Intro
Discover the food and mood connection, exploring how nutrition affects mental health, emotional wellbeing, and brain function, with insights on dietary influences, gut health, and mindful eating.
The relationship between food and mood has been a topic of interest for many years, with a growing body of research suggesting that the foods we eat can have a significant impact on our emotional well-being. It's no secret that a healthy diet can improve our physical health, but the connection between food and mood is more complex and multifaceted. In this article, we'll delve into the world of nutrition and psychology to explore the fascinating link between food and mood, and what it means for our overall health and happiness.
The idea that food can influence our mood is not new, but it's only recently that scientists have begun to understand the mechanisms behind this connection. Research has shown that the foods we eat can affect the production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which play a crucial role in regulating our mood. For example, foods rich in tryptophan, an amino acid found in turkey, chicken, and fish, can increase serotonin levels, leading to feelings of relaxation and calmness. On the other hand, foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar followed by a crash, leaving us feeling anxious and irritable.
The connection between food and mood is also closely tied to the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication network between the gut microbiome and the central nervous system. The gut microbiome, composed of trillions of microorganisms, plays a vital role in producing neurotransmitters, hormones, and other signaling molecules that influence our mood and behavior. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for maintaining a balanced mood, and an imbalance of the gut microbiome, also known as dysbiosis, has been linked to various mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
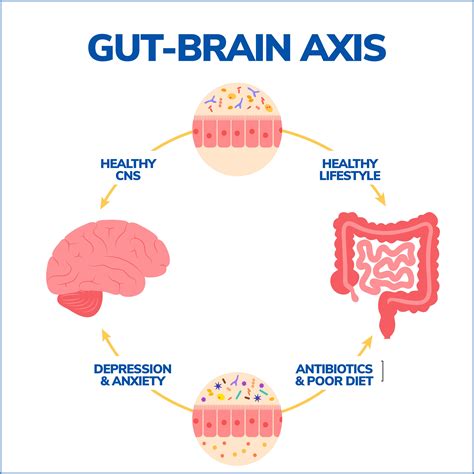
The gut-brain axis is a complex system that involves the exchange of information between the gut microbiome and the central nervous system. The gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters, hormones, and other signaling molecules that can influence our mood, appetite, and satiety. The vagus nerve, a major nerve that connects the gut to the brain, plays a crucial role in this communication network. When the gut microbiome is balanced, the vagus nerve can transmit signals that promote feelings of calmness and relaxation. However, when the gut microbiome is imbalanced, the vagus nerve can transmit signals that lead to anxiety, stress, and other negative emotions.
Key Players in the Gut-Brain Axis
- Gut microbiome: The trillions of microorganisms that live in the gut and play a vital role in producing neurotransmitters, hormones, and other signaling molecules.
- Vagus nerve: A major nerve that connects the gut to the brain and transmits signals that influence our mood, appetite, and satiety.
- Neurotransmitters: Chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons and influence our mood, such as serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine.
The Impact of Diet on Mood

The foods we eat can have a significant impact on our mood, with some foods promoting feelings of happiness and relaxation, while others can lead to anxiety and stress. A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can provide the necessary nutrients and fiber to support a healthy gut microbiome. On the other hand, a diet high in processed and sugary foods can lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, and an imbalance of the gut microbiome.
Foods that Promote a Positive Mood
- Fatty fish, such as salmon and sardines, rich in omega-3 fatty acids
- Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, rich in folate and other B vitamins
- Berries, such as blueberries and strawberries, rich in antioxidants and fiber
- Nuts and seeds, such as walnuts and chia seeds, rich in healthy fats and protein
Foods that Can Negatively Impact Mood
- Sugary drinks, such as soda and sports drinks, high in added sugars
- Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and pasta, high in empty calories
- Processed meats, such as hot dogs and sausages, high in sodium and preservatives
- Fried foods, such as french fries and fried chicken, high in unhealthy fats and calories
The Role of Nutrients in Mood Regulation

Nutrients play a crucial role in mood regulation, with some nutrients acting as precursors to neurotransmitters, while others can influence the production of hormones and other signaling molecules. For example, vitamin D, often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin," can influence the production of serotonin and dopamine, while omega-3 fatty acids can reduce inflammation and promote the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Key Nutrients for Mood Regulation
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, omega-3 fatty acids can reduce inflammation and promote the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
- Vitamin D: Found in fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and sunlight, vitamin D can influence the production of serotonin and dopamine.
- B vitamins: Found in leafy greens, beans, and whole grains, B vitamins can act as precursors to neurotransmitters and influence the production of hormones and other signaling molecules.
- Magnesium: Found in dark leafy greens, nuts, and seeds, magnesium can influence the production of neurotransmitters and hormones, and promote relaxation and calmness.
Practical Tips for Improving Mood through Diet

Improving mood through diet requires a comprehensive approach that involves making sustainable lifestyle changes. Here are some practical tips to get you started:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Incorporate mood-boosting foods, such as fatty fish, leafy greens, and berries, into your diet.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks.
- Limit your intake of processed and sugary foods, and opt for healthier alternatives instead.
- Consider taking supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, if you're unable to get enough through your diet.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, the connection between food and mood is complex and multifaceted, involving the gut-brain axis, nutrients, and lifestyle factors. By making informed food choices and incorporating mood-boosting foods into our diet, we can take the first step towards improving our mood and overall health. Remember, a healthy diet is just one aspect of maintaining good mental health, and it's essential to combine it with regular exercise, stress management, and social support.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on the connection between food and mood in the comments section below. Have you noticed any changes in your mood after making dietary changes? What are some of your favorite mood-boosting foods? Share your story and help us create a community that supports and promotes mental health and well-being.
What is the gut-brain axis and how does it affect mood?
+The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication network between the gut microbiome and the central nervous system. It plays a crucial role in producing neurotransmitters, hormones, and other signaling molecules that influence our mood and behavior.
What are some foods that can negatively impact mood?
+Foods that can negatively impact mood include sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, processed meats, and fried foods. These foods can lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, and an imbalance of the gut microbiome.
How can I improve my mood through diet and lifestyle changes?
+Improving mood through diet and lifestyle changes requires a comprehensive approach that involves making sustainable lifestyle changes. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, incorporating mood-boosting foods, staying hydrated, and limiting processed and sugary foods.
