Intro
Identify food poison symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, to seek timely treatment and prevent severe foodborne illness complications, such as dehydration and stomach cramps.
Food poisoning is a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide every year. It occurs when we consume contaminated or spoiled food, which can lead to a range of unpleasant symptoms. Understanding the symptoms of food poisoning is crucial in seeking prompt medical attention and preventing further complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of food poisoning, exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
The importance of recognizing food poisoning symptoms cannot be overstated. Food poisoning can be life-threatening, especially for vulnerable individuals such as the elderly, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), foodborne illnesses are responsible for an estimated 600 million cases of illness and 420,000 deaths worldwide each year. The economic burden of food poisoning is also significant, with estimated costs exceeding $15 billion annually in the United States alone.
The symptoms of food poisoning can vary depending on the type of contaminant, the amount of food consumed, and the individual's overall health. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever. In severe cases, food poisoning can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and even organ failure. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Types of Food Poisoning

Symptoms of Food Poisoning

Causes of Food Poisoning
The causes of food poisoning are diverse and can be attributed to various factors. These include: * Poor food handling and preparation * Contaminated food sources * Inadequate cooking or reheating * Cross-contamination * Food storage and transportation issuesTreatment Options for Food Poisoning

Prevention of Food Poisoning
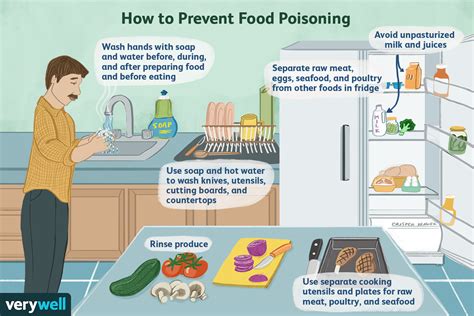
Food Safety Guidelines
Following food safety guidelines is crucial in preventing food poisoning. These guidelines include: * Cooking food to the recommended internal temperature * Refrigerating perishable foods at 40°F (4°C) or below * Freezing foods at 0°F (-18°C) or below * Avoiding cross-contamination * Washing hands frequentlyComplications of Food Poisoning

Food Poisoning in Vulnerable Populations

Food Safety Education
Food safety education is crucial in preventing food poisoning. This includes: * Teaching proper food handling and preparation techniques * Providing information on food safety guidelines * Promoting awareness of potential contaminants * Encouraging good hygiene practicesWhat are the most common causes of food poisoning?
+The most common causes of food poisoning include bacterial, viral, and parasitic contamination. Bacterial contamination, such as Salmonella and E. coli, is the most common cause of food poisoning.
How can I prevent food poisoning?
+To prevent food poisoning, follow good food handling practices, such as washing hands frequently, separating raw and cooked foods, and cooking food to the recommended internal temperature.
What are the symptoms of food poisoning?
+The symptoms of food poisoning include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever. In severe cases, food poisoning can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and even organ failure.
In summary, food poisoning is a common health issue that can have severe consequences if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for food poisoning is essential in preventing and managing this condition. By following good food handling practices, being aware of potential contaminants, and seeking medical attention when necessary, we can reduce the risk of food poisoning and promote a healthier and safer food environment. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips on preventing food poisoning, and to take an active role in promoting food safety awareness in their communities.
