Intro
Learn how Foot Mouth Disease spreads through human contact, contaminated surfaces, and airborne transmission, affecting hand, foot, and mouth symptoms, with 5 key methods of infection and prevention strategies to reduce outbreak risks.
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious and infectious viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including cattle, pigs, sheep, and goats. The disease is characterized by the formation of blisters or vesicles on the feet and in the mouth of infected animals, leading to significant economic losses in the livestock industry. Understanding how FMD spreads is crucial for preventing and controlling outbreaks. In this article, we will explore the various ways FMD spreads and discuss the importance of biosecurity measures in preventing the disease.
The spread of FMD is a complex process that involves several factors, including animal movement, human activity, and environmental conditions. The disease can spread rapidly, and it is essential to take prompt action to prevent and control outbreaks. FMD has significant economic and social implications, and it is crucial to understand the ways in which it spreads to develop effective control strategies.
FMD is a significant threat to the livestock industry, and it is essential to take proactive measures to prevent and control outbreaks. The disease can spread through various means, including direct contact with infected animals, contaminated feed and water, and human activity. In this article, we will discuss the different ways FMD spreads and provide practical advice on how to prevent and control outbreaks.
Introduction to Foot and Mouth Disease

Direct Contact with Infected Animals

Factors that Increase the Risk of Direct Contact
Several factors can increase the risk of direct contact with infected animals, including: * Overcrowding and poor animal housing * Inadequate biosecurity measures * Movement of animals between farms and markets * Sharing of equipment and vehiclesContaminated Feed and Water

Prevention and Control Measures
To prevent the spread of FMD through contaminated feed and water, the following measures can be taken: * Use high-quality feed and water sources * Implement proper cleaning and disinfection protocols * Regularly inspect and maintain equipment and vehicles * Ensure that all personnel handling feed and water are trained in biosecurity measuresAerosol Transmission
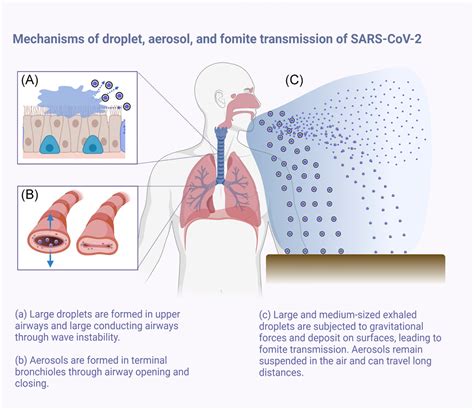
Factors that Increase the Risk of Aerosol Transmission
Several factors can increase the risk of aerosol transmission, including: * Overcrowding and poor ventilation * Inadequate biosecurity measures * Movement of animals between farms and markets * Sharing of equipment and vehiclesHuman Activity and FMD Spread
Prevention and Control Measures
To prevent the spread of FMD through human activity, the following measures can be taken: * Implement proper biosecurity measures, such as disinfecting equipment and vehicles * Ensure that all personnel handling animals are trained in biosecurity measures * Regularly inspect and maintain equipment and vehicles * Limit movement of people between farms and marketsEnvironmental Factors and FMD Spread
Factors that Increase the Risk of Environmental Transmission
Several factors can increase the risk of environmental transmission, including: * Temperature and humidity * Wind direction and speed * Presence of wildlife and other animals * Inadequate biosecurity measuresWhat is Foot and Mouth Disease?
+Foot and Mouth Disease is a highly contagious and infectious viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, causing significant economic losses in the livestock industry.
How is Foot and Mouth Disease Spread?
+Foot and Mouth Disease can spread through various means, including direct contact with infected animals, contaminated feed and water, aerosol transmission, human activity, and environmental factors.
What are the Symptoms of Foot and Mouth Disease?
+The symptoms of Foot and Mouth Disease include the formation of blisters or vesicles on the feet and in the mouth of infected animals, leading to lameness, reduced milk production, and weight loss.
How can Foot and Mouth Disease be Prevented and Controlled?
+Foot and Mouth Disease can be prevented and controlled through the implementation of biosecurity measures, such as isolating new animals, disinfecting equipment, and ensuring proper ventilation and hygiene.
What are the Economic Implications of Foot and Mouth Disease?
+Foot and Mouth Disease has significant economic implications, including reduced milk production, weight loss, and mortality, making it essential to take proactive measures to prevent and control outbreaks.
In conclusion, FMD is a highly contagious and infectious viral disease that can spread through various means, including direct contact with infected animals, contaminated feed and water, aerosol transmission, human activity, and environmental factors. Understanding the ways in which FMD spreads is crucial for preventing and controlling outbreaks, and it is essential to implement biosecurity measures to reduce the risk of transmission. By taking proactive measures, such as isolating new animals, disinfecting equipment, and ensuring proper ventilation and hygiene, we can prevent and control FMD outbreaks, reducing the economic and social implications of the disease. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on FMD prevention and control, and to take action to protect your animals and community from the spread of this disease.
