Intro
Discover 7 foods high in phosphate, including meats, fish, and dairy, which support bone health, kidney function, and energy production, while learning about phosphate-rich diets and balanced nutrition.
The importance of maintaining a balanced diet cannot be overstated, and one crucial aspect of this balance is the intake of phosphates. Phosphates are essential for various bodily functions, including the formation of bones and teeth, the production of DNA and RNA, and the maintenance of a healthy nervous system. However, excessive phosphate consumption can lead to health issues such as kidney damage and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. It is vital to be aware of the phosphate content in the foods we eat to ensure we are not overstepping the recommended daily intake.
Phosphates are found in a wide variety of foods, both naturally and as additives. Natural sources include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, and certain fruits and vegetables. Phosphate additives, on the other hand, are commonly found in processed and packaged foods. Understanding which foods are high in phosphates is key to managing phosphate intake effectively. This knowledge allows individuals to make informed dietary choices, balancing the need for phosphates with the risk of overconsumption.
The recommended daily intake of phosphorus, the element from which phosphates are derived, varies by age and other factors but generally falls within the range of 1,000 mg for adults. Exceeding this limit, especially consistently, can have adverse health effects. Therefore, being mindful of the phosphate content in daily meals is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing potential complications. This awareness is particularly important for individuals with pre-existing kidney issues, as their ability to filter excess phosphates is compromised.
Introduction to High Phosphate Foods

Phosphates are naturally found in many foods, and some of these foods are particularly high in phosphate content. Knowing which foods are high in phosphates can help individuals manage their phosphate intake more effectively. High phosphate foods include various types of meat, seafood, dairy products, and certain processed foods. Understanding the phosphate content of these foods is essential for maintaining a balanced diet.
Types of High Phosphate Foods

There are several categories of foods that are known to have high phosphate content. These include:
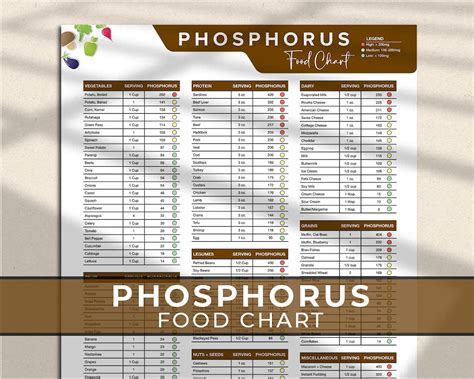
- Meat and Poultry: Foods like chicken, beef, and pork are significant sources of phosphates. A 3-ounce serving of cooked chicken, for example, can contain about 200-300 mg of phosphorus.
- Seafood: Many types of seafood, such as salmon and shrimp, are also high in phosphates. A 3-ounce serving of cooked salmon can provide approximately 250-350 mg of phosphorus.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are not only rich in calcium but also contain significant amounts of phosphates. An 8-ounce cup of milk, for instance, can contain around 230-300 mg of phosphorus.
- Processed Foods: Many processed foods, especially those with phosphate additives, can have very high phosphate content. Examples include processed meats, frozen meals, and certain types of snacks.
Benefits and Risks of Phosphate Intake
The intake of phosphates is crucial for several bodily functions, including bone health and the proper functioning of the nervous system. However, excessive phosphate consumption can lead to health complications. It is essential to strike a balance between meeting the body's needs for phosphates and avoiding overconsumption.Managing Phosphate Intake
Managing phosphate intake involves being aware of the phosphate content in the foods we consume and making dietary choices that ensure we do not exceed the recommended daily intake. This can include:
- Reading Food Labels: Checking the ingredient list for phosphate additives in processed foods.
- Balancing Diet: Ensuring that the diet includes a variety of foods and is not overly reliant on high-phosphate foods.
- Consulting a Dietician: For personalized dietary advice, especially for individuals with specific health conditions.
Practical Tips for Reducing Phosphate Intake
For individuals looking to reduce their phosphate intake, several practical steps can be taken: - **Choose Fresh Over Processed:** Opting for fresh, unprocessed foods as much as possible to minimize exposure to phosphate additives. - **Vary Protein Sources:** Including a variety of protein sources in the diet, such as beans and lentils, which are lower in phosphates compared to meat and seafood. - **Limit Dairy:** Being mindful of dairy intake, as while dairy products are nutritious, they are also high in phosphates.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, understanding which foods are high in phosphates and how to manage phosphate intake is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance of phosphates in the body. By being aware of the phosphate content in foods and making informed dietary choices, individuals can reduce the risk of health complications associated with excessive phosphate consumption. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of phosphate metabolism and its impact on health, staying informed about the latest findings and dietary recommendations will be essential for optimizing health outcomes.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations

In final thoughts, the management of phosphate intake is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health. By understanding the sources of phosphates, both natural and additive, and taking steps to balance phosphate consumption, individuals can protect against potential health risks. This includes being mindful of the phosphate content in foods, reading labels carefully, and consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Engaging with the Community

We invite readers to share their experiences and tips on managing phosphate intake in the comments below. Your insights can help others make more informed decisions about their diet and health. Additionally, consider sharing this article with friends and family who may benefit from learning more about the importance of phosphate balance in the body.
What are the primary sources of phosphates in the diet?
+The primary sources of phosphates in the diet include meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, and certain processed foods that contain phosphate additives.
How can I reduce my phosphate intake?
+You can reduce your phosphate intake by choosing fresh, unprocessed foods, varying your protein sources, limiting dairy consumption, and being mindful of phosphate additives in processed foods.
What are the health risks associated with excessive phosphate consumption?
+Excessive phosphate consumption can lead to health complications such as kidney damage and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. It is essential to maintain a balanced diet and not exceed the recommended daily intake of phosphorus.
