare provider may use a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as a rapid influenza diagnostic test (RIDT) or a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test, to diagnose the flu.
Treatment And Management
If you are diagnosed with the flu, there are several treatment options available to help manage your symptoms and prevent complications. These can include antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza), which can help shorten the duration and severity of the flu, over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers and decongestants, which can help relieve symptoms, and rest and hydration, which are essential for helping your body recover from the flu.Prevention And Vaccination

The best way to prevent the flu is to get vaccinated every year. The flu vaccine is available in several different forms, including a shot and a nasal spray, and is recommended for everyone 6 months and older. The vaccine can help protect against the flu by building antibodies in your body that can recognize and fight the virus. In addition to vaccination, there are several other steps you can take to prevent the flu, including practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, avoiding touching your eyes, nose, and mouth, and getting plenty of rest and staying physically active.
Natural Remedies
In addition to medical treatment and vaccination, there are several natural remedies that can help manage flu symptoms and prevent the flu. These can include staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broth, or electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks, using a humidifier to add moisture to the air, which can help relieve congestion and cough, practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, and getting plenty of rest and avoiding overexertion.Complications And High-Risk Groups

The flu can cause several complications, particularly in high-risk groups, such as older adults, young children, and people with certain chronic health conditions. These complications can include pneumonia, bronchitis, sinus and ear infections, and worsening of chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, or diabetes. If you are at high risk for complications from the flu, it is essential to take steps to protect yourself, such as getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, and seeking medical attention if you experience any symptoms of the flu.
Flu Season And Outbreaks
The flu season typically runs from October to May, with the peak season usually occurring between December and February. During this time, the flu can spread quickly, and outbreaks can occur in communities, schools, and workplaces. Understanding the flu season and taking steps to prevent the spread of the flu can help reduce the risk of infection and prevent complications.Flu Vaccination And Its Importance

The flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent the flu and its complications. The vaccine works by building antibodies in your body that can recognize and fight the flu virus. The flu vaccine is recommended for everyone 6 months and older, and it is especially important for high-risk groups, such as older adults, young children, and people with certain chronic health conditions. Getting vaccinated can help prevent the flu, reduce the risk of complications, and protect those around you who may be at high risk for the flu.
Common Flu Myths And Misconceptions
There are several common myths and misconceptions about the flu that can be misleading and confusing. These can include the idea that the flu is just a minor illness, that antibiotics can cure the flu, and that the flu vaccine can give you the flu. Understanding the facts about the flu and separating myth from reality can help you make informed decisions about your health and take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from the flu.Flu Treatment And Recovery
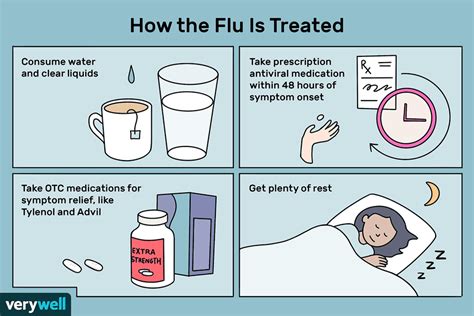
If you are diagnosed with the flu, there are several treatment options available to help manage your symptoms and prevent complications. These can include antiviral medications, over-the-counter medications, and rest and hydration. In addition to medical treatment, there are several steps you can take to help your body recover from the flu, such as staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, and getting plenty of rest. Understanding the treatment options and taking steps to manage your symptoms can help you recover from the flu and prevent complications.
Flu And Mental Health
The flu can have a significant impact on mental health, particularly in people who are already experiencing mental health conditions, such as anxiety or depression. The flu can cause feelings of fatigue, irritability, and isolation, which can exacerbate mental health symptoms. Understanding the connection between the flu and mental health can help you take steps to protect your mental health and seek support if you need it.Future Directions And Research

Researchers are continually working to improve our understanding of the flu and to develop new and effective treatments. This can include the development of new vaccines, antiviral medications, and diagnostic tests. Understanding the latest research and advancements in flu treatment and prevention can help you stay informed and take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from the flu.
Global Flu Surveillance And Response
The flu is a global health concern, and its impact can be felt across the world. Understanding global flu surveillance and response can help you stay informed about flu outbreaks and take steps to protect yourself and your community. This can include staying up-to-date with the latest flu news and developments, practicing good hygiene, and getting vaccinated.What are the symptoms of the flu?
+The symptoms of the flu can include fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, fatigue, and diarrhea or vomiting.
How is the flu diagnosed?
+The flu is typically diagnosed using a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as a rapid influenza diagnostic test (RIDT) or a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test.
What are the complications of the flu?
+The flu can cause several complications, particularly in high-risk groups, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, sinus and ear infections, and worsening of chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, or diabetes.
How can I prevent the flu?
+The best way to prevent the flu is to get vaccinated every year, practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and take steps to stay healthy, such as getting plenty of rest and staying physically active.
What are the treatment options for the flu?
+The treatment options for the flu can include antiviral medications, over-the-counter medications, and rest and hydration. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
In conclusion, the flu is a significant public health concern that can have a substantial impact on individuals and communities. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of the flu is essential in protecting yourself and your loved ones from this illness. By staying informed, getting vaccinated, and taking steps to stay healthy, you can reduce your risk of getting the flu and prevent complications. If you have any questions or concerns about the flu, we encourage you to reach out to a healthcare professional or leave a comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of flu prevention and treatment.
