Intro
Furosemide treats fluid retention, edema, and hypertension, using diuretic properties to relieve swelling, promoting kidney function and cardiovascular health.
The use of furosemide in medical treatment has become a cornerstone in managing various conditions, particularly those related to fluid retention and cardiovascular health. Furosemide, commonly known by its brand name Lasix, is a loop diuretic that works by increasing urine production, helping the body get rid of excess water and salt. This mechanism of action makes it an invaluable medication for patients suffering from conditions such as edema, hypertension, and certain types of kidney and liver diseases. The importance of furosemide lies in its ability to provide rapid relief from symptoms associated with fluid overload, making it a frequently prescribed medication in both acute and chronic care settings.
Understanding the role of furosemide in treating these conditions requires insight into how fluid balance is maintained in the body and how disruptions in this balance can lead to disease. The body's ability to regulate fluid is crucial for maintaining blood pressure, ensuring proper circulation, and supporting the functions of vital organs. When this balance is disrupted, due to heart failure, kidney disease, or liver cirrhosis, for example, the body may retain excess fluid, leading to swelling (edema) and increased blood pressure. Furosemide helps to restore this balance by promoting the excretion of sodium and water, thereby reducing fluid volume and alleviating symptoms associated with fluid overload.
The application of furosemide is not limited to the management of fluid retention; it also plays a critical role in the treatment of hypertension. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. By reducing fluid volume and subsequently lowering blood pressure, furosemide contributes to the reduction of these risks. Furthermore, its use in patients with acute pulmonary edema, a condition characterized by fluid accumulation in the lungs, can be life-saving by rapidly alleviating symptoms and improving oxygenation.
How Furosemide Works
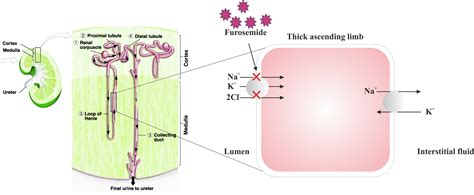
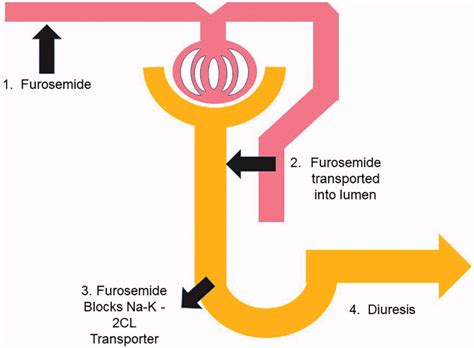
Furosemide works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, a part of the nephron in the kidney. This inhibition prevents the reabsorption of sodium, chloride, and water, leading to increased excretion of these substances in the urine. The result is a decrease in fluid volume in the body and a subsequent reduction in blood pressure. This mechanism is highly effective in managing conditions where fluid overload is a significant concern.
Benefits of Furosemide
The benefits of furosemide are multifaceted, offering relief from a range of symptoms associated with fluid retention and cardiovascular disease. Some of the key benefits include: - Rapid relief from edema, reducing swelling and discomfort - Effective management of hypertension, reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications - Improvement in symptoms associated with heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue - Reduction in fluid accumulation in the lungs (pulmonary edema), improving respiratory function - Supportive treatment in certain cases of kidney and liver disease, helping to manage fluid balanceUses of Furosemide

Furosemide is used in a variety of clinical settings due to its effectiveness in managing fluid overload and related conditions. Some of the primary uses include:
- Edema: Furosemide is commonly prescribed for the treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and a nephrotic syndrome.
- Hypertension: It is used in the management of hypertension, either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs.
- Acute Pulmonary Edema: Furosemide can be life-saving in the treatment of acute pulmonary edema, rapidly reducing fluid accumulation in the lungs.
- Kidney Disease: In certain cases of kidney disease, furosemide may be used to manage fluid balance and reduce strain on the kidneys.
Administration and Dosage
The administration and dosage of furosemide depend on the condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication. It can be administered orally or intravenously, with the dosage adjusted based on the severity of the condition and the patient's renal function. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration schedule to ensure the safe and effective use of furosemide.Side Effects and Precautions
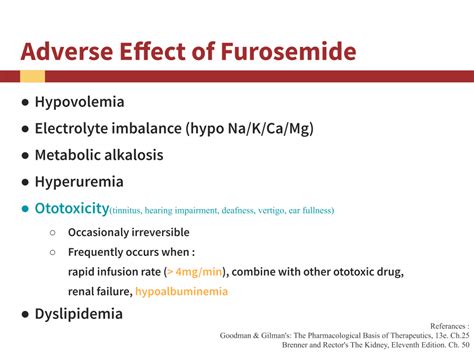
While furosemide is an effective medication, it can cause side effects and interact with other medications. Common side effects include:
- Increased urination
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Muscle cramps
- Weakness
It is crucial to monitor renal function and electrolyte levels during furosemide treatment, as it can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances if not properly managed. Patients should also be aware of the signs of overdose, which can include severe dizziness, fainting, and excessive urine production.
Interactions with Other Medications
Furosemide can interact with a variety of medications, including: - Other diuretics - Antihypertensive drugs - Lithium - Aminoglycoside antibiotics - CorticosteroidsThese interactions can either enhance or diminish the effects of furosemide, potentially leading to adverse effects. It is essential for patients to inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, furosemide remains a vital component in the management of fluid retention and cardiovascular diseases. Its effectiveness in providing rapid relief from symptoms associated with fluid overload makes it a frequently prescribed medication. However, it is crucial to use furosemide under the guidance of a healthcare provider, monitoring for potential side effects and interactions with other medications. As medical research continues to evolve, the role of furosemide may expand, offering new avenues for the treatment of related conditions.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about the use of furosemide in the comments below. This engagement can help foster a community of individuals and healthcare professionals interested in discussing the latest developments in medical treatment and management.
What is the primary use of furosemide?
+Furosemide is primarily used to treat fluid retention (edema) and hypertension.
How does furosemide work?
+Furosemide works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the kidneys, leading to increased urine production and reduction in fluid volume.
What are the common side effects of furosemide?
+Common side effects include increased urination, dizziness, lightheadedness, headache, nausea, and muscle cramps.
